* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Units 22 and 23
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
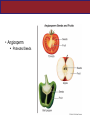
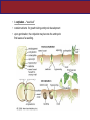
Units 22 and 23 •SEED PLANTS Life Llife Cylce of Nonseed Plant Life Cycle Seed Plant Life Cycle Flagellated sperm must swim Pollination Highlights in the History of Seed Plants • Late in the Devonian, some plants developed secondary growth: thickened woody stems of xylem How Did Seed Plants Become Today’s Dominant Vegetation? Surviving seed plants fell into two groups: • Gymnosperms: pines and cycads • Angiosperms: flowering plants Gymnosperms • Any vascular plant that reproduces by means of an exposed seed, or ovule • “Naked Seed” Gymnosperm Gymnosperms Four major phyla of living gymnosperms: • (a)Cycads: Cycadophyta Sago palm • Cone-bearing • palm like • tropical • dinosaur food ? Gymnosperms • b)Ginkgos: Ginkgophyta • One living species, Ginkgo biloba • Seed coat stinks • Polluted areas • 1945 atom bomb The ginkgo is a living fossil, recognizably similar to fossils dating back 270 million years. Gymnosperms • (c) Gnetophytes: Gnetophyta • Shrubs , trees, or vines • the group is a small one, consisting of three families, each with one genus, totaling 68 species Ephedra *ephedrine Gymnosperms • (D)Conifers Coniferophyta • largest group of gymnosperms • pines, hemlock, spruce, evergreen conifers • leaves stay all season sap ----antifreeze • first real development of wood dead transport tissue Gymnosperms • Softwood Angiosperms • Flowering plants are the dominant plant today Angiosperms • They are the largest group of plants with about 90% of all plant species. . A • Angiosperm Protected Seeds Angiosperms • FLOWERS are the exclusive reproductive organ of angiosperms • “The earth laughs in flowers ” Ralph Waldo Emerson What Features Distinguish the Angiosperms? Angiosperm: “enclosed seed” Angiosperms • Male reproductive structures Stamen Female reproductive structures Carpel Stigma, style, and ovary bear megasporangia -egg (one or more carpel make up a pistil) Anther Filament bear microsporangia - sperm ( pollen) Angiosperm • Pollen • B - Dandelion (Taraxacum sp.) Transmission electron microscopy • F - Pine (Pinus sylvestis): Light microscopy • G - Mixed pollen grains (bright field light microscopy, stained) Anigosperms • Flowers may have contributed to the enormous success of angiosperms. • The flowers attract a pollinators which carry pollen to other individuals of the same species Angiosperms Attracted to sweet smells Need landing platform Attracted to strong smells Can hover; nocturnal Need bigger landing platform Like bright colors Can hover Prefer red color Angiosperms • Double fertilization Sperm A leads to the formation of a Seed Sperm B leads to the formation of an endosperm (a nutritive tissue within the seed that feeds the developing plant embryo) Flowering plants are divided into two groups • Cotyledon? • Embryonic seed • is the first leaf or set of leaves that sprout from a seed • Store nutrients for the embryo • A cotyledon – “seed leaf” • contain nutrients for growth during embryonic development • upon germination, the cotyledon may become the embryonic first leaves of a seedling. • Dry fruit vs. Fleshy fruit