* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Today`s Powerpoint - Physics and Astronomy
Astronomical clock wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Antikythera mechanism wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy on Mars wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Lunar effect wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
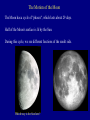
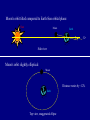
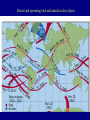
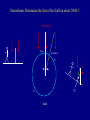
Foundations of Astronomy Part 3 • Questions on iClicker Registration • Questions on Essay Discuss Einstein Essay Clicker Question: If Earth rotated twice as fast as it currently does, but its motion around the sun stayed the same, then which of the following is true: A: the night would be twice as long B: the night would be half as long C: the year would be half as long D: the year would be twice as long E: the length of a day would be unchanged Pre-Tutorial Question Imagine you are standing in the northern hemisphere. Looking directly north, you see a star just above the horizon. A little later you notice that it has shifted position slightly. Which way did it move? a) to the right, (east) b) to the left, (west) c) up, (rising) d) down, (setting) Lecture Tutorial in Introductory Astronomy • Motion – Pages 1-6 POST-Tutorial Question Imagine you are standing in the northern hemisphere. Looking directly north, you see a star just above the horizon. A little later you notice that it has shifted position slightly. Which way did it move? a) to the right, (east) b) to the left, (west) c) up, (rising) d) down, (setting) POST-Tutorial Question You are looking toward the north and see the Big Dipper to the right of Polaris. Fifteen minutes later, the Big Dipper will appear to have moved in roughly what direction? a) east (to your right) a) west (to your left) c) up (away from the horizon) c) down (closer to the horizon) POST-Tutorial Question How much time is there between when a star rises and when it sets? a) less than twelve hours a) about twelve hours a) more than twelve hours d) it depends on the star The Motion of the Moon The Moon has a cycle of "phases", which lasts about 29 days. Half of the Moon's surface is lit by the Sun. During this cycle, we see different fractions of the sunlit side. Which way is the Sun here? See Tutorial on book’s website for animation. Cycle of phases slightly longer than time it takes Moon to do a complete orbit around Earth. Cycle of phases or "synodic month" Orbit time or "sidereal month" 29.5 days 27.3 days Eclipses Lunar Eclipse When the Earth passes directly between the Sun and the Moon. Sun Earth Moon Solar Eclipse When the Moon passes directly between the Sun and the Earth. Sun Moon Earth Solar Eclipses Diamond ring effect - just before or after total Total Partial Annular - why do these occur? Lunar Eclipse Why don't we get eclipses every month? Moon's orbit tilted compared to Earth-Sun orbital plane: Sun Moon Earth 5.2o Side view Moon's orbit slightly elliptical: Moon Distance varies by ~12% Earth Top view, exaggerated ellipse Types of Solar Eclipses Explained Certain seasons are more likely to have eclipses. Solar “eclipse season” lasts about 38 days. Likely to get at least a partial eclipse somewhere. Animation It's worse than this! The plane of the Moon's orbit precesses, so that the eclipse season occurs about 19 days earlier each year. Recent and upcoming total and annular solar eclipses Eratosthenes Determines the Size of the Earth in about 200 B.C. Sun's rays Syene Alexandria N 7.2o S Earth He knows the distance between the two cities is 5000 "stadia". From geometry then, 7.2o = 360o 5000 stadia Earth's circumference => circumference is 250,000 stadia, or 40,000 km. So radius is: 40,000 km 2p = 6366 km (very close to modern value, 6378 km!)