* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Classification
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
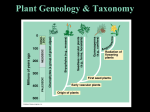
Plant Classification 2 Main Categories Vascular Plants Nonvascular Plants Nonvascular Plants • Nonvascular plants do not have tube-like structures that transports water from roots to stems and leaves – Mosses- have small root-like structures called rhizoids – Liverworts- look similar to mosses but leaves are arranged differently Mosses Liverworts Vascular Plants • Vascular plants have tubular structures that provide stability and transportation for nutrients – Seedless Vascular Plants • Horsetails- have underground stems called rhizomes • Club mosses- look like small evergreens • Ferns- grow from rhizomes and have fronds – Fronds- leafy branches of the fern – Fiddle-head- coiled up frond Horsetails Club mosses Ferns Seed-Bearing Vascular Plants • Seeds contain the embryo- newly forming plant • 2 Groups– Angiosperms- flowering seed-bearing plants – Gymnosperms- seed-bearing plants that do not flower • most have cones that contain the seed Gymnosperm • Organized into 4 smaller groups – 1. Cycads look like palm trees, but they have cones – 2. Ginkgoes have flat fanned leaves – 3. Gnetophytes found in hot dry deserts or tropical rain forests – 4. Conifers the largest group of Gymnosperms • They have cones • They are the evergreens Conifers • Pine trees– Needles are grouped in bundles – Produces resin which is used to make • Tar, turpentine, ink, paint, adhesive, rosin (for use with violins) Pine Trees Conifers – Firs and Spruce • Needles are directly attached to the branches • Firs– Cones stand upright and needles are flat and flexible – Used to make pencils and plywood • Spruce – Cones hang down and needles are stiff and prickly – Used to make canoes, furniture, musical instruments and paper Firs Spruce Angiosperms • Angiosperms are flowering seed-bearing plants – The flowers produce seeds protected by an outer coating (they do not have a hard cone to protect them like Gymnosperms) – Angiosperm trees usually have wide, flat leaves • They are called broad leaved trees Angiosperms-Growing Seasons • Angiosperms can be classified by their growing season: • Annuals • Biennial • Perenials – Annuals live for only 1 growing season – Biennial needs 2 growing seasons to fully develop • The rest in the winter the flower, produce seeds and dies the next year – Perennial can live for 3 or more years. Annuals • Annuals live for only 1 growing season – Include marigolds, tomatoes and sunflowers Biennials • Biennial needs 2 growing seasons to fully develop – The rest in the winter the flower, produce seeds and dies the next year – Include carrots, cabbage, Parsley and foxglove Perennials • Perennial can live for 3 or more years. – They grow, flower and produce seeds year after year – Include roses, oak trees, carnations, and spearmint Classifying Angiosperms by Seed Structure • Seed Structure – Cotyledons tiny seed leaves of a plant embryo used to nourish a plant until it can undergo photosynthesis • Dicotyledons- also called dicots- have 2 seed leaves • Monocotyledons- also called monocots- have 1 seed leaf DICOTS • Most angiosperms are dicots – They have a inner tube-like structure that is arranged in rings (their vascular tissue) – They have a taproot system- one large thick root with – Woody stems – Branching veins – Petals are arranged in groups of 4 or 5 MONOCOTS • • • • • Have one seed leaf Vascular tissue is randomly scattered They have a fibrous root system They have parallel veins Petals are usually arranged in groups of 3