* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Atoms - Red Hook Central Schools
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
Metallic bonding wikipedia , lookup
Electronegativity wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear binding energy wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear transmutation wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Particle-size distribution wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Molecular dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
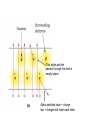
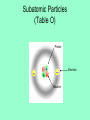
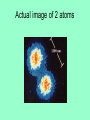
Atoms 400 b.c. Greeks • Greeks philosophers ponder the nature of matter: what is it made of? • Democritus: basic particle of matter = “atom” which means “indivisble”. Envisions these to be “hard spheres” • Aristotle: does not believe in atoms Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1803 1) All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1803 2) Atoms of one element are all alike (size, mass) Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1803 3) Atoms can’t be created, destroyed or subdivided Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1803 4) Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1803 5) In a chemical reaction, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged Conservation of mass in chemical reactions Conservation of mass in chemical reactions 1897 J.J. Thompson Cathode Ray Experiments The electron is discovered…. “PLUM PUDDING” model Rutherford’s Gold Foil Experiment 1909 Ernst Rutherford bombards a piece of gold foil with positively charged alpha particles (the nucleus of a helium atom) Some alpha particles bounce back Rutherford’s Gold Foil Experiment Observations: 1. Most of the alpha particles passed straight through the gold foil as if it wasn’t even there! 2. The nucleus of the atom is small, dense, and positively charged Rutherford’s Gold Foil Experiment Interpretation (conclusions): 1. Atoms are mostly empty space and therefore MATTER is mostly empty space 2. Atoms have a small, dense, positively charged nucleus + + + + + + This alpha particle passes through the atom’s empty space Alpha particles have + charge two + charges will repel each other Subatomic Particles (Table O) Proton Electron Neutron Protons • Located in the atom’s nucleus • Positive charge +1 • Mass = 1 amu (Atomic Mass Unit) Neutrons • Located in the atom’s nucleus • zero charge (neutral) • Mass = 1 amu (Atomic Mass Unit) Electrons • Located in the electron cloud outside the nucleus • Negative charge -1 • Mass = 1/1836 amu (negligible) What are the subatomic particles in lithium and carbon? Models of the atom A model of the atom to scale • If YOU are the nucleus of an atom, your closest electron would be…. • ……..in downtown Rhinebeck! Actual image of 2 atoms