* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Steps of Meiosis - Sonoma Valley High School
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Homologous recombination wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
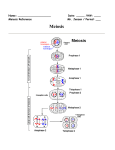
Steps of Meiosis Meiosis I: Prophase I • Homologous pairs align with each other. • Synapsis occurs: pairing of homologues. • Each pair of homologues chromosomes is called a tetrad. – Crossing over occurs. Crossing Over • Crossing over occurs during tetrad positioning of chromosomes. • Results in genetic recombination – Alleles are swapped Crossing Over • Actual picture of chromosomes crossing over. • This creates variation among offspring of a species. Meiosis I : Metaphase I • Microtubules attach only to outside kinetochores. • Homologous pairs move to equator of cell due to kinetochore fibers. Meiosis I: Anaphase I • Independent assortment – Homologues are pulled apart by kinetochore fibers. – Homologous pairs are separated and moved to opposite poles. • Note: still two chromotids Meiosis I: Telophase I • Cell goes through cytokinesis. • Cells are now 1n or haploid. Meiosis II: Prophase II • Spindle fibers form and begin to move the chromosomes toward the middle of the dividing cell Meiosis II: metaphase II • Chromosomes are lined up in the center • No replication • No synapsis • No crossing over. Meiosis II: anaphase II • Chromotids are split apart and moved to opposite poles of cell. • A second division occurs. Cells “want” identical genes Cells “want” genetic diversity Comparing Mitosis and Meiosis