* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Middle Ages Study Guide - RUSD
Post-classical history wikipedia , lookup
Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Medievalism wikipedia , lookup
History of Jerusalem during the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
England in the High Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
England in the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Dark Ages (historiography) wikipedia , lookup
Feudalism in the Holy Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Northern Crusades wikipedia , lookup
Medieval technology wikipedia , lookup
European science in the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Late Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Christianity in the 11th century wikipedia , lookup
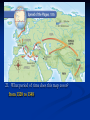
Tuesday 2/17 1. 2. wk 6 What institution survived the fall of Rome? What did a vassal owe a lord in exchange for land? Middle Ages Study Guide Due Wednesday No partner work You do not have to answer in complete sentences Middle Ages Study Guide #1-5 #6-7 #8-9 #10-13 #14-17 #18-20 Ch 9.1 Ch 9.2 Ch 10.1 Ch 10.2 Ch 10.3 Ch 10.4 pg 291 pg 299 pg 321 pg 327 pg 333 pg 341 Map #2 page 334 Wednesday 2/18 wk 6 1. Why did Feudalism develop in early medieval Europe? 2. What was one of the reasons that Feudalism collapsed at the end of the Middle Ages? Middle Ages Study Guide Due Wednesday 1. How did the decrease in trade following the fall of Rome affect cities? Many cities disappeared. 2. What institution survived the fall of Rome? the Christian Church 3. What religion did Charlemagne spread through his conquest? Christianity 4. Why did a weak and unstable Europe lead to the rise of feudalism? kings and lords needed to protect their lands against invaders 5. What did a vassal owe his lord in return for land? service and loyalty 4. Why did a weak and unstable Europe lead to the rise of feudalism? kings and lords needed to protect their lands against invaders 5. What did a vassal owe his lord in return for land? service and loyalty 6. Why did towns begin to grow around A.D. 1000? Powerful lords brought peace and stability. 7. Which is true of most medieval towns? They were dirty and crowded with a busy marketplace. 8. What did Pope Gregory do to settle the conflict with Henry IV? He excommunicated Henry. 7. Which is true of most medieval towns? They were dirty and crowded with a busy marketplace. 8. What did Pope Gregory do to settle the conflict with Henry IV? He excommunicated Henry 9. What kind of students did cathedral schools attract? sons of European nobles 10. What event led to the First Crusade? The Seljuk Turks attacked the Byzantine Empire. 11. What was the overall effect of the First Crusade? Christians captured Jerusalem and established four Crusader states. 10. What event led to the First Crusade? The Seljuk Turks attacked the Byzantine Empire. 11. What was the overall effect of the First Crusade? Christians captured Jerusalem and established four Crusader states. 12. How did the wars of the Crusades end? After nearly 200 years, the Muslims drove the Crusaders out of Palestine. 13. How were the effects of the Crusades different for the Muslims and the Christians? Most Muslims in Palestine felt few permanent effects of the Crusades. 12. How did the wars of the Crusades end? After nearly 200 years, the Muslims drove the Crusaders out of Palestine. 13. How were the effects of the Crusades different for the Muslims and the Christians? Most Muslims in Palestine felt few permanent effects of the Crusades. 14. Why was the bubonic plague known as the Black Death? Victims developed dark or black spots on their skin. 15. How did the bubonic plague help weaken feudalism? European workers became scarce enough to demand higher pay for their labor. 14. Why was the bubonic plague known as the Black Death? Victims developed dark or black spots on their skin. 15. How did the bubonic plague help weaken feudalism? European workers became scarce enough to demand higher pay for their labor. 16. What was the advantage of the longbow and gunpowder weapons? They could defeat knights in armor. 17. How did the Hundred Years’ War contribute to the rise of modern Europe? Strong monarchies strengthened trade and the growth of towns, which kept monarchies strong. 16. What was the advantage of the longbow and gunpowder weapons? They could defeat knights in armor. 17. How did the Hundred Years’ War contribute to the rise of modern Europe? Strong monarchies strengthened trade and the growth of towns, which kept monarchies strong. 18. What was one disadvantage of English common law? Decisions in one part of England might be different from those in another part. 19. How did King John influence England’s government? His poor policies pushed English nobles to create the Magna Carta and force him to sign it 18. What was one disadvantage of English common law? Decisions in one part of England might be different from those in another part. 19. How did King John influence England’s government? His poor policies pushed English nobles to create the Magna Carta and force him to sign it. 20. England’s early parliaments gained the right to do what? control the collection of taxes 21. What period of time does this map cover? from 1320 to 1348 22. In which general direction did the plague spread? east to west 23. In what year did the plague reach Genoa? 1348 24. Which area did the plague reach last? northern Europe 25. Why do you think plague first reached Europe from Kaffa primarily over water routes? The plague traveled to Europe mainly by merchant ships.