* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Topic 1.5 Cell Biology
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
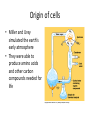
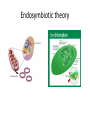
Cell Biology Topic 1.5 Origin of Cells • According to the cell theory, all cells come from pre-existing cells • Sperm and egg join to make a zygote • Zygote divides repeatedly to form embryo • What about the first cell?? • They would need to have arisen from nonliving material Origin of Cells • Spontaneous generation is the formation of living thins from non-living matter • Theophratus- Silphium plant • Aristotle-insects from dew or hair • Paracelus-mice from decaying matter • Francesco Redi-rotting meat and flies Origin of cells Origin of Cells • Louis Pasteur spontaneous generation experiments • Boiled (control) and unboiled (experimental)broth in long necked flasks Origin of cells • Cells may have formed over hundreds of millions of years of evolution • In a series of stages: 1. Production of carbon compounds such as amino acids and sugars 2. Assembly of carbon compounds into polymers 3. Formation of membranes 4. Development of a mechanism of inheritance Origin of cells • Miller and Urey simulated the earth’s early atmosphere • They were able to produce amino acids and other carbon compounds needed for life Origin of cells • Deep ocean vents also simulate the early earth • Provide and energy source for the formation of carbon compound polymers • Iron sulfide • chemosynthesis Origin of cells • Formation of membranes • Creates an inside environment different from the outside • Phospholipids behave this way naturally • Show video! Origin of cells • Mechanism of inheritance • In order for DNA to replicate it needs enzymes(catalysts) , but enzymes are coded by genes • “chicken and the egg” • May have been an earlier stage where RNA was the genetic material • It can act as genetic material and a catalyst Origin of cells Endosymbiotic theory • Supports the evolution of some prokaryotes into eukaryotes • Theory that mitochondria and chloroplasts were once free living prokaryotes • Larger anerobic prokaryotes took them in by Endocytosis (engulfing) but did not eat them! • They were instead used for energy production Endosymbiotic theory • Symbiotic relationship/mutualism • Large prokaryote provides food and small prokaryote provides energy Endosymbiotic theory Evidence that supports the theory: • Both chloroplasts and mitochondria contain their own DNA (circular piece of DNA similar to other prokaryotes) • They also contain ribosomes that are similar to the ribosome found in prokaryotes (70s subunits) • They also produce some of their own proteins • They can only be produced by division of preexisting mitochondria/chloroplasts Endosymbiotic theory