* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetics and Probability
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Human leukocyte antigen wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
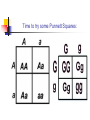
Genetics and Probability Probability refers to the chances of something happening. Probability can be used to predict. In genetics, probability can be determined using a chart called a Punnett Square. Remember! Most genes are in pairs (two alleles) One allele is from the mother (egg cell), one from the father (sperm cell). They combine in the zygote. The two alleles can be the same for a trait (homozygous). The two alleles can be different (heterozygous). Some traits are dominant, while others are recessive. Important terms: Phenotype: The physical trait itself, sometimes visible. Genotype: The genetic combination of alleles, can be homozygous dominant, homozygous recessive, or heterozygous. (Do you remember what alleles are?) But it’s not always quite so simple! Multiple allele traits: some traits are controlled by more than two alleles, so the probabilities become much more complicated. (ex human blood types) Some traits are controlled by more than one gene (ex. Human hair color, skin color, eye color). Incomplete dominance: when two alleles combine, but show up as a third - different - trait. (ex red flowers X white flowers, offspring have pink flowers) Codominance: when the alleles are neither dominant nor recessive. Both traits can show up. (ex brown cattle X white cattle, giving a mixed cow called a roan) Mutations: when entirely new traits accidentally appear. These new traits might be favorable or not! Punnett Squares Show the possible gene combinations (possible genotypes) of a certain trait when two parents produce offspring. Show the probability of certain traits showing up in the offspring. Show how some genes are “hidden” but can can be passed on to offspring. Time to try some Punnett Squares: