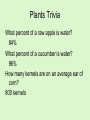* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 7 How are Plants Classified
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
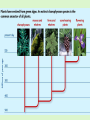
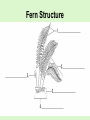
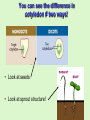
Chapter 7 How are Plants Classified Plants Trivia What percent of a raw apple is water? 84% What percent of a cucumber is water? 96% How many kernels are on an average ear of corn? 800 kernels Brainstorming Time! With a partner, answer the following questions and WRITE down what you come up with! You will have approximately 15 minutes to do this (and do it WELL!) You will be sharing your thoughts! 1. List some characteristics of all plants? 2. How do humans use plants? 3. List as many different types of plants you can think of!!! (hopefully your list is long) 4. On the blank paper, draw a plant of your choice and label its parts/structures! Put the following plants in order from most primitive (1) to most advanced (5). 4 3 2 5 1 All Plants… 1. Are multicellular! 2. Have rigid cell walls (made of cellulose) 3. Have chloroplasts in their cells for photosynthesis! • Photosynthesis: Water + Carbon Dioxide glucose + oxygen C6H12O6 Kingdom Plantae is Divided into 2 Groups: • Tracheophytes (advanced) – Are vascular plants • have transport tubes – Larger – Flowers, trees, shrubs, ferns • Bryophytes (primative) – Are non-vascular plants • no transport tubes – small – Moss, liverworts, hogworts Tracheophytes vs. Bryophytes Bryophytes • • • • Most Primitive Pants Small! “pioneer plants” Examples: mosses, liverworts, hornworts Liverworts, Hornworts (Examples of Bryophytes) • Liverwort – Marchantia • Hornwort WARM-UP (Review) What are 3 distinguishing characteristics of ALL plants? • Multicellular, cell walls, chloroplasts The kingdom Plantae is divided into what 2 groups? • Tracheophytes and Bryophytes What are the two main differences between those 2 plant groups? • Vascularity (transport tubes) What group do mosses belong to? • Bryophyte List the two phases of the moss life cycle? • • Spore-Producing Phase Gamete-Producing Phase Ferns • Oldest Tracheophyte! • Feather-like leaves • Reproduces by spores Fern Structure Fern Life Cycle Spore-Producing Phase Gamete-Producing Phase Let’s take a closer look at this life cycle! • Dissection microscope – sori on underside of leaves • Regular microscope – gametophyte Gymnosperms • Tracheophyte – Has vascular tissue! • Means uncovered, exposed/naked seeds Seed: reproductive structure of a plant. Contains own food for its growth. • Woody stems • Examples: – Conifers (pine trees) – Gingkos – Cycads Types of Gymnosperms Conifers (Produce cones) Ex- Pine, Spruce Ginkgos (Fan-like leaves) *Grow-well! Even in Pollution! Cycads (Tropical, large leaves) Here’s something you may not know…. • The needles on conifers are modified leaves. They still need to photosynthesis and exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide with the environment. • If you look at the underside of the needles, you can see the little holes. • Conifers can be identified by looking at the patterns of these holes on needles! Warm-Up • List as many angiosperms (flowering plants) as you can! Here’s a start… Angiosperms • Flowering plants! • Largest plant group! – 250,000 diff. types • All have flowers and seeds! • Tracheophytes (most advanced!) – Vascularity (transport tubes) HIGHLY DEVELOPED! – True roots, stems, and leaves • Examples: – Grasses, oak tree, tulip, corn Seeds are Protected by Fruit (not naked like the Gymnosperms) • Angiosperms are seed plants (produce seeds to reproduce) • Seeds are enclosed in a fruit • Many types of fruits! Did You Know… These are all fruits too! SEED SEED SEED SEED Angiosperms can either be… Monocot or Dicot • Monocot – flowering plant with one cotyledon in its seeds • Dicot – flowering plant with two cotyledons in its seeds • Cotyledon – leaf-like structure inside a seed that contains food for the developing plant. You can see the difference in cotyledon # two ways! • Look at seeds • Look at sprout structure! Monocot vs. Dicot Chart