* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 1: Introduction to security
Cryptanalysis wikipedia , lookup
Next-Generation Secure Computing Base wikipedia , lookup
Unix security wikipedia , lookup
Post-quantum cryptography wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Computer and network surveillance wikipedia , lookup
Airport security wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Cyberwarfare wikipedia , lookup
Information security wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Cyberattack wikipedia , lookup
International cybercrime wikipedia , lookup
Mobile security wikipedia , lookup
Social engineering (security) wikipedia , lookup
Security-focused operating system wikipedia , lookup
Cyber-security regulation wikipedia , lookup
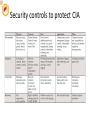
Faculty of Computing and Informatics Department of Computer Sciences Chapter 1: Introduction to security Fungai Bhunu Shava Lecturer January 2016 Faculty of Computing and Informatics Department of Computer Sciences Contents 1. What is Security? 2. Components of Security 3. Aspects of Security 4. Security services and characteristics 5. Security Issues 6. Security Attacks 7. Threats, vulnerabilities and attacks 8. Security standards and best practices 9. Domains of security (ISO & CISSP) Chapter 1: Introduction to Security Faculty of Computing and Informatics Department of Computer Sciences 1. Introduction Security • Information security is concerned with protecting information and information systems. • For successful implementation of information security an organisation must have several layers of security including: network, information, operations, communication, personal and physical security ..\Videos\Cybersecurity 101.mp4 Review What is security in general What is InfoSec? Why is it necessary to have InfoSec? Why is it difficult to address? How does interconnectivity pose a security risk for internet users? • Why is total internet security impossible? • What can users do to secure their information? • • • • • Security Security • • • • • • • • Safety Education Compliance Users Risks Identification Technology Yourself Components of Information security Security domains • ISO 27002:2005 • ISO 27002:2013 • ISO 27003:series (2010, 2012, 2013 and 2015) Security services/ characteristics • Information security services traditionally focused on confidentiality, integrity and authentication, but over the years the list has expanded to: 1. Privacy and Confidentiality 2. Integrity 3. Authentication 4. Non-repudiation 5. Availability 6. Accountability ..\Videos\Cyber Security 101_ History, Threats, & Solutions.mp4 Current security issues • Security usability • The internet is growing exponential (world stats) • More users are connecting several devices onto the internet. • Complexity in design of security due to the incompatibility in different gadgets and technologies interconnected. • Increased attack sophistication. Threats to security • Network reconnaissance and information gathering • Intrusive probes and scans • Vulnerabilities – Network ( architecture vulnerabilities and DoS) – Application/OS (Remote to Local, zero day attacks, privilege escalation, attacker access maintenance) Cyber Attack classification Different types of attacks types of attacks.png Possible attacks • Packet sniffing: To gain access to cleartext network data and passwords • Impersonation or masquerading: To gain unauthorized access to data or to create unauthorized e-mails by impersonating an authorized entity • Denial-of-service: To render network resources non-functional • Replay of messages: To gain access to information and change it in transit • Password cracking: To gain access to information and services that would normally be denied (dictionary attack) • Guessing of keys: To gain access to encrypted data and passwords (brute-force attack) • Viruses/ malicious code: programs which capture or destroy data • Port scanning: To discover potential available attack points • DNS interrogation • Social engineering Types of attacks • The attacks listed in the previous sections can broadly be classified as: – External – Hardware misuse – Masquerading – Pest programs – Bypasses – Active, passive, inactive and indirect misuse Class activity • For each type of attack listed above, define the attack and give at least 2 examples for each. • Network attacks can also be classified according to the network layers they target. For each of the following 7 layers list the corresponding attacks: – – – – – – – – Application Presentation Session Transport Network Data Link Physical Multilayer attacks Handling attacks • • • • • Prevention Deterring Deflection Detection Recovering Security controls to protect CIA Prevention/ Mitigation • Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) • Firewalling (provide perimeter security) • NAT (hiding the internal network information) • Patching applications and O/S alike • Upgrading security devices • Access control mechanism • Turning off services and ports • IPSEC Possible solutions • Encryption: To protect data and passwords • Authentication by digital signatures and certificates: To verify who is sending data over the network • Authorization: To prevent improper access • Integrity checking and message authentication codes: To protect against improper alteration of messages • Non-repudiation: To make sure that an action cannot be denied by the responsible person • One-time passwords and two-way random number handshakes: To mutually authenticate parties of a conversation • Frequent key refresh, strong keys, and prevention of deriving future keys: To protect against breaking of keys (cryptanalysis) • Address concealment(NAT): To protect against denial-of-service attacks • Disable unnecessary services: To minimize the number of attack points Possible solutions IP filtering Network Address Translation (NAT) IP Security Architecture (IPSec) SOCKS Secure Shell (SSH) Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) Application proxies Firewalls Kerberos and other authentication systems (AAA servers) • Secure Electronic Transactions (SET) • • • • • • • • • Tools • • • • • • • • • • • • Cain & Abel,John the Ripper, L0phtCrack (LC4/5) RTG Network Monitor freeware Aircrack, AIDE, Tripwire, Dsniff, FragRouter Wireshark, ethereal, tcpdump, Snoop, Ettercap, Dsniff, rhosts, rsh NMAP, IPTables, IPF, IPFW, firewalk Nessus, Whisker, Snort, ACID MBSA (Microsoft Baseline Software Analyzer) Netstumbler, Netcat, Nagios,kismet, wellenreiter Bruteforcer Passware –Ariskkey, encryption analyser, messenger key , traceroute Nslookup, dig, host, axfr Class activity • From the video, please answer the following questions: • What attacks threaten CIA? Associate each threat with the security goal it targets. • What other areas (goals) of security are critical? • When did cybersecurity begin? How? Class activity cont…. • Compare and contrast the cybersecurity threats in 2013 to those experienced in 2015. • What are the predictions for 2016? • Why will cybersecurity remain a key concern for security professionals in future? • Are social security a social ill or a benefit? why? References • Britt, D.T., Matthews, C., Davies, C., Forrester, J., Liu, W., Rosselot, N. (2006). TCP / IP Tutorial a Technical Overview IBM redbook series. USA; International Business Machines Corporation. Retrieved from ibm.com/redbooks 13 Storch Street Private Bag 13388 Windhoek NAMIBIA Faculty of Computing and Informatics Department of Computer Sciences Thank You. T: F: E: W: +264 61 207 2258 +264 61 207 9258 [email protected] www.nust.na