* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CH 3 and 4Comm and Biomes 2013
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Pleistocene Park wikipedia , lookup
Tropical Africa wikipedia , lookup
List of ecoregions in North America (CEC) wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Lake ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Reforestation wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Old-growth forest wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
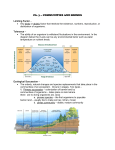
Chapter 3 Communities and Biomes Part 1 Ecosystem: interactions among populations in a community Consists A of: community of organisms The soil, water, and weather Energy Biome - a major ecosystem that shares the same type of climate and has similar life forms. 1. Salt water 2. Freshwater 3. Estuary (mix of salt and fresh water) 4. Terrestrial (dry land) Tundra (Alpine and Arctic) Permafrost - permanently frozen ground Plants - short roots; fast growing; perennials. Animals have thick fur / body fat / coloration. Taiga / Coniferous Forest Conifers - cone-bearing trees / bending branches / needles as leaves. Animals also have thick fur / body fat. Temperate / Deciduous Forest Broad-leaved trees lose their leaves yearly. Some birds migrate. Tropical Rain Forest Arboreal - tree-dwelling animals Trees / Plants: 1. Canopy 2. Understory 3. Ground Desert Most desert animals are nocturnal. Estivation - sleeping during hot days. Plants have waxy leaves / spines. Grasslands (Savanna and Temperate) What are Steppes? Most animals have good vision and speed. Plants have underground stems / survive fires. Aquatic Biomes Freshwater – Ponds, lakes, streams, rivers, wetlands. Marine – Oceans, coral reefs, estuaries. CLIMATOGRAM Measures two things: Average Temperature Average Precipitation Chapters 3-4 Communities and Biomes / Population Part 2 Succession: changes over time Primary succession – gradual growth of an ecosystem over a long period of time. Example: Hawaii. Rock -> Lichen -> moss -> grass -> shrub -> tree -> vines Succession: changes over time Pioneer species – first species in an area Succession: changes over time Climax community – shows little or no change over time Secondary succession (previously supported vegetation) – sequence of life after natural disasters (examples: Forest fires, glaciers, avalanches, flood, hurricane, tsunami, tornadoes, volcanic eruption). 1988 forest fire in Yellowstone Nat’l Park Population Dynamics Exponential Growth - as a population gets larger, it also grows faster. Carrying capacity - the maximum number of organisms that an environment can support. Limiting factors: Factors that affect an organism’s ability to survive. Density dependent factors: Disease Competition Parasites Food & water Space Density independent factors (abiotic factors): Temperature Storms Floods Drought Habitat disruption (logging, burning, draining swamps, moving in exotic species) Demography - human population growth Immigration - moving in Emigration - moving out Growth rate Natality - birth rate Fatality - death rate