* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Help to T cells
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
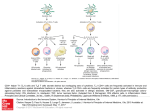
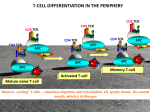
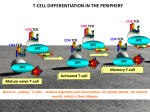
T cells Jan Novák The immune system Protection against infectious agents Clearance of dying, damaged and dangerous cells Regulation of the immune responses The immune system Non-specific defence mechanisms Innate immune system Adaptive immune system The adaptive immune system T cells - cellular immune responses B cells – humoral immune responses T cells Central role in the immune system Coordination of the immune response Cytotoxic functions Suppression of the immune responses T cells versus B cells Minimal morphological differences Differentiation based on the detection of surface markers B cells: CD19, B220, T cells: TCR, CD3, CD4, CD5, CD8 etc. T cell receptor (TCR) Antigen recognition (ab + CD4/8 – MHC class I/II) Signalization (CD3 transmembrane complex) defosforilations Proliferation, differentiation, effector functions Phenotype of T cells T cell receptor (TCR) Other receptors involved in the antigen recognition and signalization (CD4, CD8, CD3) Receptors and molecules involved in the migration of T cells Receptors for cytokines Activation markers (CD25, CD28, CD69) T cells ab - T cells CD4 helpers Th1 Th2 Th3 Th17 CD4+CD25+ CD8 cytotoxic T cells iNKT (CD4+CD8- a CD4-CD8-) gd T cells The pathway of T cell development 10 Thymus Today Thursday 12 TCR development The development of infinite repertoire of TCRs Each TCR of each T cell can recognize one antigen The repertoire of all TCR has the capacity to recognize any antigen Formation of TCR repertoire Organization of genes coding for TCR is similar to the genes coding for immunoglobulins Gene complexes TCRa (TCRg) gene complex for IgH Gene complexes TCRb (TCRd) gene complex for IgL TCR development TCR is encoded by several gene segments V - variability D - diversity J - joining C - constant TCR development Random rearrangement of V,D,J and C segments Recombination of gene segments (D-J, VD) Recombination controlled by RAG TCR development Rearrangement of gene segments for b chains Expression of pre-TCR b chain CD3 complex pre-a chain Rearrangement of gene segments for a chains Formation of definitive TCR Central education/deletion The maintenance of T cell tolerance T cells ab - T cells CD4 helpers Th1 Th2 Th3 Th17 CD4+CD25+ CD8 cytotoxic T cells iNKT (CD4+CD8- a CD4-CD8-) gd T cells CD4+ T cell activation MHC class II – TCR-CD4 interaction CD4+ T cell APC Costimulation CD80/86-CD28 CD4+ T cells – T helpers Th1 IL-12 Th0 Naive Th0 cell Th0 APC TCR – MHC interaction Engagement of costimulation pathways IL-4 Th2 TGF-b Cytokine milie Th3 Th1 cells Inflammatory cells Production of cytokines: (IFN) – g interleukin (IL) – 2 tumor necrosis factor (TNF) - a interferon Th1 cells Help to macrophages (M) Activation of M (IFN–g) Stimulation of their killing activities Elimination of intracellular agents Help to T cells Differentiate into Th1 profile (due to the IL12 production by APC) Secretion of autocrinne growth factor of T cells IL-2 Th1 cells Involved in the clearance of intracellular pathogens Involved in the delayed type of hypersensitivity Involved in some autoimmune diseases Th2 cells Production of cytokines IL-4 IL-5 IL-6 IL-13 Th2 cells Help to B cells Antibody production by B cells is dependent on the help of T cells (Th2) Cytokine dependent help: IL-4 Cell contact dependent help: CD40 (B cell) - CD154 (T cell) interaction Th3 Th2 cells Specific (direct) help T APC Nonspecific (bystander) help T APC B B Th3 Th2 cells Participation in the defense against extracellular agents Participation in the allergic reactions Th3 Th1 – Th2 competition Th1 cytokines inhibit the development of Th2 responses Th2 cytokines inhibit the development of Th1 responses Th3 Th3 cells Develop in the presence of TGF-b, IL-10 and IL-4 Secretion of TGF-b and IL-10 Induced after oral administration of antigens, play a role in the induction of oral tolerance Th3 Cytotoxic CD8+ T cells Elimination of dangerous cells Direct elimination of cells infected by intracellular pathogens Elimination of stressed cells (tumors, damaged cells) Activation of CD8+ T cells Recognition, activation CD8 MHC class I - TCR Somatic cell CD4 help CD4 CD8 APC APC activation Killing by CD8+ T cells CD8 Somatic cell Perforin-granzyme system (degranulation, perforation, apoptotic death) Fas-FasL interaction (apoptotic death) Cytokine dependent lymphotoxin (apoptotic death) Killing by CD8+ T cells – Perforin-granzyme system Killing by CD8+ T cells – Fas – dependent killing CD8+ T cells in immune reactions Clearance of infected cells – viruses, bacteria, parasites) Elimination of tumor cells in cooperation with NK cells Elimination of dying and damaged cells Literature Immunobiology – The immune system in health and disease: Charles A. Janeway Jr., Garland Publishing, 2001 The autoimmune diseases: Noel A. Rose, Academic Press – Third edition, 1998 Medical Immunology: Tristam G. Parslow, Lange – Tenth edition, 2001 Nature Reviews Immunology [email protected]