* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download patrick_ch22_p3
Magnesium in biology wikipedia , lookup
Development of analogs of thalidomide wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
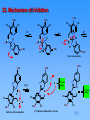
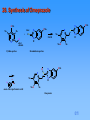
Patrick An Introduction to Medicinal Chemistry 3/e Chapter 22 ANTIULCER AGENTS Part 3: Proton pump inhibitors ©1 Contents Part 3: Proton pump inhibitors 23. 24. 25. 26. Parietal Cells and the Proton Pump Proton Pump Inhibitors Mechanism of inhibition Design of omeprazole (Losec) 26.1. The lead compound 26.2. Modification of the thiourea group 26.3. Modify the imidazole ring 26.4. Drug metabolism studies 26.5. Add substituents to the heterocyclic rings 26.6. Substituents varied on the pyridine ring 26.7. Substituents varied on the benzimidazole ring 27. Esomeprazole (Nexium) 28. Synthesis of Omeprazole [11 slides] ©1 23. Parietal Cells and the Proton Pump M3 H2 Cck2 ATP ADP + Pi Receptors Proton pump H+ K+ Cl Canaliculus The proton pump • • • • • • • HCl Ion channels - Lumen of the stomach Pumps protons out of the parietal cell and potassium ions back in Requires energy - provided by hydrolysis of ATP to ADP, catalysed by ATPase The proton pump is also called H+/K+-ATPase Chloride ions depart through a separate ion channel HCl is formed in the canaliculus The potassium ions exit the parietal cell as counterions for the chloride ions and are then pumped back in A separate potassium ion channel is used for K+ ions leaving the cell ©1 24. Proton Pump Inhibitors methylsulfinyl benzamidazole 'linker' H OCHF2 N pyridine O N S N MeO H N O N S N Me OMe OMe MeO Omeprazole Me Pantoprazole H N O N S N S N O F3C N Me O Lansoprazole MeO • • Na N O Me Rabeprazole Act as prodrugs Activated by strongly acidic conditions found in the canaliculae of parietal cells ©1 25. Mechanism of inhibition Me O Me Me N O N S N Me -H+ N H NH S H N OMe Me Me H+ N H N S OMe OMe OMe O OMe H N H OMe Spiro intermediate H OMe OMe OMe H N -H2O N N HS N N N H S Me Me S MeO OH Me Sulfenic acid intermediate Proton pump MeO Me Pyridinium sulfenamide structure N NH N S Me MeO Me ©1 S Proton pump 26. Design of omeprazole (Losec) 26.1. The lead compound N S NH2 CMN 131 • • • Originally an antiviral drug Inhibits gastric acid secretion Liver toxicity due to the thioamide group 26.2. Modification of the thiourea group N N S N H H 77/67 • • Inhibits gastric acid secretion The pyridine ring and bridging CH2S moiety are important to activity ©1 26. Design of omeprazole (Losec) 26.3 Modify the imidazole ring benzimidazole pyridine N N S N H H 124/26 • Increase in activity due to the benzimidazole ring 26.4 Drug metabolism studies O N N S N H Timoprazole • • • • Timoprazole formed by metabolism of H124/26 Timoprazole is the active drug Pyridinylmethylsulfinyl benzimidazole structure Side effect - inhibits iodine uptake by the thyroid gland ©1 26. Design of omeprazole (Losec) 26.5 Add substituents to the heterocyclic rings O N CO2Me N H Me S Me • • • N Picoprazole Potent antisecretory properties over long periods of time No toxic side effects on the thyroid No other serous side effects ©1 26. Design of omeprazole (Losec) 26.6 Substituents varied on the pyridine ring O N • N H Me Me H 159/69 Substituents which increase the basicity of the pyridine ring are good for activity Promotes the mechanism of activation Methyl substituents at the meta position have an inductive effect Methoxy substituent are more effective at para position than meta position Resonance effect increases electron density on the nitrogen • • • • N N Me R MeO • CO2Me S Me MeO N Me Me MeO N N R Me Me MeO H159/69 is potent but chemically too labile R Me Me R MeO ©1 Me 26. Design of omeprazole (Losec) 26.7 Substituents varied on the benzimidazole ring • • Substituents were varied to get the right balance of potency, chemical stability and synthetic accessibility Omeprazole was found to have the best balance H N O N S N Me MeO • • OMe Me Omeprazole Launched in 1988 by Astra World’s biggest selling drug ©1 27. Esomeprazole (Nexium) • Omeprazole has an asymmetric centre • The S-enantiomer has better potency and pharmacokinetic profile • Example of chiral switching N O OMe S N Me MeO H N Me ©1 28. Synthesis of Omeprazole OMe Me Pyridine portion N H Me Benzimidazole portion N Cl S Me MeO O N OMe S N H Me O N NaOH N H Cl alkyl chloride N OMe N thiol + HS Me N O2H meta-chloroperbenzoic acid MeO Me Omeprazole ©1 OMe