* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download NEKSDC CCSSM HS Geometry
Shape of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Mirror symmetry (string theory) wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Cartan connection wikipedia , lookup
Algebraic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Lie sphere geometry wikipedia , lookup
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Brouwer fixed-point theorem wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Geometrization conjecture wikipedia , lookup
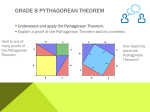
GRADE 8 PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM Understand and apply the Pythagorean Theorem. Explain a proof of the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse. Here is one of many proofs of the Pythagorean Theorem. How does this prove the Pythagorean Theorem? GRADE 8 PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM Apply the Pythagorean Theorem to determine unknown side lengths in right triangles in real-world and mathematical problems in two and three dimensions. Apply the Pythagorean Theorem to find the distance between two points in a coordinate system. From Kahn Academy GRADE 8 VOLUME Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving volume of cylinders, cones, and spheres. Know the formulas for the volumes of cones, cylinders, and spheres and use them to solve real-world and mathematical problems. http://www.math.com TURN AND TALK TO YOUR NEIGHBOR What concepts and skills that HS Geometry have traditionally spent a lot of time on are now being introduced in middle school? How does that change your ideas for focus in HS Geometry? What concepts and skills do you predict will be areas of major focus in HS Geometry? STRUCTURE OF THE HS GEOMETRY CONTENT STANDARDS Congruence (G-CO) Similarity, Right Triangles, and Trigonometry (G-SRT) Circles (G-C) Expressing Geometric Properties with Equations (G-GPE) Geometric Measurement and Dimension (G-GMD) Modeling with Geometry (G-MG) STRUCTURE OF THE HS GEOMETRY CONTENT STANDARDS Congruence (G-CO) • Experiment with transformations in the plane • Understand congruence in terms of rigid motions • Prove geometric theorems (required theorems listed) • Theorems about Lines and Angles • Theorems about Triangles • Theorems about Parallelograms Make geometric constructions (variety of tools and methods…by hand and using technology) (required constructions listed) STRUCTURE OF THE HS GEOMETRY CONTENT STANDARDS Similarity, Right Triangles, and Trigonometry (G-SRT) • Understand Similarity in terms of similarity transformations • Prove theorems involving similarity • Define trigonometric ratios and solve problems involving right triangles • (+) Apply trigonometry to general triangles • Law of Sines • Law of Cosines STRUCTURE OF THE HS GEOMETRY CONTENT STANDARDS Circles (G-C) Understand and apply theorems about circles • All circle are similar • Identify and describe relationships among inscribed angles, radii, and chords. • Relationship between central, inscribed, and circumscribed angles • Inscribe angles on a diameter are right angles • The radius of a circle is perpendicular to the tangent where the radius intersects the circle Find arc lengths and sectors of circles STRUCTURE OF THE HS GEOMETRY CONTENT STANDARDS Expressing Geometric Properties with Equations (G-GPE) • Translate between the geometric description and the equation for a conic section • Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraically STRUCTURE OF THE HS GEOMETRY CONTENT STANDARDS Geometric Measurement and Dimension (G-GMD) • Explain volume formulas and use them to solve problems • Visualize relationships between two-dimensional and three-dimensional objects Modeling with Geometry (G-MG) • Apply geometric concepts in modeling situations HS GEOMETRY CONTENT STANDARDS Primarily Focused on Plane Euclidean Geometry Shapes are studied Synthetically & Analytically • Synthetic Geometry is the branch of geometry which makes use of axioms, theorems, and logical arguments to draw conclusions about shapes and solve problems • Analytical Geometry places shapes on the coordinate plane, allowing shapes to defined by algebraic equations, which can be manipulated to draw conclusions about shapes and solve problems. FORMAL DEFINITIONS AND PROOF HS Students begin to formalize the experiences with geometric shapes introduced in K – 8 by • Using more precise definitions • Developing careful proofs When you hear the word “proof”, what do you envision? INSTRUCTIONAL SHIFT: MORE FOCUS ON TRANSFORMATIONAL PERSPECTIVE Congruence, Similarity, and Symmetry are understood from the perspective of Geometric Transformation extending the work that was started in Grade 8 INSTRUCTIONAL SHIFT: MORE FOCUS ON TRANSFORMATIONAL PERSPECTIVE Rigid Transformations (translations, rotations, reflections) preserve distance and angle and therefore result in images that are congruent to the original shape. G-C0 Cluster Headings Revisited • Experiment with transformations in the plane • Understand congruence in terms of rigid motions • Prove geometric theorems • Make geometric constructions