* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Tracheophyta -Seedless Vascular Plants
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
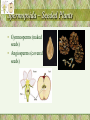
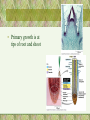
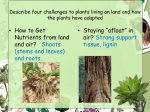
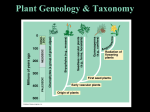
Kingdom: Plantae General Characteristics • Multicellular, Photoautotrophic, Eukaryotic • Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll a and b, and carotenoids • Cell wall made of cellulose, Starch is the food storage compound • Adaptations to life on land include waxy cuticle and stomata to allow for exchange of gases through cuticle Multicellular Algae to Plants • Plants began the movement onto land about 425 million years ago • Evolutionary history involves increasing adaptations to changing terrestrial conditions Adaptations for Life on Land DIFFICULTY ALGAE PLANT Moisture Loss None Cuticle Exposure to Sun Transport Near Surface of Around Stem Water Diffusion Xylem and Phloem Gas Exchange Diffusion Reproduction Water Required Pollen Stomata Support of Tissue Water Pressure Lignin, xylem, phloem Vascular Tissue • Xylem – transports water and minerals up from root (Xylem is dead at functional maturity) • Phloem – transports sugars (food) throughout plant Four major periods in Plant Evolution • Origin of plants from green algae • Adaptation of vascular tissue (tissue which allows transport of materials throughout plant) • Origin of seeds (embryos enclosed with food in coating) • Emergence of flowering plants (bear seeds in protective coating) Evolutionary trends • The reduction of the haploid generation with increasing dominance of the diploid generation • Adaptations to terrestrial life Classification Bryophyta (mosses) • No vascular tissue • Gametophyte generation is dominant • Sperm must swim to egg • Plants must live in moist environments Bryophyta (mosses) • Gametophyte is the dominant (photosynthetic) generation, Sporophyte is brown capsule and stalk Reproduction and Life Cycle • Life cycle involves Alternation of Generations between haploid gametophyte and diploid sporophyte • Moss Animation Liverwort, Hornwort and Moss Phylum Tracheophyta Adaptations Cuticle Stomata Retains water, prevents evaporation Pore for Gas Exchange Xylem (Vascular Tissue) Moves water up plant Phloem (Vascular Tissue) Moves food up and down Lignin Support Seed Coat Protect seed, still need water for fertilization Vascular System – 3 areas • Roots - Tubes gathered in center, anchor plant, absorb moisture and nutrients • Leaves – Major site of photosynthesis, stomata, veins of vascular tissue • Stems – Contains vascular tissue for transport, xylem and phloem Tracheophyta -Seedless Vascular Plants • Psilophyta – whisk ferns Tracheophyta – Seedless Vascular Plants • Sphenophyta - horsetails Tracheophyta – Seedless Vascular Plants • Lycophyta – Club Moss Tracheophyta -Seedless Vascular Plants • Pterophyta - Ferns • Produce spores • Able to live in drier environments than the Bryophytes, but sperm still must swim to egg Fern Life Cycle • Life cycle of a fern Spermopsida – Seeded Plants • Gymnosperms (naked seeds) • Angiosperms (covered seeds) Gymnosperms – Seeded Plants Cone-bearing plants that produce seeds in cones Seeds are not contained in fruits – seed has thin protective coating that is part of seed itself Coniferophyta – cone bearers Cycadophyta - cycads Ginkgophyta – Ginkgo biloba Angiosperms -Seeded Plants • II.Angiosperm (“covered seeds”) Anthophyta – Flowering plants with protected seeds Fruit is ripened in ovary of flower that helps disperse seeds Angiosperms, cont. • Monocots vs. Dicots Monocot Dicot • Plants exhibit indeterminate growth • Primary growth is at tips of root and shoot • Secondary growth increases a plant’s girth