* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Rotational Inertia and Angular Momentum
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Uncertainty principle wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Sagnac effect wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Quantum vacuum thruster wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (mechanics) wikipedia , lookup
Routhian mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Rotating locomotion in living systems wikipedia , lookup
Mitsubishi AWC wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Old quantum theory wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Laplace–Runge–Lenz vector wikipedia , lookup
Tensor operator wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Accretion disk wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Moment of inertia wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Rotational spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
Angular momentum operator wikipedia , lookup
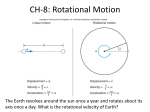
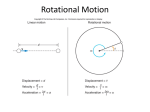
Rotational Inertia and Angular Momentum Inertia • The resistance of an object to change its state of motion • Depends on mass (the bigger the mass, the bigger the inertia). Rotational Inertia • The resistance of an object to change its state of rotation • Depends on the distribution of mass: the further the mass is from the axis of rotation, the more rotational inertia vs vs Why do some racing bicycles have solid wheels? vs • Which has more rotational inertia, a spoke wheel or a solid wheel? • Why? Which has more rotational inertia? • Spoke wheel has more rotational inertia because mass is distributed farther from axis of rotation. • Harder to start and stop rotating than solid wheels. Rotational Inertia Application • Tight rope walkers typically carry long poles with lots of mass on the ends. • Why? Rotational Inertia Wrap Up • Mass is further from the axis of rotation. • An object will have _______ rotational inertia. • It will be _______ to rotate. • It will be _______ to balance. • Mass is closer to the axis of rotation. • An object will have _______ rotational inertia. • It will be _______ to rotate. • It will be _______ to balance. Force vs. Torque • Force causes things to accelerate. • If you want something to accelerate, apply a force. • F = ma • Units: Newtons (N) • Torque causes things to rotate. • If you want something to rotate, apply a torque. • Torque = perpendicular force x lever arm • Units: mN or Nm Torque For example: Let’s say you are opening a door. Loosening a bolt • To get a bolt to turn you must apply a torque to it. • Describe a few different ways force a bolt to turn. Some torque more torque, Even more torque, ____________ ____________ Torque & dragsters • In terms of torque, why do dragsters have really big back tires? Torque and Balancing • If a teeter-totter is balanced, that means that the torque on both sides is equal but in the opposite direction. • A common mistake is that students think the force is the same on both sides but that is not true. THE TORQUE MUST BE THE EQUAL! Torque Practice Problem F =? 40 kg • A 40 kg child sits 1.5 meters away from the center of a teeter-totter. How much force does his dad need to exert 2 meters from the center (on the other side) to prevent the child from moving? Angular Momentum • Linear Momentum = mass x velocity ( p = mv ) • Angular Momentum = rotational inertia x angular speed Conservation of Angular Momentum QuickTime™ QuickTime™and and aa Microsoft Video 1 decompressor are needed to see this picture. Why do ice skaters spin so much faster when they bring their arms close to their bodies? Conservation of Angular Momentum To understand why ice skaters, divers, & gymnasts spin faster when they bring their bodies in we must discuss the Conservation of Angular Momentum. Law of Conservation of Angular Momentum • If no external torque acts on a rotating system, the angular momentum of that system is constant. Angular Momentum Before = Angular Momentum After Rot. Inertia x Rot. Velocity = Rot. Inertia x Rot. Velocity (before) (after) big rotational inertia small rotational velocity small rotational inertia big rotational velocity The Angular Momentum for both is the same because they have to be the same…IT’S A LAW! Angular Momentum and Vectors Angular Momentum like linear momentum is a vector. • What does that mean? Direction is important! The Direction of Angular Momentum Because the direction of something rotating is hard to determine, physicists say that the direction of angular momentum is in the plane of the rotation. If this wheel was rotating, we would say its angular momentum is pointed in this direction. So it would want to stay rotating in that direction. Examples of Angular Momentum So next time you play: - Football - Frisbee - Ride your bike Remember you are just conserving angular momentum.