* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diapositiva 1
Colonoscopy wikipedia , lookup
Cholangiocarcinoma wikipedia , lookup
Wilson's disease wikipedia , lookup
Bariatric surgery wikipedia , lookup
Liver transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Glycogen storage disease type I wikipedia , lookup
Gastric bypass surgery wikipedia , lookup
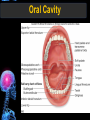
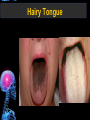
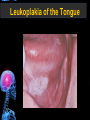
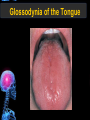
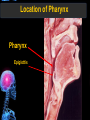
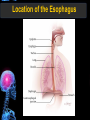
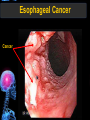
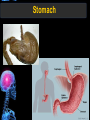
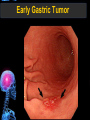
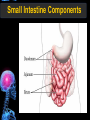
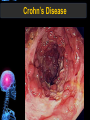
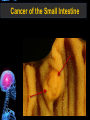
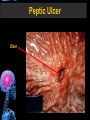
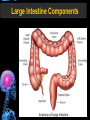
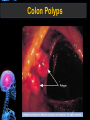
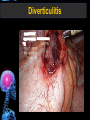
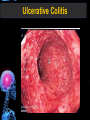
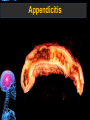
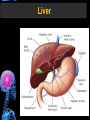
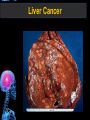
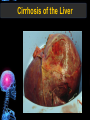
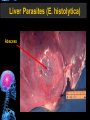
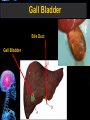
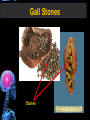
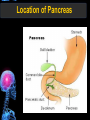
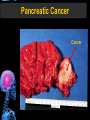
Digestive Tract Some Definitions • Enzymes-proteins that help control a biochemical reaction • Gland-an organ that produces specific enzymes or hormones • Duct-a type of tube • Gastric-related to the stomach • Metabolism-breaking down big molecules into smaller molecules • Pathology-study of the characteristics, causes, and effects of diseases Oral Cavity Oral Cavity Functions • Teeth help break food into smaller pieces • Tongue helps form bolus of food • Salivary glands provide moisture for the bolus • Salivary glands produce an enzyme (amylase) to start breaking down starch into sugars Tongue Pathologies • • • • • • Hairy Tongue Geographical Tongue Leukoplakia Glossodynia Painful papillae Yellow Tongue Hairy Tongue Leukoplakia of the Tongue Glossodynia of the Tongue Salivary Gland Pathologies • Salivary gland infections • Salivary gland stones • Salivary gland tumors Pharynx • Initial point of entry for the bolus of food • Epiglottis prevents food from going down the respiratory tract (trachea). Location of Pharynx Pharynx Epiglottis Location of the Esophagus Esophageal Functions • Pathway for the bolus into the stomach • Very muscular to help food get into the stomach • Esophagus moves in waves (peristaltic action) to force bolus downward Esophageal Pathologies • Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) • Heartburn • Esophageal cancer Esophageal Cancer Cancer Stomach • Storage site for ingested food (bolus) • Produces acid and gastric enzymes • Entry and exit of stomach is controlled by sphincters (cardiac on top and pyloric on bottom) • Very muscular gland to help mix and break up bolus • Action of acid and enzymes convert bolus in chyme Stomach Stomach (Gastric) Pathologies • • • • • Indigestion Heartburn Peptic ulcers GERD Gastric tumors Early Gastric Tumor Small Intestine • Comprised of duodenum, jejunum, and ileum • Duodenum contains the entry site for the bile duct and pancreatic duct • Proteins, Fats, and Carbohydrates are metabolized in the small intestine Small Intestine (cont.) • Proteins are broken down into peptides and amino acids • Fats are broken down into fatty acids and glycerol • Carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars • Harmful acid from the stomach is neutralized by bicarbonate in the small intestine Small Intestine (cont.) • Fine capillaries are found in structures called the microvilli which allow absorption of nutrients into the blood stream • Some water is also absorbed by the small intestine Small Intestine Components Small Intestine Pathologies • • • • • • • • Bleeding Celiac disease Crohn's disease Infections Intestinal cancers Intestinal obstructions Irritable bowel syndrome Peptic ulcers Crohn’s Disease Cancer of the Small Intestine Peptic Ulcer Ulcer Large Intestine • Comprised of cecum, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, and rectum • Major site for reabsorption of water • Majority of food metabolism has occurred Large Intestine (cont.) • Possibly up to 700 different species of “normal” bacteria occupy the large intestine • Normal bacteria help break down some undigested food into smaller molecules as well as gas formation (carbon dioxide and nitrogen and some methane, hydrogen sulfide, and hydrogen Large Intestine Components Large Intestine Pathologies • • • • • • • • • • Constipation Diarrhea Celiac disease Colon polyps Diverticulitis Irritable bowel syndrome Intestinal parasites Lactose intolerance Ulcerative colitis Appendicitis Colon Polyps Diverticulitis Ulcerative Colitis Appendicitis Liver • Large organ comprised of four lobes • Large amount of blood flow throughout this organ • Controls both metabolic (larger to smaller molecules and anabolic reactions (smaller to larger molecules Liver Biochemical Reactions • • • • • • • • • • • • • Amino acid synthesis Carbohydrate metabolism Cholesterol synthesis Lipogenesis (making of fats) Synthesis of blood clotting factors Makes red blood cells (in the fetus) Bile synthesis (emulsifies fats) Makes many enzymes and hormones Breaks down hemoglobin (makes pigment in bile) Converts ammonia to urea (to be excreted in the urine) Makes albumin for blood serum Stores vitamins and minerals Alters toxicity of chemicals (e.g., drug metabolism) Liver Liver Pathologies • • • • • • Liver cancer Cirrhosis of the liver Jaundice Hepatitis Liver parasites Variety of metabolic disorders Liver Cancer Cirrhosis of the Liver Liver Parasites (E. histolytica) Abscess Gall Bladder • Stores the bile that is made in the liver • Bile is introduced into the small intestine (duodenum) by the common bile duct • Bile contains biliary salts that emulsify fats (make them more soluble in water; can be used as detergents) • Many of the bile chemicals are pigmented and add color to the content of the small and large intestines) Gall Bladder Bile Duct Gall Bladder Gall Bladder Pathologies • Gall stones • Spastic bile duct • Gall bladder cancers Gall Stones Stones Pancreas • Produces both digestive enzymes and hormones • Pancreatic hormones include insulin (removes glucose) and glucagon (releases glucose) • Insulin is made in specialized cells called the islets of Langerhans • Releases pancreatic juice which is a mixture of enzymes that breaks down the proteins, fats, and carbohydrates in the chyme • Pancreatic juice travels from the pancreas through the pancreatic duct into the duodenum of the small intestine Location of Pancreas Pancreatic Pathologies • Pancreatitis • Pancreatic cancer • Diabetes Pancreatic Cancer Cancer The End of the Digestive Tract