* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HEPATITIS: Etiology, Differential and Transmission
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Bioterrorism wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Influenza A virus wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Antiviral drug wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Chikungunya wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Infectious mononucleosis wikipedia , lookup
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis wikipedia , lookup
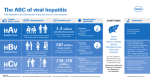
HEPATITIS: Etiology, Differential and Transmission Etiologies 1. Infections: a) targeting liver: Hep A, B, C, D, E, F, G viruses b) liver not 1 target: CMV, HSV, EBV, Coxackieviruses, Yellow fever, Ebola, Marburg, Toxoplasma, Q Fever The non-hepatitis infectious agents may cause elevations in serum aminotransferase and less commonly in serum bilirubin levels 2. Drugs: many drugs and certain anesthetic agents (e.g. INH, halothane) 3. Alcohol - usually the serum aminotransferase levels are not as markedly elevated in alcoholic hepatitis 4. Others: gallstones, tumors, genetic Clinical Features Acute Viral Hepatitis - Non-specific: anorexia, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, weight loss, fatigue - Fever, pruritis, dark urine, light stools, jaundice, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly Chronic Hepatitis - Non-specific: fatigue, RUQ pain, weight loss - jaundice, ascites Laboratory Features high serum bilirubin, high liver enzymes (AST, ALT, LDH, GGT), low albumin, high PT and PTT Viruses Hep A - fecal-oral transmission (may transmit through blood and secretions) - Only 1 serotype - 2 – 7 weeks incubation (avg. 4 wks) - Fecal shedding of the virus occurs during the incubation period and usually ceases a few days after symptoms begin infectivity often has already ceased when diagnosed - Most infections are subclinical or unrecognized - no chronic carrier state; lifelong immunity - low mortality - Diagnosis: IgM, IgG - Vaccine: yes; killed virus - No Tx Hep B - Transmission: blood (high), semen, vaginal secretion, saliva (moderate), vertical transmission (usually during delivery) BUT doesn’t X placenta - 2-5 month incubation - Insidious onset of symptoms. Tends to cause a more severe disease than Hep A. Asymptomatic infections occur frequently. - Most likely of the viruses to have symptoms - Chronic carriers: approximately 5% of infected individuals fail to eliminate the virus completely and become persistently infected. Opp stats for kids. (if don’t clear virus within one month will likely not be able to in future) - See most symptoms after 5 years - Very low rate of acute cases, 1% Dx: - no culture - HBsAg – person has virus and is infectious; virus is replicating; can be chronic state; don’t know when person got it - Anti HBs - immunity to HBV; not found in chronic carriers - Anti HBc - IgG; not a neutralizing Ab - indicates past or active infection both in immune and carrier If IgM indicates a recent infection - HBeAg – shows virus is replicating in liver, highly infectious, more likely to be chronic - Anti HBe - good prognostic indicator; less infectious means will eventually clear virus - HBV DNA – for monitoring Prevention -vaccine: injection of HBsAg, therefore will only have Anti HBs and not HBc; can tell that it was a vaccine and not prior infection -recombinant, from yeast - 5% don’t produce Abs after vaccine -HBIG – post-exposure prophylaxis; health care workers, infants of infected mothers (screen all pregnant women) Tx Acute – supportive/none Chronic – interferon and lamivudine (3TC) for some patients Hep C Dx Tx - transmission: blood, vertical, sexual contact 1.5 – 2 months incubation 6 types Causes a milder form of acute hepatitis than does hepatitis B (mild acute illness) Low case fatality rate But 80% individuals develop chronic infection, following exposure. Most commonly don’t have symptoms progression of disease is slow look for anti HCV; no IgM test does NOT mean have immunity monitor by HCV RNA (no culture test) interferon and Ribavirin liver transplant -both B and C increase risk of hepatocellular carcinoma Risk of infection by needle stick: HBV > HCV > HIV Severity of disease HBV > HCV > HAV Incubation: A and E: a few weeks B and C: a few moths (C is shorter) Hep D - RNA virus with Hep B surface Ag - Replicates only in presence of HBV - Not endemic in Asia - Co-infection: mild; low prevalence of chronic carriers - Super-infection: severe disease; high chronic carriers - Dx: HDV IgM; if high titers ongoing chronic infection - HDV RNA Hep E - similar to Hep A; fecal-oral transmission - not like Hep A in that: there’s no vaccine, infection of pregnant W will cause mortality in 10-20% (gen. Pop. 1%)