* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ANCIENT GREECE NOTES PPT
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Greek contributions to Islamic world wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek architecture wikipedia , lookup
Pottery of ancient Greece wikipedia , lookup
History of science in classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek literature wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of Greece and the Greek world wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek warfare wikipedia , lookup
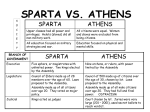
ANCIENT GREECE The Role of Geography: Greece • Greece: A mountainous peninsula along the Mediterranean Sea. Also: 2,000 islands along the Ionian and Aegean Seas. • 1. SEA: • “They did not live on land but rather around the sea” • -Used the seas around them as travel ways between themselves and other societies • -Trade was essential: Greece lacks natural resources • 2. LAND: • -80% of land almost unlivable: Rocky Terrain that divided up the land. • Result: Divided up land=divided up government • -Few roads on land, relied on sea • -1/4 on the land farmable • - A lot of small streams: not good for irrigation • RESULTS: lack of fertile ground and fresh water=Greece’s inability to support a large population • 3. CLIMATE: • -varied temperature: 40s in winter, 80s in summer • -Thus, outdoor lifestyle could be fostered CIVILZATION DEVELOPS!! • Cultures: MYCENAEAN & MINOAN & the DORIANS • MYCENAEAN: • came to Greece 2000BC • leading city: Mycenae • Fortified city! - What does this mean? • Ruled by a Warrior King • had strongest influence 1600-1100BC • sea travelers/traders • TROJAN WAR!!!- 10 year war with city of Troy (Anatolia) • MINOAN • Met w/ Mycenae in 1500 BC: war or trade? • RESULT: Mycenae see benefit of meeting other cultures: Mycenae then travel all over…became great sea traders! • Mycenae adapted Minoan writing, art, religion, politics, and literature • DORIAN • Greek culture declines • 1200 BC the Doric people caused collapsed of Mycenaean • No written documents from 1150 BC- 750 BC • Homer: Iliad and Odyssey – Blind storyteller – Wrote of Trojan War: EPICS & MYTHS WARRING CITY-STATES • -750 BC: Most Greeks lived in a Polis or City-state • - In a polis • - Agora: marketplace • - ACROPOLIS: A fortified hilltop: temples, gov bds. • - city center-village-farmland • -Different forms of Gov’t • -monarchy: king (one) • - Aristocracy: small group of elite: NOBILITY • - Oligarchy: small group of powerful people • - Tyranny: Diff. view compared today’s people who seized the throne to appeal to ordinary people • • • • • • ATHENS Had a democracy All citizens equal in society, not necessarily in government Education: Mind and Body Council made up of men ages 30 and older Assembly made of men Juries were random and large • • • • • • • SPARTA Military State: Military very important Upper class had power in society Education focuses on military Council was men 60 or older Assembly men 20 or older Kings acted as judges ATHENIAN GOLDEN AGE 477-431 BCE • Period of Growth: drama, sculpture, poetry, philosophy, architecture • PERICLES: 1. Strengthen Athenian Democracy 2. Hold and strengthen the Empire 3. GLORIFY ATHENS!!! Ex: Parthenon • -Direct Democracy: citizens rule directly-not through representatives PHILOSOPHY • Socrates: most of what we know came from his student: Plato – Did not write his feelings down • “The unexamined life is not worth living” • Plato: created a school named the Academy – Wrote The Republic – Believed only the intelligent should be able to vote – Everything has an ideal form • Aristotle: Plato’s student – Created a school called the Lyceum: more scientific • Taught Alexander the Great What was the Parthenon? The Parthenon was a white marble temple built in Athens in honor of Athena. It is considered the finest example of Greek Architecture. Where is most Greek Painting found today? Who was Praxiteles? How did Greek art glorify the human being? What was the Acropolis? Where was it located? It How did Greek art show pride in Greece’s City-States? What was the Parthenon? The Parthenon was a white marble temple built in Athens in honor of Athena. It is considered the finest example of Greek Architecture. Where is most Greek Painting found today? Who was Praxiteles? How did Greek art glorify the human being? The best preserved examples are found on vases. Greek vase painters illustrated scenes from everyday life as well as mythological events. What was the Acropolis? Where was it located? How did Greek art show pride in Greece’s City-States? What was the Parthenon? The Parthenon was a white marble temple built in Athens in honor of Athena. It is considered the finest example of Greek Architecture. Where is most Greek Painting found today? Who was Praxiteles? The best preserved examples are found on vases. Greek vase painters illustrated scenes from everyday life as well as mythological events. Praxiteles was a Greek sculptor who sculpted figures that were more lifelike and natural in form and size than other sculptors before him.. How did Greek art glorify the human being? What was the Acropolis? Where was it located? It How did Greek art show pride in Greece’s City-States? What was the Parthenon? The Parthenon was a white marble temple built in Athens in honor of Athena. It is considered the finest example of Greek Architecture. Where is most Greek Painting found today? Who was Praxiteles? How did Greek art glorify the human being? The best preserved examples are found on vases. Greek vase painters illustrated scenes from everyday life as well as mythological events. Praxiteles was a Greek sculptor who sculpted figures that were more lifelike and natural in form and size than other sculptors before him.. Greek artists placed great importance on human qualities and actions. Their works often glorified human beings. Their artists also showed qualities like strength, intelligence, pride, grace and courage which were greatly admired by the Greeks What was the Acropolis? Where was it located? How did Greek art show pride in Greece’s City-States? What was the Parthenon? The Parthenon was a white marble temple built in Athens in honor of Athena. It is considered the finest example of Greek Architecture. Where is most Greek Painting found today? Who was Praxiteles? How did Greek art glorify the human being? The best preserved examples are found on vases. Greek vase painters illustrated scenes from everyday life as well as mythological events. Praxiteles was a Greek sculptor who sculpted figures that were more lifelike and natural in form and size than other sculptors before him.. Greek artists placed great importance on human qualities and actions. Their works often glorified human beings. Their artists also showed qualities like strength, intelligence, pride, grace and courage which were greatly admired by the Greeks What was the Acropolis? Where was it located? How did Greek art show pride in Greece’s City-States? Art was meant for public enjoyment, and the architecture and public buildings were meant to be a monument to the power and glory of the polis. What was the Parthenon? The Parthenon was a white marble temple built in Athens in honor of Athena. It is considered the finest example of Greek Architecture. Where is most Greek Painting found today? Who was Praxiteles? How did Greek art glorify the human being? The best preserved examples are found on vases. Greek vase painters illustrated scenes from everyday life as well as mythological events. Praxiteles was a Greek sculptor who sculpted figures that were more lifelike and natural in form and size than other sculptors before him.. Greek artists placed great importance on human qualities and actions. Their works often glorified human beings. Their artists also showed qualities like strength, intelligence, pride, grace and courage which were greatly admired by the Greeks How did Greek art show pride in Greece’s City-States? Art was meant for public enjoyment, and the architecture and public buildings were meant to be a monument to the power and glory of the polis. What was the Acropolis? Where was it located? It was a high hill in the center of Athens. The Parthenon stood there as well as other important buildings and art works. The Peloponnesian War • Sparta Declares War: 431 BCE • Athens: NAVY • Pericles’Strategy: avoid land battles and fight at sea • Sparta: ARMY • Strategy: located inland: can not be easily invaded by sea: want to fight on land • What Happened?: • Sparta marches into Athens, burns food supply • Athens get food from allies • PLAGUE hits Athens: kills 1/3 of population including: PERICLES!!!!!! • 421 BC: Both sides call a truce • 415 BC: Athens sends 20,000 soldiers to Sicily to destroy Syracuse, Sparta’s wealthiest ally • Sparta CRUSHED the Athenians! • Athens tried to keep fighting…within 9 years 404 BC: their power, wealth, fleet, army, empire….all was lost!!! • An Athenian aristocrat, Thucydides proclaimed, “The Athenians were destroyed with a total destruction- their fleet, their army- there was nothing that was not destroyed, and few out of many returned home.” KING PHILLIP II • -King of Macedonia (north of Greece) • -transformed Macedonia from poor and weak and rich and POWERFUL!!! • -built a war machine: well trained army and advance strategy • -PLAN: to conquer Persian Empire: need Greece to have the power to succeed • -Greek city-states lacked a plan to stop Phillip from invading • -Although Athens and Thebes tried, GREECE WAS CONQUERED by King Phillip II, all city-states except Sparta. • -Battle of Chaeronea: marks the defeat of Greece • -Phillip dies and his son takes over goal of conquering PERSIA ALEXANDER THE GREAT • -student of Aristotle, became king at age 20 • -Alexander moved towards Persia and Darius III: king of Persia • -333BC: Alexander won the 1st battle but Darius III escaped • -Alexander and the Macedonians swept through more and more of the Persian Empire ALEXANDER IN EGYPT, PERSIA AND INDUS VALLEY • EGYPT • -Alexander conquered Egypt, became pharaoh • -created city of Alexandria: became center of commerce and culture • -Ptolemy: one of Alexander’s general was left to rule over Egypt • PERSIA • -After Egypt, Alexander continued through Persia • -331 BC- Battled with Darius III again and won…again • -Darius III was killed by his own men • -Alexander wins Persia! Burns Persepolis down • INDUS VALLEY • -Alexander conquered Indus River Valley (India) • -He wanted to go deeper, his men did not • -Alexander turned back THE DEATH OF ALEXANDER • Culture • Alexander wanted the culture of Greece and his conquered lands to mix. • He saw Europe and Asia as one, even married an Asian woman. • Death • -Had more dreams to expand but fell sick and died at age 33 • -after death, his culture he created declined and his empire was divided up between his generals into smaller empires