* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Adolescence
Paleoconservatism wikipedia , lookup
Ethics in religion wikipedia , lookup
Bernard Williams wikipedia , lookup
Divine command theory wikipedia , lookup
Individualism wikipedia , lookup
Role-taking theory wikipedia , lookup
Sexual ethics wikipedia , lookup
Alasdair MacIntyre wikipedia , lookup
Ethics of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Moral psychology wikipedia , lookup
On the Genealogy of Morality wikipedia , lookup
Consequentialism wikipedia , lookup
The Sovereignty of Good wikipedia , lookup
The Moral Landscape wikipedia , lookup
Ethical intuitionism wikipedia , lookup
Moral disengagement wikipedia , lookup
Critique of Practical Reason wikipedia , lookup
Moral responsibility wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Hill Green wikipedia , lookup
Moral relativism wikipedia , lookup
Lawrence Kohlberg wikipedia , lookup
Moral development wikipedia , lookup
Morality and religion wikipedia , lookup
Lawrence Kohlberg's stages of moral development wikipedia , lookup
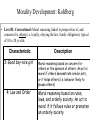
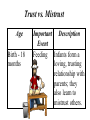
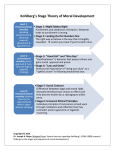
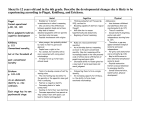
Adolescence The transition period from childhood to adulthood. Bio/Psycho /Social Pre-natal, Infancy, Childhood Lifespan Development! Bio/Psycho /Social Adulthood & Death Adolescence Social Bio Psycho *Puberty *Primary v. Secondary Sexual Characteristics *Brain Development We are here Puberty • The period of sexual maturation, during which a person becomes capable of reproducing. Primary Sexual Characteristics Penis Vagina Testes • Body structures that make reproduction possible. Ovaries Secondary Sexual Characteristics • Nonreproductive sexual characteristics. Body Hair Widening of the Hips Breast Development Deeper Voice When does puberty start? The Landmarks • First ejaculation for boys •Menarche for girls Do we remember these things? Sequence is way more predictable than the timing. How might timing differences effect an adolescent socially? Why is Puberty Beginning Earlier in Girls? • http://www.smithsonianmag.com/sciencenature/puberty-beginning-earlier-girls-sowhat-can-parents-do-180953738/?noist&utm_content=bufferb5f69&utm_mediu m=social&utm_source=facebook.com&utm _campaign=buffer Brain Development • Frontal Lobe maturation lags behind the emotional limbic system – Remember Phineas Gage! – Explains impulsive behavior (emotional storms!) • Not fully equipped for long-term decision making either – Why many teens smoke – Juvenile death penalty – Should the driving age be raised? Bio/Psycho /Social Pre-natal, Infancy, Childhood Lifespan Development! Bio/Psycho /Social Adulthood & Death Adolescence Social Bio Psycho *Puberty *Primary v. Secondary *Reasoning Ability Sexual Characteristics *Formal Operational *Brain Development We are Thought here *Moral Thinking (Kohlberg) Moral Development Three Stage Theory by Lawrence Kohlberg!!! Ethics v Morals • An ethical man knows he shouldn’t cheat on his wife. A moral man doesn’t cheat on his wife. Lawrence Kohlberg and his stages of Morality • Preconventional Morality • Conventional Morality • Postconventional Morality Morality Development: Kohlberg • Level I: Pre-conventional: Egocentric orientation focusing on moral consequences for the self; reasoning found until about 10 years of age Characteristic 1: Punishment Obedience 2: Individualism and Exchange Description Moral reasoning based on immediate consequences for the individual. An act is moral if a person isn’t punished for it. It is immoral if the person is punished. Moral reasoning based on reciprocity. An act is moral if a similar act occurs in return (i.e. satisfies own needs) Morality Development: Kohlberg • Level II: Conventional: Moral reasoning linked to perspectives of, and concerns for, others (i.e. loyalty, obeying the law, family obligation); typical of 10 to 20 yr olds. Characteristic Description 3: Good boy-nice girl Moral reasoning based on concern for others or the opinions of others. An act is moral if others demonstrate similar acts, or it helps others (i.e. behavior likely to please others) 4: Law and Order Moral reasoning based on rules, laws, and orderly society. An act is moral if it follows rules or promotes an orderly society. Morality Development: Kohlberg • Level III: Post-conventional. Reasoning transcends society’s rules; reflects an understanding that rules sometimes need to be changed/ignored. Characteristic Description 5: Social Contract Moral reasoning based on principled agreements among people. An act is moral if it is consistent with a principled agreement. (ex: Bill of Rights) 6: Universal Ethical Moral reasoning based on abstract principles. An act is moral if it is consistent with an abstract principle that transcends an individual’s society. Preconventional Morality • Morality of self- interest • Their actions are either to avoid punishment or to gain rewards. Conventional Morality Morality is based upon obeying laws to 1. Maintain social order 2. To gain social approval Postconventional Morality • Morality based on your own ethical principles. Practice: Heinz Dilmema • In a country in Africa, a woman was near death from a very bad disease, a special kind of cancer. There was one drug that the doctors thought might save her. It was a form of radium that a pharmacist in the same town had recently discovered. The drug was expensive to make, but the pharmacist was charging ten times what the drug cost him to make. He paid $200 for the radium and charged $2,000 for a small dose of the drug. The sick woman’s husband, Heinz, went to everyone he knew to borrow the money, but he could get together only $500. He told the pharmacist that his wife was dying and asked him to sell it cheaper or let him pay later. But the pharmacist said, “No, I discovered the drug and I’m going to make money from it.” Heinz got desperate and broke into the man’s store to steal the drug for his wife. Was Heinz right or wrong to steal the drug? Explain your answer. The Heinz Dilemma: Preconventional Morality 1. Avoids punishment—“Heinz’s father-in-law might make big trouble for him if he let his wife die.” 2. Gains rewards—“Heinz will have someone to fix fine dinners for him if his wife lives.” Conventional Morality 3. Gains approval/avoids disapproval—“What would people think of Heinz if he lets his wife die?” 4. Does duty to support society/avoids dishonor or guilt—“Heinz must live up to his marriage vow of protecting his wife.” Postconventional Morality 5. Affirms agreed-upon rights—“Everyone agrees that people have the right to live.” 6. Abstract, autonomous moral principle—“Saving a life takes precedence over everything else, including the law.” Criticisms of Kohlberg • Carol Gilligan pointed out that Kohlberg only tested boys. • Boys tend to have more absolute value of morality. • Girls tend to look at situational factors. Talk is Cheap How do we turn morality into action? • Teach Empathy • Self-discipline to delay gratification • Model moral behavior (service learning) Cognitive Development •Experience formal operational thought • Have the ability to reason but……. Imaginary Audience Personal Fable Social Development Its all about forming an identity!!! Erik Erikson 1902-1994 Erik Erikson • A neo-Freudian • Worked with Anna Freud • Thought our personality was influenced by our experiences with others. • Stages of Psychosocial Development. • Each stage centers on a social conflict. Trust vs. Mistrust Age Birth - 18 months Important Description Event Feeding Infants form a loving, trusting relationship with parents; they also learn to mistrust others. Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt Age 18 months - 3 Years Important Event Toilet Training Description Child's energies are directed toward physical skills: walking, grasping, and toilet training. The child learns control along with a healthy dose of shame and doubt. Initiative vs. Guilt Age Important Description Event 3 - 6 Years Independence Child becomes more assertive, takes more initiative, becomes more forceful. Competence vs. Inferiority Age 6 - 12 Years Important Description Event School The child must deal with demands to learn new skills while risking a sense of inferiority and failure Identity vs. Role Confusion Age Important Description Event Adolescence Peers Teens must achieve self-identity while deciphering their roles in occupation, politics, and religion. Intimacy vs. Isolation Age Important Description Event Young Adult Relationships The young adult must develop marriage-seeking relationships while combating feelings of isolation. Generativity vs. Stagnation Age Important Description Event Middle Adult Parenting Assuming the role of parents signifies the need to continue the generations while avoiding the inevitable feeling of failure. Integrity vs. Despair Age Late Adult Important Description Event Life Acceptance of Reflection one's lifetime accomplishments and sense of fulfillment. Is adolescence getting longer or shorter?