* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Astronomy - Needham.K12.ma.us
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy on Mars wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
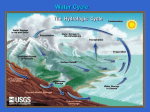
Our Solar System The Sun Observe the sun at different wavelengths of the EM spectrum Two Kinds of Motion Rotation Explore a model of Earth's daily rotation. Revolution Explore a model of Earth's yearly revolution around the sun. Why the Earth has seasons Is it because Earth is closer to the sun in the summer, and farther away in the winter? NO! Is it because the Earth revolves around the sun? NO! It’s all about the tilt of the Earth’s axis. When one hemisphere is tilted toward the sun, it gets more direct sunlight, and the season is summer. The opposite occurs in winter. Northern hemisphere is tilted toward sun, so it’s summer there. Northern hemisphere is tilted away from sun, so it’s winter there. Click here to see an animation of Earth’s orientation toward the sun at different times of the year. Phases of the Moon Moon phases Click here to see an animation of a solar eclipse. Click here to see an animation of a lunar eclipse. HIGH and low tides Gravity pulls on the Earth with different levels of strength. The parts closer to the moon are pulled on harder than those parts further away. A Tidal Bulge (High Tide) is produced on the side of the Earth DIRECTLY below the moon. Another is produced on the EXACT opposite side of the Earth. The bulge under the moon is produced due to gravity "stretching" the water, pulling it toward the moon. The bulge produced on the opposite side of the Earth is made because the moon tries to pull the Earth out from under the water! Tides are caused by gravity pulling on the Earth’s bodies of water and upon the Earth itself. There are 2 gravitational bodies that affect the tides: the sun and the moon. The moon is much closer to the Earth than the sun is, so it has a much greater influence upon the tides. Notice that when the Earth, Moon, and Sun are all in a line (Full and New Moon phases) the high tides are MUCH higher than at other times. These are called SPRING TIDES. When the Moon and Sun are at right angles to each other (First and Third Quarter Moon phases) the high tides are lower than at other times. These are called NEAP TIDES. View auroras are terrestrial planets (made of rock and metal) are gas giants Oops! Pluto’s not a planet any more! X X Click on the link below for a simulation of the huge distances between planets in the solar system. Space travel in our solar system The universe is mostly empty space. Even in a "crowded" region like our solar system, the distances between planets are so vast that they are difficult to imagine. This animation simulates a voyage from the sun past all nine planets. The animation shows each planet's average distance from the sun. At the speed of today's fastest spacecraft (~20 km/second), it would take almost ten years to travel this distance. Even at the speed of light, the trip would last 5 1/2 hours. In this animation, the apparent speed of the viewer is over 300 times the speed of light. cool Mars website Comets Orbital data from Voyager III, Carina Software A comet is a small body that orbits the sun. It consists of a nucleus (rock, dust, ice), coma (atmosphere of dust and gas around the nucleus), and tail (stream of dust and gas that points away from the sun). Comets have a very elliptical orbit. Comet animation Life Stages of a Star Life stages animation The Milky Way Galaxy Examine the Milky Way Galaxy at different scales. Observe different types of galaxies Formation of the solar system Observe the view of the night sky from the same location over the course of a year. Photos from Hubble Space Telescope