* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecology
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Soundscape ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem services wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Pleistocene Park wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Biosphere 2 wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
River ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
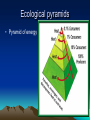
Ecology What is ecology? • The study of interactions between organisms and their environment Biosphere • Where life is found/supported • Exists between the bottom of the ocean to the tops of the atmosphere Abiotic factors • Non-living parts of the environment – Examples: temperature, air currents, moisture, light, soil, weather Biotic factors • Living factors in an environment • examples: other organisms (all living organisms depend on each other) Levels of organization Biosphere (Earth) Ecosystem (abiotic & biotic) Communities (all biotic factors living together) Populations (same biotic factors living together) Organisms (individual species) Ecosystem Biosphere Communities Population Organism Ecosystems • Two main types • Terrestrial = land • Aquatic = water – Saltwater (oceans) – Freshwater ( lakes, ponds, rivers) Habitat • Where an organism lives out its life • Examples: grass, wetlands, parking lot, pond – Can be anywhere Niche • All the interactions a species has with biotic and abiotic parts – How it finds shelter, food, where it reproduces – the role it has in the environment Survival relationships • Mutualism – both species benefit • Commensalism – one species benefits, but the second is neither helped nor harmed • Parasitism – one species benefits at the expense of another Symbiosis = living together commensalism Mutualism parasitism Nutrition & Energy Flow • Autotrophs produce their own energy – Also called producers – Examples: plants • Heterotrophs have to consume other organisms to obtain energy – Also called consumers – examples: humans, cows, deer, tigers Types of heterotrophs • Herbivores – eat plants only – Rabbits, bees, elephants, beavers • Carnivores – eat meat only – Lions, tigers • Omnivores – eat both plants and animals • Scavengers – eat animals that are already dead • Decomposers – break down decaying remains Food Chains • Shows how energy travels thru an ecosystem • Algae fish bear • Grass cow human • Arrows = energy flow • 5 or less links Trophic levels • Each link is called a trophic level • Also called feeding steps Food webs • Shows all feeding relationships • A large set of connected food chains Ecological pyramids • Pyramid of energy Pyramid of numbers Pyramid of biomass Nutrient cycles • Matter is cycled thru ecosystems • Matter is recycled, never lost • 4 main cycles – – – – Water Carbon Phosphorus nitrogen Water cycle Carbon cycle Nitrogen cycle Phosphorus cycle