* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organ Doctor
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
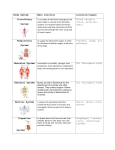
Chapter 1 Human Body Orientation Anatomy • Study of the structure and shape of the body and body parts and their relationship to one another • Gross Anatomy – studying large body structures – easy to see • Microscopic anatomy – studying small parts of the body – microscopic Ex. Cells and tissues Physiology • The study of how the body and its parts work or function • Neurophysiology – explain how the nervous system works • Cardiac physiology – studies the function of the heart • Anatomy and physiology are always related. The parts form a well organized unit. • Structure determines function. Levels of Structural Oranization • Atoms molecules cells Tissue organ organ system organism • Molecules – water • Cell – smallest unit of living things • Tissue – groups of cells with similar functions • Organ – structure composed of 2+ tissues Figure 1.1 Chapter 3 Body Tissues Four Types: • • • • Epithelium – covering Connective – support Nervous – control Muscle - movement Epithelial tissue • Lines and covers all free body surfaces Functions • • • • Protection Absorption Filtration secretion Special Characteristics of Epithelium • Fit closely together to form sheets • One surface or edge is free and the other attaches to a basement membrane • No blood supply • Regenerate easily Classification of Epithelium Two Names 1. Number of cell layers a. Simple – one b. Stratified – 1+ 2. Shape a. Squamous – flattened like fish scales b. Cuboidal – cube shape c. Columnar – shaped like columns Simple Squamous Connective Tissue • Connects body parts • Found everywhere Functions – protection, support, binding together Special Characteristics of Connective Tissue • Variations in blood supply • Extra-cellular matrix Matrix – secreted by the cells - non-living substances Ex. – blood, fat, bone Muscle Tissue • Highly specialized to contract or shorten to produce movement Types: skeletal, cardiac and smooth Nervous Tissue • Neurons • Highly specialized to receive and transmit impulses The Eleven Organ Systems 1. Integumentary System – Skin – Covers the body Functions – a. Waterproofs b. Cushions and protects c. Perspiration – excretes salts and urea d. Regulates body temperature e. Temperature, pressure, pain receptors Organs – hair, nails, sweat glands, sebaceous glands (oil) 2. Skeletal System Functions – a. Support – store minerals b. Framework for muscles – aids movement c. Protective – ex. Skull d. Hematopoiesis – formation of blood cells Organs – bones, ligaments, joints and cartilage 3. Muscular System Functions – Muscles contract and cause movement – Primary source of body heat Organs – Skeletal muscles 4. Nervous System • Fast acting control system Functions – allows the body to respond to irritants and stimuli Organs – brain, spinal cord, nerves and sense organs 5. Endocrine System Functions a. Controls body activities – slow b. Produces chemical molecules – Hormones c. Hormones released in blood and travel to distant organs d. Hormones control growth, reproduction and food 6. Cardiovascular System Functions a. Blood vessels, transport blood which carries oxygen, carbon dioxide and waste Organs – heart, arteries, capillaries, veins, blood Blood vessels are in red 7. Lymphatic System (Immune System) • Complements the cardiovascular system Functions – returns fluid leaked from the blood to the blood vessels Organs – lymph fluids, lymph nodes, thymus, spleen Lymph nodes • Cleanses blood • Houses cells involved in immunity 8. Respiratory System Functions a. Keeps body supplied with oxygen b. Removes carbon dioxide Organs: nasal passages, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs Lungs- tiny air sacs where gas exchange with the blood occurs 9. Digestive System • Tube from mouth to anus Functions: a. Breaks down food b. Products to the blood for dispersal Organs • Mouth, esophagus, stomach, Intestines (small and large), rectum • Liver – produces bile to break down fats • Pancreas – digestive enzymes for small intestines 10. Urinary System Functions – a. Removes nitrogen wastes from the blood, exits body through urine b. Maintains the balance of water, salt, acid-base Organs – kidneys, ureters, bladder urethra 11. Reproductive System Male – sperm – testes Organs – scrotum, penis, accessory glands, duct system Female – eggs – ovary Organs – uterine tubes, uterus, vagina Maintaining Life The highly organized human body does: 1. Maintains boundaries 2. Responds to environmental changes – Irritability 3. Takes in and digests nutrients 4. Carry out metabolism 5. Dispose of wastes 6. Reproduce 7. Grow • The highly organized human body is able to carry out the 7 characteristics. The Seven Characteristics of Life 1. Maintaining Boundaries – cell membrane Body System - Integumentary 2. Movement Body System – muscular system 3. Responsiveness or Irritability (sense changes and respond) Body System – Nervous System 4. A. Digestion Body system - Digestive B. Metabolism – all the chemical reactions that occur in the body Body Systems – Digestive, Respiratory, Cardiovascular and Endocrine 5. Excretion Body System – Digestive and Urinary 6. Reproduction Body System – Reproductive 7. Growth Survival Needs of the Human Body • Goal of the body systems – Maintain Life 1. Nutrients (food) 2. Oxygen 3. Water 4. Appropriate Temperature 5. Atmospheric Pressure Homeostasis • The ability of the body to maintain relatively stable internal conditions • Homeo – same • Statis – standing still • Happens when the body has its needs meet and is functioning smoothly The Language of Anatomy • A set of terms that allows body structures to be located and identified clearly with a few words Anatomical Position • Standard reference point Regional Terms • The many visible landmarks on the surface of the body Figure 1.6a Figure 1.6b Figure 1.6c Figure 1.7 Directional Terms • Used to explain exactly where one body structure is in relation to another • The ________ is ___________ to the _____________. • The ________ is ___________ to the _____________. • The ________ is ___________ to the _____________. • The ________ is ___________ to the _____________. • The ________ is ___________ to the _____________. • The ________ is ___________ to the _____________. • The ________ is ___________ between the ________ and _____________. • The ________ is ___________ to the _____________. • The ________ is ___________ to the _____________. • The ________ is ___________ to the _____________. • The ________ is ___________ to the _____________. Body Planes The End