* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download THE PLANT KINGDOM - Welcome to Cherokee High School
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
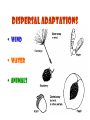
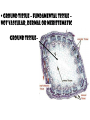
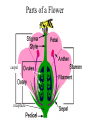
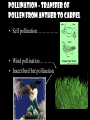
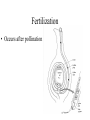
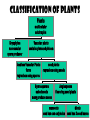
THE PLANT KINGDOM All plants: • Are Multicellular • Are Autotrophic – photosynthetic • Have cell walls with cellulose (that polysaccharide that we can’t digest – burp!) • Have chloroplasts in their cells. Basic plant Parts: • • • • • Leaves Stems Roots Flowers seeds Leaves • Main site of photosynthesis • Consist of: – Blade – Veins – Petiole Leaves can be simple or compound • Simple – have one blade • Compound - have many blades per leaf Veins in leaves • Pinnate • palmate stems • Support leaves and flowers • Transport water and nutrients within plant • May be used for storage (potato) Types of stems: 1. Herbaceous 2. Shrub 3. Vine 4. tree roots • Absorb water and minerals • Anchor plant • Some store food (carrot) Root tip Types of roots: • Tap root • Fibrous root Flower – reproductive organ • Produces male and female gametes • Provides structure for fertilization seeds • Reproductive structure containing stored food and plant embryo Dispersal adaptations • Wind • Water • animals fruit • Structure containing seeds Plants in the biosphere • Producers – base of the food chain. – Energy in plants is transferred to all other organisms when the plants get eaten •Provide oxygen for aerobic organisms •Provide shelter for many organisms Human uses: • Agriculture: 90% of the food you eat directly or indirectly comes from only 20 different kinds of cultivated plants: – Rice, corn, wheat, potatoes, etc. Medicines from plants industry Uses of cellulose Fossil fuels Problems caused by plants • Some are poisonous… • Weeds • Root damage……….. Plant cells • Rigid cell wall of cellulose and other tough materials • Cells are connected to each other by shared cytoplasm • Large central vacuoles Plant tissues tissue= group of similar cells performing the same function • Dermal – protective, covering – Outermost layer – Protection – includes bark in trees – Some cells contain chloroplasts, so they perform photosynthesis • Vascular tissue – transport or conduct materials around plant Xylem – water and minerals up phloem – food down • Ground tissue – fundamental tissue – not vascular, dermal or meristematic ground tissue– Parts of a Flower carpel receptacle Pollination – transfer of pollen from anther to carpel • Self pollination……………. • Wind pollination………. • Insect/bird/bat pollination Fertilization • Occurs after pollination Seeds embryo Dicot seed Monocot seed embryo Seedling growth Classification of Plants Plants multicellular autotrophic Bryophytes nonvascular spore producer Vascular plants contain xylem and phloem Seedless Vascular Plants ferns reproduce using spores seed plants reproduce using seeds Gymnosperms naked seeds many produce cones Angiosperms flowering seed plants monocots dicots seed has one cotyledon seed has 2 seed leaves Plant diversity Nonvascular plants: Bryophytes – mosses – no xylem or phloem Vascular plants – xylem and phloem • Nonseed vascular plants - Ferns – reproduce using spores Seed producing vascular plants • Gymnosperms – Naked seeds (oh my!) • Angiosperms– flowers Length of life of a plant • Annual biennial perennial The end