* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
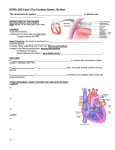
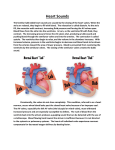
D.4 The Heart Understanding: - Structure of cardiac muscle cells allows propagation of stimuli through the heart wall - Signals from the sinoatrial node that cause contraction cannot pass directly from atria to ventricles - There is a delay between the arrival and passing on of a stimulus at the atrioventricular node - This delay allows time for atrial systole before the atrioventricular valves close - Conducting fibres ensure coordinated contraction of the entire ventricle wall - Normal heart sounds are caused by the atrioventricular valves and semilunar valves closing causing changes in blood flor Applications: Use of artificial pacemakers to regulate the heart rate Use of defibrillation to treat life-threatening cardiac conditions Causes and consequences of hypertension and thrombosis Nature of science: Developments in scientific research followed improvements in apparatus or instrumentation: the invention of the stethoscope led to improved knowledge of the workings of the heart Skills: Measurement and interpretation of the heart rate under different conditions Interpretation of systolic and diastolic blood pressure measurements Mapping of the cardiac cycle to a normal ECG trace Analysis of epidemiological data relating to the incidence of coronary heart disease Review Topic 6 Aorta Pulmonary vein Pulmonary artery Vena cava Left atrium Right atrium Left ventricle Right ventricle Semi lunar valves Atrioventricular valves Septum Review Topic 6 Semi lunar valves (Arteries) Atrioventricular valves (Atria/Ventricles) Right Left Pressure changes - Aorta (black) - Left atrium (Blue) - Left ventricle (red) Systole and Diastole of ventricles and atria Heart Sounds Valves opening and closing (Aortic valve = semilunar valve) Aorta Pressure decreasing during atrial and ventricular diastole. Semi lunar valve is closed Blood has left the ventricle and the heart relaxes Aorta Atrial systole begins followed by ventricular systole Immediately the semi lunar valve opens Pressure increases rapidly as blood enters the Aorta Pressure reaches a maximum point At the end of ventricular systole the semilunar valve closes and pressure in Aorta decreases Atrium and Ventricle Pressure is low during atrial and ventricular diastole Heart is relaxed Atrioventricular valve is open Blood starts to fill atrium and moves into ventrcle Atrium and Ventricle Pressure increases in both atrium and ventricle as blood fills Atrium contracts to push blood into ventricle Atrioventricular valve closes and pressure in atrium decreases Atrium and Ventricle Rapid increase in pressure in ventricle as it contracts As the pressure rises, the semilunar valve opens Pressure has reached a maximum and blood is pumped out of ventricle and into aorta Atrium and Ventricle Semilunar valve closes and pressure in ventricle decreases rapidly Blood slowly fills atrium Atrioventricular valve opens and blood continues to fill the atrium and now the ventricle Atrium contracts and the cycle starts again Defibrillator No/reduced bloody supply to the heart = cardiac arrest Heart tissues deprived of oxygen Causes ventricular fibrillation = twitching of muscle cells in ventricles Defibrillators detect if this is happening Then used to restore rhythm to the heart Paddles must be placed diagonally across the heart Applications: Use of defibrillation to treat life-threatening cardiac conditions Heart Beat Caused by valves snapping shut Atrioventricular valves closing = lub Semilunar valves closing = dub Stethoscopes invented in 19th century Doctors used to place ears on patients chest before Difficulty with female or obese patients Now a lot easier and non invasive Understanding: - Normal heart sounds are caused by the atrioventricular valves and semilunar valves closing causing changes in blood flor Nature of science: Developments in scientific research followed improvements in apparatus or instrumentation: the invention of the stethoscope led to improved knowledge of the workings of the heart ECG machine ELECTROCARDIOGRAM Use the ECG machine to measure your heart rate under the following different conditions • • • • • • Exercise Relaxation Lying down Holding your breathe Fast breathing Facial immersion in water (OPTIONAL!!) Skills: Measurement and interpretation of the heart rate under different conditions Blood Pressure Measuring blood pressure Pressure on artery walls by circulating blood Higher number = ventricular systole pressure Lower number = ventricular diastole pressure Many different blood pressure machines Take your blood pressure! Skills: Interpretation of systolic and diastolic blood pressure measurements Review Topic 6 The heart is myogenic Sinoatrial node initiates and sets pace for heart beat Atrial systole Ventricular systole Diastole SA node Uniquely structured cardiac cells Initiate action potential without stimulation by other nerves Contractions spread rapidly across atrium Understanding: - Signals from the sinoatrial node that cause contraction cannot pass directly from atria to ventricles Cardiac Muscle Cardiac muscle is unique Striated appearance Understanding: - Structure of cardiac muscle cells allows propagation of stimuli through the heart wall Cardiac Muscle Y shaped cells Joined end to end in complex network of interconnected cells Gap junctions called intercalated discs Provide channels of connected cytoplasm between cells Allows rapid movement of ions Very fast wave of depolarization Understanding: - Structure of cardiac muscle cells allows propagation of stimuli through the heart wall Cardiac Cycle Signals pass from SA node to atrioventricular node. Passes down to Bundle of His Moves down left and right bundle branches to the apex of the heart Down to the Purkinje fibres Causes the ventricles to contract at apex Understanding: - Signals from the sinoatrial node that cause contraction cannot pass directly from atria to ventricles Purkinje Fibres Able to conduct signal at high speed - Large diameter of cells - Many Na+ channels - Many mitochondria Understanding: - Signals from the sinoatrial node that cause contraction cannot pass directly from atria to ventricles - Conducting fibres ensure coordinated contraction of the entire ventricle wall Cardiac Cycle Delay needed between nodes Ensures staggering of contractions Atria empty first before ventricles contract AV node has many features delaying the contractions of the ventricles Understanding: - There is a delay between the arrival and passing on of a stimulus at the atrioventricular node - This delay allows time for atrial systole before the atrioventricular valves close AV node o Smaller cell diameter o Reduced number of Na+ channels o Fewer gap junctions between cells Slower conduction overall compared to SA node Understanding: - There is a delay between the arrival and passing on of a stimulus at the atrioventricular node - This delay allows time for atrial systole before the atrioventricular valves close ECG machine ELECTROCARDIOGRAM Use the ECG machine detect the electrical signals in your heart P wave: Atrial systole QRS complex: Ventricular systole T wave: Ventricular diastole Doctors use this to see if your heart pattern is normal Able to detect fibrillations Skills: Mapping of the cardiac cycle to a normal ECG trace Hypertension and thrombosis Revisit atherosclerosis – what is it? Then answer the following questions - What is thrombosis? - What is hypertension? - What causes each of these? - What are the consequences? - How do the factors on the right affect thrombosis and/or hypertension? Applications: Causes and consequences of hypertension and thrombosis Height Genetics Age Gender Smoking Diet Exercise