* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Populations and Humans in the Biosphere
Wildlife corridor wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Mission blue butterfly habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Maximum sustainable yield wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Human population planning wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Source–sink dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Conservation biology wikipedia , lookup
Extinction debt wikipedia , lookup
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Decline in amphibian populations wikipedia , lookup
Holocene extinction wikipedia , lookup
Habitat destruction wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
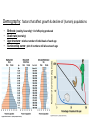
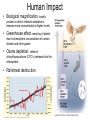
Populations and Humans in the Biosphere Population Density • What can cause a population to grow? – Births, immigration • What can cause a population to decline? – Deaths, emigration Population Growth Models • Exponential model (red) • idealized population in an unlimited environment (J-curve); r-selected species (r=per capita growth rate) • Logistic model (blue) •carrying capacity (K): maximum population size that a particular environment can support (S-curve); Kselected species Population limiting factors • Density-dependent factors •competition •predation •stress/crowding •waste accumulation • Density-dependent factors regulate population size • Density-independent factors (abiotic) • •weather/climate •periodic disturbances Question • No matter where you live, would you say that the total human population is growing faster today or that it grew faster 50 years ago? Answer • The rate of growth was faster 50 years ago, but the total number of people being added to the population each day is greater today. Demography: factors that affect growth & decline of (human) populations • • • • Birthrate (natality, fecundity)~ # of offspring produced Death rate (mortality) Age structure~ relative number of individuals of each age Survivorship curve~ plot of numbers still alive at each age Human Populations • Not all countries have the same growth rate – Highly developed countries (US, Germany, Japan, etc.) • Low birth rates and infant mortality rates and longer life expectancies – Developing countries • Moderately developing countries (Mexico, Thailand, etc.): birth and infant mortality rates high, but declining • Less developed countries (Bangladesh, Niger, Ethiopia, Laos, Cambodia, etc.): highest birth and infant mortality rates and lowest life expectancies Biodiversity • What is it? The genetically-based variety of all organisms in the biosphere • Species diversity – the number of different species in the biosphere • The greater the biodiversity, the more stable (able to rebound from disturbance) an ecosystem is Word Clue • From the words used, what do you think these words mean? – habitat fragmentation – invasive species – biological magnification Word Clue • From the words used, what do you think these words mean? – habitat fragmentation – when a habitat is split into pieces, usually due to development – invasive species – non-native species – biological magnification – concentrations of a harmful substance increase in organisms at higher trophic levels Threats to Biodiversity • What are some threats to biodiversity? – Invasive species, – Overexploitation, – destruction of habitat, – disruption of habitat, – fragmentation of habitat, – pollution Pollution and Biodiversity • What three kinds of pollution affect biodiversity? • Biological magnification (DDT), • Acid rain (plants), • Eutrophication from fertilizers, sewage, etc. that lead to algae growth Endangered and Extinction • What is the difference between background extinction and mass extinction? – Background extinction is a gradual process; mass extinction is a large percentage of species gone extinct • Which one is going on now? – Mass Extinction • What is its cause? – People • What is extinction? Endangered? How can we help? • Conservation and preservation the two main ways of slowing the decrease of biodiversity. What is the difference? – Conservation involves maintaining species and habitats as resources for use; preservation involves complete protection • What is a renewable resource? Nonrenewable resource? Human Impact • Biological magnification: trophic process in which retained substances become more concentrated at higher levels • Greenhouse effect: warming of planet due to atmospheric accumulation of carbon dioxide and other gases • Ozone depletion: effect of chlorofluorocarbons (CFC’s) released into the atmosphere • Rainforest destruction • Cause: Overpopulation?