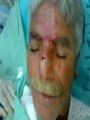
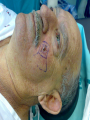
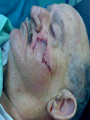
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download OTITIS MEDIA WITH EFFUSION
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
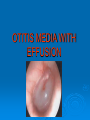
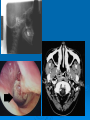
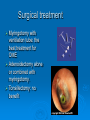
OTITIS MEDIA WITH EFFUSION What is OME? Presence of fluid without signs or symptoms of ear infection Decreased TM mobility Mild hearing loss generally 90% of children suffer from OME before school age (usually 6 months to 4 years) 30-40% of children with recurrent OME 5-10% last greater than 1 year ETIOLOGY 1. Poor Eustachian Tube Function anatomic blockade like adenoid ,congenital ,traumatic ,tumour… 2. Inflammatory response following AOM 45% have persistent effusion after 1 month, but this number decreases to 10% after 3 months. history Hearing loss: TV too loud, “what?” Pain ,ear itching(rubbing) mainly at night with sleep disturbances Problems with school performance Recurrent AOM In adults aural fullness and/or pressure, an ear being plugged, or decreased hearing Speech and language delay PHYSICAL EXAM Poorly mobile TM Yellow(serous) or grey(mucoid) Neutral,bulging or retracted Air bubbles or fluid level Nasal ,oral and neck exam audiologic examination Investigations Audiogram :mild – mod conductive hearing loss Tympanometery :type B management Medical treatment Surgical treatment Medical treatment 1. 2. 3. 4. Antimicrobials: have benefit for treatment Steroids: have no benefit alone but thy are beneficial in combination with antibiotics(short term improvment Antihistamines and decongestants :no benefit Mucolytics,topical steroids ,autoinflation : no benefit Surgical treatment Myringotomy with ventilation tube: the best treatment for OME Adenoidectomy alone or combined with myringotomy. Tonsillectomy: no benefit Surgical Complications Anesthesia – mortality reported as 1:50,000 for ambulatory surgery Tympanostomy tube sequelae Perforations in 2% after short-term tubes, 17% after long-term tubes Usually transient (otorrhea) or do not affect function (tympanosclerosis, atrophy, shallow retraction) Adenoidectomy 0.2-0.5% incidence hemorrhage 2% incidence of transient VPI Surgery OME relapse 20-50% of children with prior tubes relapse after extrusion. Adenoidectomy confers 50% reduction in need for future operations. Benefit of adenoidectomy apparent at age 2 years, greatest for children >3 years, independent of adenoid size.