* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A & P of the Gastrointestinal Tract
Hydrochloric acid wikipedia , lookup
Colonoscopy wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Bariatric surgery wikipedia , lookup
Intestine transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Hepatotoxicity wikipedia , lookup
Surgical management of fecal incontinence wikipedia , lookup
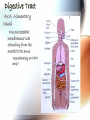
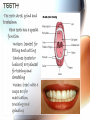
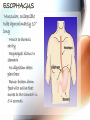
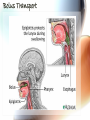
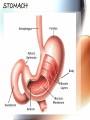
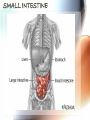
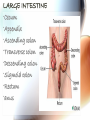
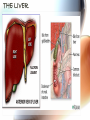
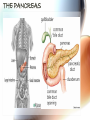
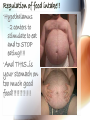
A & P of the Gastrointestinal Tract By: Sara Anderson Food!!!!! • It is necessary for existence – Pssstt…and it’s darn good too!!!!! – What happens once we chew & swallow it????? • The rest of the world may never know..but YOU will!!!!! Digestive Tract •AKA: Alimentary Canal –Musculoskeletal membranous tube extending from the mouth to the anus •Approximately 30 FEET long!!! What is peristalsis? •Coordinated, rhythmic, serial contraction of smooth muscle that forces food through the digestive tract, bile through the bile duct, and urine through the ureter. •**Interesting note** –During peristalsis, the tract shortens from approximately 30 feet to 15 feet! Accessory Organs • These aid in the digestive tract but AREN’T considered part of the digestive tract: – – – – – – Teeth Tongue Salivary Glands Liver Gall Bladder Pancreas I’m hungry..let’s eat!!! •We should all know it all begins at our MOUTHS! –TONGUE: •Muscular appendage •Aids in chewing, swallowing and formation of speech •Papillae contain taste buds – BITTER, SWEET, SOUR AND SALTY TEETH •The teeth shred, grind and breakdown –Each tooth has a special function •Incisors (center) for biting and cutting •Canines (posterior incisors) are pointed for tearing and shredding •Molars (rear) with 4 cusps are for mastication; crushing and grinding SALIVARY GLANDS •3 Pairs: –Parotid –Submandibular –Sublingual –Secrete saliva – 99% water with enzymes & mucus –1,000 – 1,500 mL of saliva every day –After food is ingested, continue to secrete saliva to cleanse the mouth •Salivary amylase (ptyalin) - major enzyme – initiates carbohydrate metabolism •Lysozyme – destroys bacteria ESOPHAGUS •Muscular, collapsible tube approximately 10” long –Mouth to thoracic cavity –Esophageal hiatus to stomach –No digestion takes place here –Bolus: broken down food with saliva that moves to the stomach in 5-6 seconds Bolus Transport STOMACH •Located in the LUQ •When full it’s the size of a football •Holds approximately 1 Liter •Entrance- Cardiac sphincter –Churns, contracts & compresses contents with gastric juices & water –Protein digestion begins Hydrochloric acid •softens connective tissue of meat •kills bacteria •activates pepsin, which converts proteins into proteoses & peptones •Mucin- protects stomach lining •Intrinsic factor- absorption of B12 •Broken down into viscous semiliquid called CHYME •Exit- Pyloric sphincter STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE •90% of digestion •20 feet long •1” diameter •Starts at the pyloric sphincter and ends at the ileocecal valve •3 major sections –Duodenum –Jejunum –Ileum Lacteals absorb metabolized fats •Intestinal juices finish carb & protein metabolism •Bile breaks molecules into smaller droplets •Pancreatic juices – break down proteins to amino acids –Dietary fats to glycerol & fatty acids –Starch to simple sugars SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE •Cecum •Appendix •Ascending colon •Transverse colon •Descending colon •Sigmoid colon •Rectum •anus LARGE INTESTINE •2” diameter, 5’ long •4 Major functions –Completion of absorption –Manufacture certain vitamins –Formation of feces –Expulsion of feces **NOTE** No function for appendix is known as of today •Bacteria –Changes chyme into fecal material by releasing remaining nutrients –Synthesizes Vitamin K –Produces some Bcomplex vitamins •Remaining water & vitamins are absorbed into bloodstream through OSMOSIS RECTUM • Last 8” of Large intestine • Fecal material is expelled • This is the desired outcome…. ACCESSORY ORGANS: THE LIVER •Largest glandular organ & one of the most complex •3 lbs •Divided into 2 lobes •15oo mL of blood are delivered to the liver every minute via the portal vein & hepatic artery •Bile –Yellow-brown or greenbrown color –Necessary for metabolism of fats •500-1,000 mL/daily •Many functions: –Manages blood coagulation –Manufactures cholesterol –Manufactures albumin (maintains normal blood volume) –Filters old RBC’s & bacteria –Detoxifying poisons (alcohol, nicotine, drugs) –Turns ammonia into urea –Main source of body heat –Stores back up glycogen –Activates Vitamin D –Breaks down nitrogenous waste –And that’s it!!!!!!!!!! THE LIVER ACCESSORY ORGANS: THE PANCREAS • Endocrine & EXOCRINE • 1,000 – 1,500 mL juice to aid in digestion • Protease (trypsin), lipase (steapsin), & amylase (amylopsin) digest proteins, fats and carbohydrates • Empties through the duodenum in the papilla of Vater • Contains sodium bicarbonate to neutralize hydrochloric acid THE PANCREAS Regulation of food intake!! •Hypothalamus –2 centers to stimulate to eat and to STOP eating!!!! •And THIS..is your stomach on too much good food!!!!!!!!!!!!!