* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ppt
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Topological quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Scalar field theory wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Geiger–Marsden experiment wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
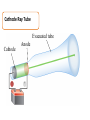
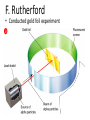
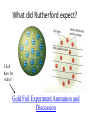
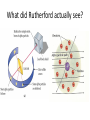
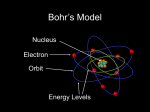
Atomic Theory and Structure of the Atom A. Democritus • first to suggest the existence of atoms • believed atoms were small indivisible particles • Atom: smallest particle of an element that retains all properties of the element. (460 B.C. – 370 B.C) B. Dalton • Atomic theory composed of 4 postulates Name of theory – Elements are composed of atoms – Atoms of the same element are Billard Ball identical, each element is unique – Compounds are composed of atoms Model of more than 1 element, atoms combine in fixed ratios to form compounds – Chemical rxn involves separation, combination, or rearrangement of atoms C. Electron 1. Symbol: e− – Charge −1 **after Dalton, there was a big hiatus in the theory of the atom. Everyone accepted Daltons theory and went on to study radiation for a while, and this is when the electron was discovered D. J.J. Thomson • An atom is thought of as a uniform positive sphere with electrons evenly distributed through out (like plum pudding or a chocolate chip cookie) Name of theory Plum Pudding Model Cathode Ray Tube Evacuated tube Cathode Anode − + Battery E. Millikan Millikan Oil Drop • Found the mass of an electron to be 9.10×10−28 g F. Rutherford • Conducted gold foil experiment What did Rutherford expect? Click here for video! Gold Foil Experiment Animation and Discussion What did Rutherford actually see? F. Rutherford • Concluded all positive charge and mass is concentrated in small region called nucleus and the electrons are outside the nucleus • Proposed atom is mostly empty space Name of theory Nuclear Model Proton – p+ – Charge: +1 – Mass:1.673×10−24 g G. Bohr • Expanded on the nuclear atom • Electrons travel in circular orbits around the nucleus Name of theory Planetary Model H. Schrödinger • model allowed the electron to occupy three-dimensional space like an electron “cloud” Name of theory Quantum Mechanical Model or Electron Cloud Model I. Chadwick The Neutron Symbol: n0 Charge: none Mass:1.675×10−24 g **The neutron was found by comparing the mass of hydrogen to helium, since He increased by 1proton, the mass should be double, but it was four times, leading to a subatomic particle that had mass but no charge. Fun Facts • The volume of a hydrogen nucleus is a trillion times smaller than the volume of a hydrogen atom, yet the nucleus contains most of the mass. • If the nucleus (proton) of a hydrogen atom were as large as the width of a human thumb, the electron would be on the average about one kilometer away in a great expanse of empty space.