* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Communities and Biomes
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Old-growth forest wikipedia , lookup
List of ecoregions in North America (CEC) wikipedia , lookup
Tropical rainforest wikipedia , lookup
Operation Wallacea wikipedia , lookup
Lake ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Reforestation wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
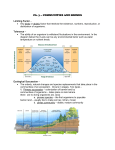
Communities and Biomes Limiting factors Any biotic or abiotic factor that restricts the existence, numbers, reproduction, or distribution of organisms. (examples - food availability, predation, climate, disease, temperature, etc.) Succession: Changes over time What would your backyard look like if you didn’t mow it or do anything to it? What would it look like in 5 years? 10 years? 20 years? First, grass gets taller and weeds grow... Then, bushes start growing, trees appear… Later, animals move in and everything grows… Years later, the area is a forest! Ecologists refer to the orderly, natural changes and species replacements that take place in the communities of an ecosystem as succession. Primary Succession colonization of new sites by communities of organisms Lava destroyed everything in this area. When it cooled, it formed new land. The first species in this area is called a pioneer species. Secondary succession - the sequence of community changes that occurs after the community is disrupted by natural disaster or human actions. There was a fire here several years ago. Several species are starting to grow back. The difference between primary and secondary succession... Secondary succession occurs in areas that previously contained life and soil. In primary succession, everything is new, including the land and soil. A climax community is a stable, mature community that undergoes little or no change. Biomes - a large group of ecosystems that share the same type of climax community. Biomes on land - terrestrial biomes Biomes in salt water - marine biomes Biomes in fresh water - freshwater biomes Marine Biomes Estuary - where salt and freshwater mix (brackish water) Intertidal zone portion of the shoreline between high and low tides Freshwater Biomes Ponds, lakes, streams, or rivers Terrestrial Biomes There are many examples, including NC’s very own biome… Temperate deciduous forest Desert - dry region with very little rainfall Tropical Rain Forest - warm temperatures, wet weather, many plants and animals Tundra - treeless land with frozen ground called permafrost Taiga – (also called boreal forest) northern coniferous forest containing mostly firs, hemlock, and spruce trees Grasslands They are called different things in different places: Australia, Canada, US - prairies Russia - steppes Africa - savannas Argentina - pampas