* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Digestion
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Colonoscopy wikipedia , lookup
Bariatric surgery wikipedia , lookup
Ascending cholangitis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatotoxicity wikipedia , lookup
Gastric bypass surgery wikipedia , lookup
Fecal incontinence wikipedia , lookup
Intestine transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Surgical management of fecal incontinence wikipedia , lookup
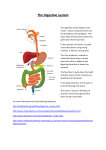
Digestive System The Oral Cavity The Pharynx The Esophagus The Stomach The Small Intestine Accessory Organs of Digestion The Large Intestine The Rectum Digestive System • Functions of the Digestive System 1. Ingestion – foods enter digestive tract through mouth. 2. Mechanical processing – physical manipulation of solid foods by tongue & teeth and by movements of the smooth muscle of digestive tract. 3. Digestion – chemical breakdown of food into small organic fragments that can be absorbed. Duodenum; ileum. Digestive System • Functions of the Digestive System 4. Secretion – release of water, acid, enzymes, & buffers by the digestive tract & accessory organs. Salivary glands; pancreas; gall bladder; small intestine 5. Absorption – movement of small organic molecules, electrolytes, vitamins, & water across the digestive epithelium. Jejunum; ileum; large intestine. Digestive System • Functions of the Digestive System 6. Excretion – removal of waste products from body fluids. Within the digestive tract, waste is compacted as feces & defecated. Large intestine; rectum; anal canal & sphincters The Oral Cavity • Mouth • Tongue • Teeth • Salivary Glands Oral Cavity • Mouth Entrance to Dig. Syst. - ingestion Vestibule – btw cheeks/lips & teeth • Tongue Manipulation of food – mechanical processing Assists chewing Assists moistening & mixing: H2O; saliva Taste sensation: sweet; salty; bitter; sour Oral Cavity • Teeth Mastication of solid food – mechanical processing Upper & lower dental arches Incisors – clipping & cutting • 2 central; 2 lateral Cuspids (canines) – tearing & shearing Bicuspids (premolars) – crushing & grinding • 1st & 2nd Molars – crushing & mashing • 1st, 2nd, & 3rd Oral Cavity • Salivary Glands Moistening of food – mechanical processing & secretion Production of saliva – secretion & digestion Saliva: 99.4% H2O + mucins, enzymes, etc Oral Cavity • Salivary Glands Parotid salivary glands – lateralposterior surface of mandible Sublingual salivary glands – floor of the mouth under tongue Submandibular salivary glands – floor of the mouth along inner surfaces of the mandible The Pharynx & Esophagus • Oropharynx • Laryngopharynx • Esophagus & Esophageal Sphincters Pharynx Cooperate w/ muscles of the oral cavity & esophagus to initiate swallowing • Oropharynx Distal to oral cavity Common passageway with Resp. Syst. • Laryngopharynx Distal to oropharynx Common passageway with Resp. Syst. Esophagus Conveys food & liquids to the stomach • Upper esophageal sphincter Not usually in active contraction unless swallowing • Lower esophageal (cardiac) sphincter Actively contracted Note term: Peristalsis Prevents backflow of food & stomach acid into esophageal tube Digestive Pathways The Stomach • Cardia • Fundus • Body • Pylorus & Pyloric Sphincter Cardia & Fundus Secretion of HCl & Pepsin – digestion of protein peptides • Cardia Point of connection to esophagus smallest region • Fundus Superior bulge of stomach Superior to cardia Body & Pylorus • Body of the Stomach Food (chyme) churns in this region due to contractions of the pylorus Expandable due to ruggae • Pylorus Muscular portion of the stomach Contracts to churn chyme into body Pylorus • Pyloric sphincter (valve) permits movement of chyme into the small intestine in small amounts Prevents backflow of food into stomach from small intestine Digestive Pathways The Small Intestine • Duodenum • Jejunum • Ileum & Ileocecal Valve (Sphincter) Duodenum Receives chyme from stomach Secretes intestinal juice (enzymes) that digest carbs, peptides, fats, & nucleic acids Receives pancreatic juice (enzymes) via pancreatic duct Receives bile from gall bladder via bile duct to emulsify fats Receives bicarbonate from pancreas to neutralize stomach acid Duodenum • Duodenum Shortest segment; pancreas attaches to duodenum Involved in initial chemical breakdown (digestion) of food: lipids; polypeptides; disaccharides; nucleic acids • Jejunum Receives chyme from duodenum Bulk of chemical digestion Bulk of nutrient absorption Jejunum & Ileum • Ileum Longest segment Digestion & absorption continue • Ileocecal Valve (sphincter) Permits chyme to move into large intestine Prevents backflow from LI to SI Digestive Pathways Accessory Digestive Organs • Pancreas • Liver • Gall Bladder Pancreas • Pancreas Produces digestive enzymes Carbohydrases – breakdown CH2O Lipases – breakdown lipids Proteases – breakdown proteins/peptides Nucleases – breakdown nucleic acids Pancreas • Pancreas (cont) Secreted in pancreatic juice Produces endocrine hormones Insulin – promotes uptake of sugar by cells Glucagon – promotes release of glucose from stored liver glycogen Liver • Liver Lobes Right & left Caudate & quadrate Blood retuning from intestines passes through liver on the way to the heart Metabolic regulation Hematological regulation Liver & Gall Bladder • Liver (cont) Production of bile salts (stored in gall bladder) Stores glycogen • Gall Bladder Secretes bile into duodenum Emulsifies fats into tiny droplets Allows enzyme lipase to break down triglycerides, etc in small intestine Liver & Hepatic Portal System The Large Intestine • Cecum • Ascending Colon • Descending Colon • Sigmoid Colon Large Intestine Reabsorption of H2O & compaction of waste into feces Absorption of vitamins: vit K; vit ; B5 biotin • Cecum Pouch-like Vermiform appendix attached – contains lymphoid nodules Large Intestine: Colon Haustra Pouches – permit extension & elongation • Ascending Colon Anatomical right • Transverse Colon Traverses right to left Large Intestine: Colon • Descending Colon Anatomical left • Sigmoid Colon S-curve to direct colon to midline of the body The Rectum & Anal Structures • Rectum • Anal Canal & Anal Sphincters • Anus Rectum • Rectum Temporary storage of feces Expandable – Anal Canal Leads to anus • Internal Anal Sphincter Not under voluntary control • External Anal Sphincter Under voluntary control Anus Introductory Video • To View Video: – Move mouse cursor over slide titlelink – When hand appears, click once • ASX Video plays about 22 min