* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Conservation Biology
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Unified neutral theory of biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Fauna of Africa wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
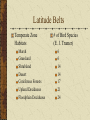
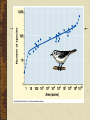
Conservation Biology Biodiversity Trophic Levels Primary Producers Primary Consumers Secondary Consumers Tertiary Consumers Quaternary Consumers Trophic Levels Primary Producers Primary Consumers Secondary Consumers Tertiary Consumers Quaternary Consumers Keystone Species Keystone Species Keystone Species Coyote –Keystone species in Walnut Killing coyotes means an increase in a few dominant species Residents complain about rodent problems when coyotes disappear Biodiversity – Number of Species? Biodiversity Levels Genetic Species Community and Ecosystem Biodiversity Levels Alpha Number of taxa in a local area Gamma Number of taxa in a region Beta The turnover of species from one habitat to another Geographic Patterns in Species Diversity Latitude 60 degrees N 40 degrees N 20 degrees N Ant Species 10 species 50 – 100 species 100 – 200 species Geographic Patterns in Species Diversity Country Greenland New York Guatemala Colombia Bird Species 56 species 105 species 469 species 1395 species Bird Diversity in North and Central America Geographic Patterns in Species Diversity Location Arctic Waters Temperate Waters Tropical Seas Marine Species (Tunicates) 100 species 400 species 600 species Latitude Belts Temperate Zone Habitats Marsh Grassland Shrubland Desert Coniferous Forests Upland Deciduous Floodplain Deciduous # of Bird Species (E. J. Tramer) 6 6 14 14 17 21 24 Foliage Height Diversity Adding new layers adds new habitats for additional species North American Diversity (MacArthur and MacArthur) Mammals and Breeding Land Birds Increase from North to South More in the west • Increases with heterogeneity Reptiles and Amphibians More abundant in East • Reptiles – mountains • Amphibians - water Island Biogeography MacArthur and Wilson (1960’s) Primary Productivity The amount of light energy that is converted into chemical energy Often expressed as biomass Pyramid of Net Productivity Secondary Productivity The rate at which an ecosystem converts the chemical energy of the food they eat into their own biomass 10% rule Biodiversity Crisis Extinction Rates are increasing Toxins (biological magnification) Greenhouse effect / Ozone depletion Overpopulation Major threats to Biodiversity Habitat Destruction Overexploitation Introduction of exotics Conservation Endangered Species in danger of becoming extinct Threatened Species likely to become endangered in the near future Genetic Diversity Losing individuals or populations loses genetic diversity Habitat Fragmentation Conservation Edges Corridors Protect landscapes not individual species Sustainable development Edge Effect Corridors Population Viability Analysis Predicts whether a species will persist in an environment minimum viable population effective population size Extinction Background Several species a year just go extinct – They are replaced Mass Large scale extinction – species replaced due to adaptive radiation of remaining species Anthropogenic Large scale extinction – species being replaced by a single species (humans)