* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Body Planes and Anatomical Terms
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
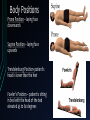
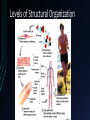
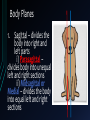
Human Anatom y What is anatomy? Anatomy is the study of structures or body parts and their relationships to one another. Anatomy: Gross anatomy – macroscopic Histology – microscopic Anatomical Position: body is erect, feet together, palms face forward and the thumbs point away from the body. Body Positions Prone Position – laying face downwards Supine Position – laying face upwards Trendelenburg Position- patient’s head is lower than the feet Fowler’s Position – patient is sitting in bed with the head of the bed elevated 45 to 60 degrees Levels of Structural Organization Body Planes 1. Sagittal – divides the body into right and left parts i) Parasagittal – divides body into unequal left and right sections ii) Midsagittal or Medial – divides the body into equal left and right sections Body Planes 2. Frontal or Coronal – divides the body into anterior (front) and posterior (back) parts Body Planes 3. Transverse or horizontal Horizontal plane that divides the body into upper and lower portions; also called crosssection. Body Planes 4. Oblique Section – cuts made diagonally Directional Terms Superior vs. Inferior Superior means the part that is above or closer to the head (cranial) Inferior means the part that is below another or towards the feet (caudal) Directional Terms Anterior vs. Posterior Anterior means towards the front (ventral) Posterior means towards the back (dorsal) Directional Terms Medial vs. Lateral vs. Intermediate Medial towards or at the midline of the body; on the inner side of Lateral away from the midline of the body; on the outer side of Intermediate between a more medial and a more lateral structure Directional Terms Ipsilateral vs. Contralateral Ipsilateral – the same side Contralateral – refers to the opposite side Directional Terms Proximal vs. Distal Proximal – closer to the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk. Distal – farther from the origin of body part of the point of attachment of a limp to the body trunk. Directional Terms Superficial (external) vs. Deep (internal) Superficial – toward or at the body surface Deep – away from the body surface; more internal Regional Terms Axial part – includes the head, neck and trunk. Appendicular part – includes the limbs which are attached to the body’s axis Body Cavities These are hollow spaces within the human body that contain internal organs. There are two main cavities: 1) The Dorsal Cavity - Located toward the back of the body - Is divided into the cranial cavity (holds the brain) and the vertebral or spinal cavity (which holds the spinal cord) 2) The Ventral Cavity - Located toward the front of the body - Is divided into abdominopelvic cavity and the thoracic cavity 2) The Ventral Cavity - The abdominopelvic cavity is subdivided into abdominal cavity (liver, gallbladder, stomach, pancreas, spleen, kidney, small and large intestines) and the pelvic cavity (urinary bladder and reproductive organs) 2) The Ventral Cavity - The thoracic cavity is subdivided into the pleural cavity (holds the lungs) and the pericardial cavity (holds the heart)