* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Anatomy & Physiology
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
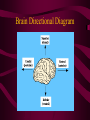
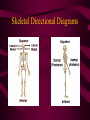
The Human Body Orientation Introduction What is anatomy? • It is the study of the structure and shape of the body and body parts and their relationship to one another. What is physiology? • It is the study of how the body and its parts work or function. What are the 11 systems of the human body? • • • • • Integumentary system Skeletal system Muscular system Nervous system Endocrine system • • • • • • Cardiovascular system Lymphatic system Respiratory system Digestive system Urinary system Reproductive system What are the levels of structural organization? • Chemical level – made up of atoms • Cellular level – made up of molecules • Tissue level – made up of similar groups of cells that have a common function • Organ level – made up of two or more tissue types to perform a specific function • System level – made up of a group of organs to accomplish a common purpose • Organismal level – made up of the 11 organ systems What are the necessary life functions for maintaining life? • • • • • • • • Maintaining boundaries - skin Movement – walking, swimming, running Responsiveness – sense changes or stimuli in the environment Digestion – breaking down food into molecules Metabolism – all chemical reactions that occur in the body cells Excretion – removal wastes from body Reproduction – production of offspring Growth – increase in size What are the survival needs? • Nutrients (food) – needed for energy and cell building • Oxygen – needed for release of energy from food • Water – needed for body secretions and excretions (60% to 80% of body weight) • Body temperature (37ºC or 98ºF) • Atmospheric pressure – needed for breathing and exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs What is homeostasis? • It is the body’s ability to maintain stable internal conditions even though the outside environment is changing • Controlled by nervous and endocrine systems example: control mechanism Receptor – sensor responds to change Control center – maintains the level or set point Effector – response to stimulus What is the language of anatomy? • Define the following directional terms: (Pg. 19) • 1. Superior (cranial) 2. Inferior (caudal) 3. Anterior (ventral) 4. Posterior (dorsal) 5. Medial 6. Lateral 7. Intermediate 8. Proximal 9. Distal 10. Superficial 11. deep Define the following body plane terms: 1. Median (midsagittal) plane 2. Frontal (coronal) plane 3. Transverse plane What are the body cavities? • Dorsal body cavity A. Cranial cavity – space inside the bony skull B. Spinal cavity – from cranial cavity to the end of the vertebral column • Ventral body cavity C. Thoracic cavity – separated from the rest of the ventral cavity by the diaphragm D. Abdominopelvic cavity – inferior to thoracic cavity a) Abdominal cavity b) Pelvic cavity Body Planes Diagram Body Directional Diagram Body Plane Diagrams Brain Directional Diagram Skeletal Directional Diagrams