* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecosystem Notes
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
No-till farming wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Arctic ecology wikipedia , lookup
Canadian Arctic tundra wikipedia , lookup
Pleistocene Park wikipedia , lookup
Soil salinity control wikipedia , lookup
Polar ecology wikipedia , lookup
List of ecoregions in North America (CEC) wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable agriculture wikipedia , lookup
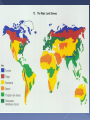
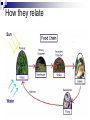
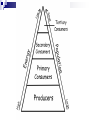
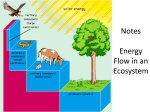
Many subcategories… Which one are you interested in? › Animals, plants, insects › Biomes (formations that exist over regions.. The Arctic, the tropics, the desert) Ways to study ecology: › Field studies - very common › Laboratory studies › Computer Simulations What possible environmental change in the future could be studied? Organisms environments include two different properties: › Abiotic: physical, non-living properties Sunlight, climate, soil, water, air › Biotic: Biological, living properties Other organisms same or different species in the same habitat Wide range of levels – from smallest to largest › Individual level › Population › Community › Ecosystem › Biome › Biosphere Smallest unit – one organism Two or more individuals of the same species Occupy the same area Interact with one another Two or more populations of different species Occupy the same area Interact with one another Living and non-living (biotic and abiotic) factors in an area interacting with each other Regions organized by climate (Arctic, Grasslands, Tropic, Desert, etc.) Terrestrial Tundra – › Located between the ice-cap and timber line of North America, Europe and Asia. Little rain, soil is frost, short plants, very cold Taiga › Subartic coniferous forests, south of the tundra. › Forests. Moderate rain, fertile soil, 4 seasons. › Lands dominated by grasses. Fertile soil. › Hot, Dry, Poor soil, hot days/cold nights. › Hot year round, a lot of rain › Rivers, lakes, ponds, swamps › Ocean, Salt lakes and seas. Largest amount of life. Temperate Grasslands Deserts Tropical Rain Forest Aquatic Fresh Water Salt Water Collection of all ecosystems – The Earth!! The portion of the planet occupied by living matter Producers, Consumers, Decomposers Its all about what you eat! The three categories of the food chain are….. 1) 2) 3) Producers Consumers Decomposers They are all dependent on each other. Producers Are Producers get their food and energy from the sun. (PLANTS) They make their food through a process called photosynthesis…. Which makes them autotrophs (self feeding). Consumers Consumers need to eat their food to get energy. (ANIMALS or Heterotrophs) Types of consumers are There are THREE types of Consumers Carnivores Herbivores Omnivores. Its still all about what you eat! Decomposers Decomposers eat dead things and turn them back into dirt, or soil. YUK! Examples: Mushrooms Worms Bugs What would the world look like without decomposers (bacteria and fungi? How they relate . Stop…Review…Check… Turn to your partner and tell them the meaning of each word. Also give two example of each. Producers; Autotrophs: Consumers; Heterotrophs: Decomposers: Energy Flows From the Sun to…. Energy Flows from the Producers; Autotrophs to the….. Energy Flows from the Primary Consumer to the…. What captures the most amount of energy? http://www.poetv.com/video.php ?vid=16788