* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Middle Ages
Medieval Muslim Algeria wikipedia , lookup
Islamic Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
Early Muslim conquests wikipedia , lookup
High Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Rashidun Caliphate wikipedia , lookup
Muslim conquest of the Maghreb wikipedia , lookup
Northern Crusades wikipedia , lookup
History of Jerusalem during the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
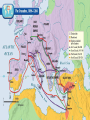
Let’s link Medieval Europe to the Middle East The Muslim Empire and the Crusades Islam (things to know) Mohammed (pbuh) 570 CE Caravan Khadija Mecca Kaaba Medina (622 CE) Hajj Islam (things to know) – Quarysh – Qur’an – Hadiths – 630 victory – 632 death – Sectarian split Early Muslim Leaders 632 - 661C.E. • After the Prophets death in 632 C.E., the Muslim community that was called the Ummah needed a leader. The successor to the Prophet was called the Caliph. • The selection process for the successor was the cause of great disagreement. Abu Bakr 632 – 634 C.E. • Abu Bakr was chosen by the ummah to be the first caliph. • Fought the Riddah Wars against the Apostasy, uniting the Arab Peninsula under Islam and the caliph. A term generally employed to describe the formal abandonment or renunciation of one's religion. Omar 634 – 644 C.E. • Omar lived a simple life in Medina while ruling the new Islamic Empire. Scholars report that he repaired his own clothing, ate simple meals of dates and bread. • He was killed by a Persian Christian slave. • Damascus fell in 336 C.E. and after a prolonged siege, Muslims took Jerusalem in 637 C.E.. • Re-claimed the area of the al-Aqsa mosque. Osman(Uthman) 664 – 656 C.E. • As he was a member of the Quraysh tribe, his election as caliph was controversial. • This scandal followed as he promoted family members, increased taxation, ignored fellow Muslims and became very wealthy. • Ruled when Persia was conquered. Cyprus was added to the empire, and the Muslim fleet sailed on Constantinople. • Uthman is perhaps best known for forming the committee which compiled the basic text of the Qur'an. Ali 656 – 661 C.E. Picture of the swearing of allegiance to Ali at Kufah in the seventh century following the murder of 'Uthman, from a late-16th century Turkish manuscript on the martyrdom of Husayn. • A cousin of the Prophet, Ali was the first leader of the Shia. While support for Ali was not unanimous, he was chosen as Caliph. • His nephew, Muawiya, opposed Ali’s authority and Ali was murdered at Kufah in 661 C.E. The Islamic Empire around 711 - 750 C.E. • October 10, 732 C.E. marks the conclusion of the Battle of Tours which pitted Charles “The Hammer” Martel vs. Abd ar-Rahman ibn-Abdallah for the control of modern France. • This was arguably one of the most decisive battles in all of history. Not only did this prove to be an extremely decisive battle for the Christians, but the Battle of Tours is considered the high water mark of the Moslem invasion of Western Europe. Point of View • This cartoon could be titled; “The Cultural Battle for Tours.” • What assumptions does it make? What views are represented? What might it look like drawn from the opposite perspective? ://www.laughyourheadoff.org Expansion of the Islamic Empire The Crusades • From the 11th to the 13th century, European Christians carried out military expeditions to regain the Holy Land from Muslims. • In 1095, Pope Urban II challenged all Christians to take up weapons. He promised: “All who die... Shall have immediate remission of sins.” Early Crusades • The First Crusade began as three organized bands of mostly French warriors. • They avoided well-defended Palestinian coastal cities. • Jerusalem was captured in 1099 amid a horrible massacre of its inhabitants. Crusades Part Deux • The crusaders organized the lands into 4 Latin states – heavily supported by Italian port cities (especially Venice) • 1140s, the Muslims struck back and then monastic leader Bernard of Clairvaux called for another crusade. • It was a total failure Crusades III • 1187, Jerusalem fell to the Muslim forces under Saladin. • German (Barbarossa), English (Richard the Lionheart), and French (Philip II) Kings lead a 3rd crusade. Crusades III • Barbarossa drowns on his way • Lionheart and Philip II can’t get inland so Philip takes his army and goes home. • Lionheart negotiates a deal with Saladin that permitted Christian pilgrims free access to Jerusalem. Kingdom of Heaven Later Crusades • 4th Crusade (1193) got caught up with a fight over the Byzantine throne. • 1204, crusaders sacked Constantinople – causing a HUGE rift between an already divided Church • 1212, a youth Crusade (never made it) Tragic 20,000 French Children Crusade: - Ship owners agree to take them to the Holy Land - 2 ships sink, the others sell the kids into slavery in North Africa Legacy? • How did the Crusades impact European society? 1. Added incredible wealth to Italian port cities 2. Instigated attacks on European Jews (Not only did they kill J.C., but while crusading, these Jews were allowed to run around free?) 3. Helped break down feudalism a) b) c) To raise money for crusades, kings had to sell land Serfs became free, nobles lost power, and kings established stronger central governments (and greater wealth) Paved way for nation-states (Portugal, Spain, England, and France)