* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Genetic Disorders
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering in science fiction wikipedia , lookup
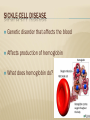
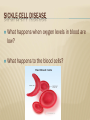
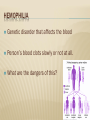
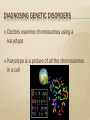
1/7/15 Mr. Faia 6th Grade Science HUMAN GENETIC DISORDERS GENETIC DISORDERS Genetic disorder is an abnormal condition that a person inherits through the genes or chromosomes GENETIC DISORDERS Genetic disorders are caused by a mutation in a person’s DNA CYSTIC FIBROSIS Genetic disorder in which the body produces an abnormally thick mucus It is produced in the lung and intestines CYSTIC FIBROSIS How does the mucus affect the lungs? How does the mucus affect the intestines? What else can be caused by the mucus? CYSTIC FIBROSIS The mutation is carried on a recessive allele Mostly in ancestors from Northern Europe What are the medical treatments? SICKLE-CELL DISEASE Genetic disorder that affects the blood Affects production of hemoglobin What does hemoglobin do? SICKLE-CELL DISEASE What happens when oxygen levels in blood are low? What happens to the blood cells? SICKLE-CELL DISEASE Most common in people of African ancestry What type of allele is the trait? What are the medical treatments? HEMOPHILIA Genetic disorder that affects the blood Person’s blood clots slowly or not at all. What are the dangers of this? HEMOPHILIA Caused by a recessive allele on the X chromosome Who is more likely to be affected by hemophilia? HEMOPHILIA What are the medical treatments for hemophilia? What do doctors advise patients to avoid? DOWN SYNDROME Caused when a person’s cells have an extra copy of chromosome 21 Often occurs because chromosomes fail to separate properly during meiosis DIAGNOSING GENETIC DISORDER’S What did doctors previously use to predict genetic disorders? What do doctors use today? DIAGNOSING GENETIC DISORDERS Amniocentesis is when doctors remove a small amount of fluid from around a developing baby Doctors then examines the chromosomes from the cells DIAGNOSING GENETIC DISORDERS Doctors examine chromosomes using a karyotype Karyotype is a picture of all the chromosomes in a cell SECTION REVIEW Explain how genetic disorders occur in humans. Give 2 examples. Describe 2 tools that doctors use to detect genetic disorders. How do the cells of people with Down syndrome differ from those of others? How might this difference happen? A couple with a family history of hemophilia is about to have a baby girl. What information about the parents would you want to know? How would this help determine whether the baby will have hemophilia?