* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2 science powerpoint
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
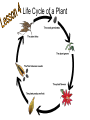
Energy from Plants Chapter 2 Lesson 1 What are the plants’ characteristics? • Plants are made up of many cells. • These cells all do different jobs in the plant • Plants have special cells they use to absorb water and nutrients from the soil • Plants contain Chlorophyll, which makes them green How Plants Make Food • Photosynthesis – The process of making sugar • Plants use sugar as food • Carbon dioxide is absorbed from the air, water is absorbed from the soil, and chloroplasts trap the sunlight PHOTOSYNTHESIS • The plant uses the sugars it makes • The plant releases Oxygen that we breathe Chloroplasts Photosynthesis Song Edublogs.tv Photosynthesis Song Parts of a Plant Stems • Can be as thick as a tree trunk or as thin as a blade of grass • Have 2 major functions – 1. carry water, minerals and food between the roots and leaves – 2. Support the plant, holding up the leaves so they can get sunlight Roots • Anchor or hold the plant to the ground • Absorb or take in water and mineral nutrients from the soil • Fibrous Roots – Grow away from the plant in search of water • Taproots – Has a large main root, called the taproot. – It grows straight down – Stores food for the plant How Plants Reproduce • Petals-colorful outer layer of flowers that help protect the insides that make new plants • Sepals- the small, green leaves below the petals. They cover and protect the flower as it grows inside the bud How Plants Reproduce • Pistil-small knoblike structures in the middle of the plant • Stamens-smaller stalks surrounding the pistil. Pollen is made here. How Do Plants Reproduce? Pollen on the Move • Pollen has to move from the stamen to a pistil in order for a seed to form. • HOW CAN THIS HAPPEN??? • Animals help this happen! • Animals are attracted by the colors of the petals and to eat the nectar deep inside the flower. • Pollen from the stamen is rubbed off onto the animals body • The pollen is then rubbed off onto the pistil of the next flower the animal visits. Pollen in the Move • Wind also can blow pollen from the stamen of one plant to the pistil of another • After the fertilization, the flower begins to dry up and fall off • A seed develops inside How a Plant Grows from a Seed Life Cycle of a Plant Seeds on the Move • Seeds have to move away from each other to have room to grow. • If they grew too close to one another they would compete for water, nutrients from the soil, and sunlight. Animal Helpers • Animals eat fruit and when they do they eat the seeds also. • The seed will pass through the digestive system onto the ground in the animal’s droppings. • The animal will usually carry the seeds far from the adult plant so this helps scatter the seeds Wind as a Helper • Many seeds have wing-shaped seeds to carry them far from the adult plant. • When the seeds land, many are buried and new plants grow Water as a Helper • Water can carry seeds from one location to another. • Coconut seeds can float from one island to another and create new trees. New Plants from Plant Parts • Some plants grow from stems, roots, or leaves • Bulbs are underground stems that grow into new plants • Potato plants sprout new plants right from the potato