* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download fibrous skeleton insulates atria from ventricles
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
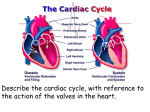
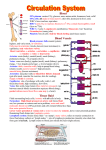
Circulatory system Cardiovascular system carries blood to lungs for gas exchange Systemic circuit - left side of heart 19-2 heart, arteries, veins and capillaries Two major divisions: Pulmonary circuit - right side of heart heart, blood vessels and blood supplies blood to all organs of the body One side pumps to the lungs One side pumps to the lungs One side pumps to the rest of the body 19-6 Located in mediastinum, between lungs Base - broad superior portion of heart Apex - inferior end, tilts to the left, tapers to point 3.5 in. wide at base, 5 in. from base to apex and 2.5 in. anterior to posterior; weighs 10 oz Pericardial cavity contains 5 to 30 ml of pericardial fluid Allows heart to beat without friction, room to expand and resists excessive expansion Parietal pericardium Pericardial cavity outer, tough, fibrous layer of CT filled with pericardial fluid Visceral pericardium (a.k.a. epicardium of heart wall) 19-7 Pericardial cavity contains 5 to 30 ml of pericardial fluid Epicardium (a.k.a. visceral pericardium) Myocardium serous membrane covers heart thick muscular layer fibrous skeleton network of collagenous and elastic fibers Endocardium - smooth inner lining 19-8 Right and left atria two superior, posterior chambers receive blood returning to heart Right and left ventricles two inferior chambers pump blood into arteries 19-9 Interatrial septum Interventricular septum wall that separates ventricles Pectinate muscles wall that separates atria internal ridges of myocardium in right atrium and both auricles Trabeculae carneae internal ridges in both ventricles 19-10 Atrioventricular (AV) valves right AV valve has 3 cusps (tricuspid valve) left AV valve has 2 cusps (mitral, bicuspid valve) chordae tendineae - cords connect AV valves to papillary muscles (on floor of ventricles) Semilunar valves - control flow into great arteries pulmonary: right ventricle into pulmonary trunk aortic: from left ventricle into aorta 19-11 Where are the semi-lunar valves? Pulmonary and aortic valves are semilunar valves? Ventricles relax pressure drops semilunar valves close AV valves open blood flows from atria to ventricles Ventricles contract AV valves close pressure rises semilunar valves open blood flows into great vessels Ventricles relax pressure drops semilunar valves close AV valves open blood flows from atria to ventricles 19-14 Ventricles contract AV valves close pressure rises semilunar valves open blood flows into great vessels Sympathetic nerves from upper thoracic spinal cord, through sympathetic chain to cardiac nerves directly to ventricular myocardium can raise heart rate to 230 bpm Parasympathetic nerves right vagal nerve to SA node left vagal nerve to AV node vagal tone – normally slows heart rate to 70 - 80 bpm 19-15 Properties myogenic - heartbeat originates within heart autorhythmic – regular, spontaneous depolarization 19-16 SA node: pacemaker, initiates heartbeat, sets heart rate fibrous skeleton insulates atria from ventricles 19-17 AV node: electrical gateway to ventricles AV bundle: pathway of signals from AV node 19-18 Right and left bundle branches: divisions of AV bundle that enter interventricular septum Purkinje fibers: upward from apex spread throughout ventricular myocardium 19-19 Short, branched cells, one central nucleus Sarcoplasmic reticulum, large T-tubules Intercalated discs join myocytes end to end 19-20 interdigitating folds - surface area mechanical junctions tightly join myocytes electrical junctions - gap junctions allow ions to flow 19-21 Aerobic respiration Rich in myoglobin and glycogen Large mitochondria Organic fuels: fatty acids, glucose, ketones Fatigue resistant Auscultation - listening to sounds made by body First heart sound (S1), louder and longer “lubb”, occurs with closure of AV valves Second heart sound (S2), softer and sharper “dupp” occurs with closure of semilunar valves S3 - rarely heard in people > 30 19-23 Pressure causes a fluid to flow pressure gradient - pressure difference between two points • Resistance opposes flow – great vessels have positive blood pressure – ventricular pressure must rise above this resistance for blood to flow into great vessels 19-24 One complete contraction and relaxation of all 4 chambers of the heart Atrial systole, Ventricle diastole Atrial diastole, Ventricle systole Quiescent period Systole is the contraction of a chamber of the heart Diastole is the relaxation of a chamber of the heart 19-25 19-26 Quiescent period Ventricular filling Isovolumetric contraction Ventricular ejection Isovolumetric relaxation Quiescent period all chambers relaxed AV valves open and blood flowing into ventricles Atrial systole SA node fires, atria depolarize P wave appears on ECG atria contract, force additional blood into ventricles ventricles now contain end-diastolic volume (EDV) of about 130 ml of blood 19-27 19-28 Atria repolarize and relax Ventricles depolarize QRS complex appears in ECG Ventricles contract Rising pressure closes AV valves - heart sound S1 occurs No ejection of blood yet (no change in volume) 19-29 Rising pressure opens semilunar valves Rapid ejection of blood Reduced ejection of blood (less pressure) Stroke volume: amount ejected, 70 ml at rest SV/EDV= ejection fraction, at rest ~ 54%, during vigorous exercise as high as 90%, diseased heart < 50% End-systolic volume: amount left in heart T wave appears in ECG Ventricles repolarize and relax (begin to expand) Semilunar valves close - heart sound S2 occurs AV valves remain closed Ventricles relax but do not fill (no change in volume) 19-30 Rapid ventricular filling 1. • Diastasis 2. • sustained lower pressure, venous return Atrial systole 3. • 19-31 AV valves first open filling completed Atrial systole, 0.1 sec Ventricular systole, 0.3 sec Quiescent period, 0.4 sec Total 0.8 sec, heart rate 75 bpm 19-32 Both ventricles must eject same amount of blood. They should have the same stroke volume. 19-33 Both ventricles must eject same amount of blood. They should have the same stroke volume. 19-34