* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 10 - The University of Texas at Dallas
Cyberwarfare wikipedia , lookup
Post-quantum cryptography wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Next-Generation Secure Computing Base wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Access control wikipedia , lookup
Data remanence wikipedia , lookup
Computer and network surveillance wikipedia , lookup
Multilevel security wikipedia , lookup
Information security wikipedia , lookup
Cyber-security regulation wikipedia , lookup
Cyberattack wikipedia , lookup
Mobile security wikipedia , lookup
Unix security wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
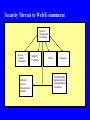
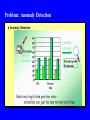
Cyber Security Lecture for June 25, 2010 Unit #2: Selected Topics in Cyber Security Dr. Bhavani Thuraisingham The University of Texas at Dallas June 25, 2010 Outline Operating Systems Security Network Security Designing and Evaluating Systems Web Security Data Mining for Introduction Detection Other Security Technologies Operating System Security Access Control - Subjects are Processes and Objects are Files - Subjects have Read/Write Access to Objects - E.g., Process P1 has read acces to File F1 and write access to File F2 Capabilities - Processes must presses certain Capabilities / Certificates to access certain files to execute certain programs - E.g., Process P1 must have capability C to read file F Mandatory Security Bell and La Padula Security Policy - Subjects have clearance levels, Objects have sensitivity levels; clearance and sensitivity levels are also called security levels - Unclassified < Confidential < Secret < TopSecret - Compartments are also possible - Compartments and Security levels form a partially ordered lattice Security Properties - Simple Security Property: Subject has READ access to an object of the subject’s security level dominates that of the objects - Star (*) Property: Subject has WRITE access to an object if the subject’s security level is dominated by that of the objects\ Covert Channel Example Trojan horse at a higher level covertly passes data to a Trojan horse at a lower level Example: - File Lock/Unlock problem - Processes at Secret and Unclassified levels collude with one another - When the Secret process lock a file and the Unclassified process finds the file locked, a 1 bit is passed covertly - When the Secret process unlocks the file and the Unclassified process finds it unlocked, a 1 bit is passed covertly - Over time the bits could contain sensitive data Steps to Designing a Secure System Requirements, Informal Policy and model Formal security policy and model Security architecture - Identify security critical components; these components must be trusted Design of the system Verification and Validation Product Evaluation Orange Book - Trusted Computer Systems Evaluation Criteria Classes C1, C2, B1, B2, B3, A1 and beyond - C1 is the lowest level and A1 the highest level of assurance - Formal methods are needed for A1 systems Interpretations of the Orange book for Networks (Trusted Network Interpretation) and Databases (Trusted Database Interpretation) Several companion documents - Auditing, Inference and Aggregation, etc. Many products are now evaluated using the federal Criteria Network Security Security across all network layers - E.g., Data Link, Transport, Session, Presentation, Application Network protocol security Ver5ification and validation of network protocols Intrusion detection and prevention - Applying data mining techniques Encryption and Cryptography Access control and trust policies Other Measures - Prevention from denial of service, Secure routing, - - - - Data Security: Access Control Access Control policies were developed initially for file systems - E.g., Read/write policies for files Access control in databases started with the work in System R and Ingres Projects - Access Control rules were defined for databases, relations, tuples, attributes and elements - SQL and QUEL languages were extended GRANT and REVOKE Statements Read access on EMP to User group A Where EMP.Salary < 30K and EMP.Dept <> Security - Query Modification: Modify the query according to the access control rules Retrieve all employee information where salary < 30K and Dept is not Security What is an MLS/DBMS? Users are cleared at different security levels Data in the database is assigned different sensitivity levels-- multilevel database Users share the multilevel database MLS/DBMS is the software that ensures that users only obtain information at or below their level In general, a user reads at or below his level and writes at his level Why MLS/DBMS? Operating systems control access to files; coarser grain of granularity Database stores relationships between data Content, Context, and Dynamic access control Traditional operating systems access control to files is not sufficient Need multilevel access control for DBMSs Summary of Developments in MLS/DBMS Early Efforts 1975 – 1982; example: Hinke-Shafer approach Air Force Summer Study, 1982 Research Prototypes (Integrity Lock, SeaView, LDV, etc.); 1984 - Present Trusted Database Interpretation; published 1991 Commercial Products; 1988 - Present Inference Problem Inference is the process of forming conclusions from premises If the conclusions are unauthorized, it becomes a problem Inference problem in a multilevel environment Aggregation problem is a special case of the inference problem - collections of data elements is Secret but the individual elements are Unclassified Association problem: attributes A and B taken together is Secret - individually they are Unclassified Security Threats to Web/E-commerce Security Threats and Violations Access Control Violations Denial of Service/ Infrastructure Attacks Integrity Violations Fraud Sabotage Confidentiality Authentication Nonrepudiation Violations Data Mining for Intrusion Detection: Problem An intrusion can be defined as “any set of actions that attempt to compromise the integrity, confidentiality, or availability of a resource”. Attacks are: Intrusion detection systems are split into two groups: Host-based attacks Network-based attacks Anomaly detection systems Misuse detection systems Use audit logs - Capture all activities in network and hosts. But the amount of data is huge! Misuse Detection Misuse Detection Problem: Anomaly Detection Anomaly Detection Other Security Technologies Digital Identity Management Identity Theft Management Digital Forensics Digital Watermarking Risk Analysis Economic Analysis Secure Electronic Voting Machines Biometrics Other Applications Digital Identity Management Digital identity is the identity that a user has to access an electronic resource A person could have multiple identities - A physician could have an identity to access medical resources and another to access his bank accounts Digital identity management is about managing the multiple identities - Manage databases that store and retrieve identities - Resolve conflicts and heterogeneity - Make associations - Provide security Ontology management for identity management is an emerging research area Digital Identity Management - II Federated Identity Management - Corporations work with each other across organizational boundaries with the concept of federated identity - Each corporation has its own identity and may belong to multiple federations Individual identity management within an organization and federated identity management across organizations Technologies for identity management - Database management, data mining, ontology management, federated computing - Identity Theft Management Need for secure identity management - Ease the burden of managing numerous identities - Prevent misuse of identity: preventing identity theft Identity theft is stealing another person’s digital identity Techniques for preventing identity thefts include - Access control, Encryption, Digital Signatures - A merchant encrypts the data and signs with the public - key of the recipient Recipient decrypts with his private key Digital Forensics Digital forensics is about the investigation of Cyber crime Follows the procedures established for Forensic medicine The steps include the following: - When a computer crime occurs, law enforcement officials - who are cyber crime experts gather every piece of evidence including information from the crime scene (i.e. from the computer) Gather profiles of terrorists Use history information Carry pout analysis Digital Forensics - II Digital Forensics Techniques - Intrusion detection - Data Mining - Analyzing log files - Use criminal profiling and develop a psychological profiling - Analyze email messages Lawyers, Psychologists, Sociologists, Crime investigators and Technologists have to worm together International Journal of Digital Evidence is a useful source Steganography and Digital Watermarking Steganography is about hiding information within other information - E.g., hidden information is the message that terrorist may be sending to their pees in different parts of the worlds - Information may be hidden in valid texts, images, films etc. - Difficult to be detected by the unsuspecting human Steganalysis is about developing techniques that can analyze text, images, video and detect hidden messages - May use data mining techniques to detect hidden patters Steganograophy makes the task of the Cyber crime expert difficult as he/she ahs to analyze for hidden information - Communication protocols are being developed Steganography and Digital Watermarking - II Digital water marking is about inserting information without being detected for valid purposes - It has applications in copyright protection - A manufacturer may use digital watermarking to copyright a particular music or video without being noticed - When music is copies and copyright is violated, one can detect two the real owner is by examining the copyright embedded in the music or video Risk Analysis Analyzing risks - Before installing a secure system or a network one needs to conduct a risk analysis study - What are the threats? What are the risks? Various types of risk analysis methods Quantitative approach: Events are ranked in the order of risks and decisions are made based on then risks Qualitative approach: estimates are used for risks - Economics Analysis Security vs Cost - If risks are high and damage is significant then it may be worth the cost of incorporating security - If risks and damage are not high, then security may be an additional cost burden Economists and technologists need to work together - Develop cost models - Cost vs. Risk/Threat study Secure Electronic Voting Machines We are slowly migrating to electronic voting machines Current electronic machines have many security vulnerabilities A person can log into the system multiple times from different parts of the country and cast his/her vote Insufficient techniques for ensuring that a person can vote only once The systems may be attacked and compromised Solutions are being developed Johns Hopkins University is one of the leaders in the field of secure electronic voting machines Biometrics Early Identication and Authentication (I&A) systems, were based on passwords Recently physical characteristics of a person are being sued for identification - Fingerprinting - Facial features - Iris scans - Blood circulation - Facial expressions Biometrics techniques will provide access not only to computers but also to building and homes Other Applications Biometric Technologies Pattern recognition Machine learning Statistical reasoning Multimedia/Image processing and management Managing biometric databases Information retrieval Pattern matching Searching Ontology management Data mining Data Mining for Biometrics Determine the data to be analyzed - Data may be stored in biometric databases - Data may be text, images, video, etc. Data may be grouped using classification techniques As new data arrives determine the group this data belongs to - Pattern matching, Classification Determine what the new data is depending on the prior examples and experiments Determine whether the new data is abnormal or normal behavior Challenge: False positives, False negatives Secure Biometrics Biometrics systems have to be secure Need to study the attacks for biometrics systems Facial features may be modified: - E.g., One can access by inserting another person’s features Attacks on biometric databases is a major concern Challenge is to develop a secure biometric systems - Secure Biometrics - II Security policy for as biometric system - Application specific and applicatyion independent policies - Security constraints Security model for a biometrics systems Determine the operations to be performed - Need to include both text, images and video/animation Architecure foe a biometric system - Need to idenify securiy critical components Reference monitor Detecting intrusions in a biometric system - - Other Applications Email security - Encryption - Filtering - Data mining Benchmarking - Benchmarks for secure queries and transactions Simulation and performance studies Security for machine translation and text summarization Covert channel analysis Robotics security - Need to ensure policies are enforced correctly when operating robots