* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Key Concepts
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
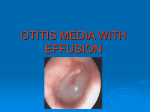
Chapter 18 ■■■ Key Concepts • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Although hearing is fully developed at birth, visual development continues to progress until about age 7 years. The relatively short and horizontally positioned eustachian tubes of infants and young children make them more susceptible than adults to otitis media. Binocular vision develops by age 4 months; visual acuity progresses to 2050 by age 3 years and usually reaches 2020 by age 7 years. To maximize speech and language development, hearing loss should be identified early and intervention begun immediately. The corneal light reflex test and cover test are useful tools for identifying strabismus and amblyopia. Tympanometry is used to determine the presence of fluid behind the eardrum (such as with OME). Topical ophthalmic medications are used to treat certain infectious eye disorders. Systemic antibiotics are used for the treatment of periorbital cellulitis and AOM. Very premature infants are at high risk for developing visual deficits related to ROP and are also at increased risk for hearing impairment compared with other infants. Children with genetic syndromes or family history are at increased risk for visual and hearing impairments. Strabismus, glaucoma, and cataracts may all lead to visual impairment if left untreated. Recurrent or constant nasal congestion contributes to OME. Asymmetry of the corneal light reflex occurs with true strabismus. A cloudy cornea indicates the presence of cataract. Eye strain, eye rubbing, and headaches may indicate a visual deficit. Delay in language acquisition may occur when hearing loss is present. Appropriate handwashing is the single most important factor in reducing the spread of acute viral or bacterial conjunctivitis. Otitis externa can be prevented by keeping the ear canal dry and altering canal pH. Children with visual disorders should be encouraged to use prescribed corrective lenses. The child with hearing loss should receive early intervention with hearing aids or other augmentative devices. Hearing andor vision impairment can significantly hinder developmental progress. The fluctuating hearing loss associated with recurrent AOM and the hearing loss associated with chronic OME can both significantly hinder language development in the infant and toddler. • Amblyopia must be identified early and treated with patching, corrective lenses, or surgery to prevent visual deterioration and promote appropriate vision development.