* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
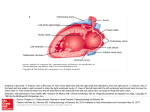
Download Position of the Heart
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
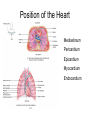
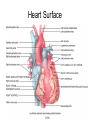
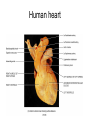
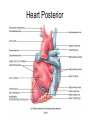
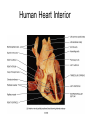
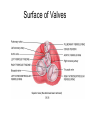
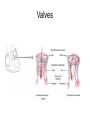
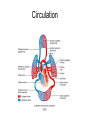
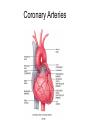
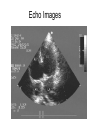
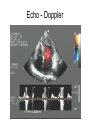
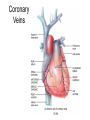
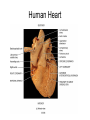
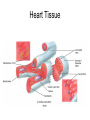
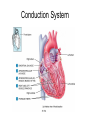
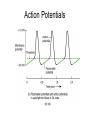
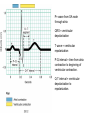
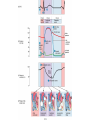
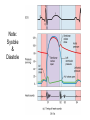
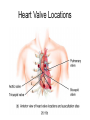
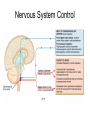
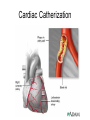
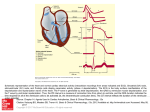
Chapter 20 The Heart Position of the Heart Mediastinum Pericardium Epicardium Myocardium Endocardium Heart Surface Human heart Heart Posterior Heart Interior Human Heart Interior Surface of Valves Valves Circulation Circulation Coronary Arteries The Echo Image Echo Images Echo - Doppler Mitral Valve Prolapse Coronary Veins Human Heart Heart Tissue Conduction System Pacemakers • Located in the right chest wall, a catheter is threaded through the subclavian vein, into the brachiocephalic vein, into the superior vena cava , then into the right atrium. • The pacemaker overrides the impulse from the SA node. Action Potentials Action Potential – Ventricle P= wave from SA node through atria QRS = ventricular depolarization T wave = ventricular repolarization P-Q interval = time from atria contraction to beginning of ventricular contraction. Q-T interval = ventricular depolarization to repolarization. Note: Systole & Diastole Heart Valve Locations Cardiac Output CO = SV x HR SV = ml/beat HR = Heart Rate Cardiac Output Affected By • Frank-Starling Law / Marey’s Law • Cardiac Reserve (Max CO – CO at rest) • Contractility (hormones, drugs, sympathetic reactions, etc. • Afterload (remaining blood in ventricles) • Congestive heart failure Regulation of Heart Rate Affected/Monitored by: • Cardiovascular center (sympathetic and parasympathetic systems) • Proprioceptors • Chemoreceptors • Baroreceptors • Blood pH • Hormones • Ions • Age, gender, temp, etc. Nervous System Control Risk Factors for CAD • • • • • • • High blood cholesterol High blood pressure Smoking Obesity Diabetes mellitus Type “A” personality Sedentary lifestyle Cardiac Catherization Terms to Know • • • • • • • Fossa Ovalis Coronary artery disease Arteriosclerosis Atherosclerosis PTCA Ischemia Myocardial infarction More Terms • • • • • • • Hypoxia Angina pectoris Coarctation of the aorta Arrhythmia Heart Block Flutter and fibrillation Bradycardia and tachycardia More Terms • • • • • • • • Cardiac arrest Cardiomegaly Cor pulmonale Palpitation Asystole Endocarditis / myocarditis Mitral valve prolapse Auscultation