* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 26.2 Magnetic field
Magnetosphere of Jupiter wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Magnetosphere of Saturn wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic storm wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Edward Sabine wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic stripe card wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Giant magnetoresistance wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic nanoparticles wikipedia , lookup
Magnetometer wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
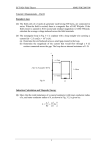
Physics Comb. Sci. NSS Physics in Life In-class Worksheets ◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄ 26 Electromagnetism 26.1 Permanent magnets Learning objectives Realize the interactions between magnetic poles and their interaction with magnetic materials. Key ideas A magnet has two magnetic poles: the magnetic __________________ (N-pole) and the magnetic __________________ (S-pole). When a permanent magnet approaches another magnet, they exert ________________________ on each other. Unlike magnetic poles __________________ each other; like magnetic poles __________________ each other. Magnetic poles always exist in pairs of __________________ polarities. Isolated magnetic poles do not exist. When a piece of magnetic material is brought close to the pole of a permanent magnet, it is __________________ and behaves like a temporary magnet. 1. NSS Physics in Life In-class Worksheets ►►►►►►►►►►►►►►►► Example 26.1A Physics Comb. Sci. Permanent magnets or iron bars? ( p.248) Bars A, B and C can either be magnets or iron bars. The figures below show the interaction between bars A and B, and that between bars B and C. State whether they are iron bars or permanent magnets. Explain briefly. A Solution 2. B B C Physics Comb. Sci. NSS Physics in Life In-class Worksheets ◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄ 26.2 Magnetic field Learning objectives Understand the concept of magnetic field and examine the field around a magnet qualitatively. Use field lines to represent a magnetic field. Key ideas A ______________________ is defined as a region in which a magnet or a magnetic body experiences a magnetic force. The SI unit of magnetic field is the _________________ (T). Magnetic fields can be represented by __________________________: – The direction of a field line gives the ______________ of the magnetic field at a point. For a point where the field line is curved, the direction of the field is indicated by the ________________ of the field line at that point. – The density of field lines is proportional to the ______________ of the magnetic field in a local region. Magnetic field lines start from _________________________ and end at _________________________. Magnetic field lines do not cross one another or branch at any point. A ___________________ is used for measuring steady magnetic fields. A search coil is used for measuring time-varying magnetic fields. 3. NSS Physics in Life In-class Worksheets ►►►►►►►►►►►►►►►► Example 26.2A Physics Comb. Sci. Magnetic field pattern of a cylindrical magnet ( p.254) Cylindrical magnets can be found in moving-coil microphones. Sketch the magnetic field pattern of the magnet. Solution S N 4. Physics Comb. Sci. 26.3 NSS Physics in Life In-class Worksheets ◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄ Magnetic fields due to electric currents Learning objectives Realize the existence of magnetic fields due to currents. Examine the magnetic field patterns associated with current-carrying long straight wires, circular coils and long solenoids qualitatively. Apply equations of the magnetic fields around a current-carrying long straight wire and a long solenoid to solve problems. Key ideas _____________________ or, more precisely, moving charges set up magnetic fields around them. The magnetic field lines around a long current-carrying straight wire are concentric circles. The direction of the field can be obtained by the ___________________________________. The magnetic field B at a point with a distance r away from a long straight wire carrying a current I is given by The magnetic field lines at the centre of a flat circular coil are straight and _____________________ to the plane of the coil. 5. NSS Physics in Life In-class Worksheets ►►►►►►►►►►►►►►►► Physics Comb. Sci. The magnetic field lines outside a current-carrying _____________________ is similar to those around a bar magnet. The poles of a solenoid can be determined by the ___________________________________ for solenoids. For an N-turn solenoid of length l carrying a current I, the magnetic field B at a point on the axis near the centre of the solenoid is given by The magnetic field at the ends of the solenoid on the axis drop to ____________ of the value at the centre. 6. Physics Comb. Sci. Example 26.3A NSS Physics in Life In-class Worksheets ◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄ Resultant magnetic field pattern ( p.262) Sketch the magnetic field lines around two current-carrying wires. Solution (a) (b) 7. NSS Physics in Life In-class Worksheets ►►►►►►►►►►►►►►►► Example 26.4A Physics Comb. Sci. Magnetic field around a wire ( p.265) A long straight carrying wire is aligned with the Earth’s magnetic field on the ground. A current of 3 A flows through it from south to north. Find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at 10 cm east from the wire. Neglect the Earth’s magnetic field. Solution 8. Physics Comb. Sci. NSS Physics in Life In-class Worksheets ◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄ Example 26.5A The magnitude of magnetic field between current-carrying wires ( p.265) Two parallel long straight wires P and Q are separated by a distance of 10 cm. They carry the same size of current of 2 A but in opposite directions. Q P 10 cm Find the magnitude of the magnetic field along line PQ at 1 cm, 2.5 cm and 5 cm from P. Solution 9. NSS Physics in Life In-class Worksheets ►►►►►►►►►►►►►►►► Example 26.6A Physics Comb. Sci. Resultant magnetic field ( p.269) A 500-turn solenoid of length 40 cm, carrying a current of 45 mA, is oriented with its axis pointing northeast. Assume the Earth’s magnetic field around the solenoid is fairly uniform and has a magnitude of 50 μT. N B 500 turns 45 mA A (a) What are the poles at the ends A and B of the solenoid? (b) What is the magnitude and direction of the resultant magnetic field at the midpoint on the axis of the solenoid? Solution (a) _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ (b) _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 10. Physics Comb. Sci. 26.4 NSS Physics in Life In-class Worksheets ◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄ Electromagnets Learning objectives Know the applications of electromagnets and examine the factors affecting their strength. Key ideas An ____________________ is usually a current-carrying solenoid with a soft iron core. It can be switched on and off and its magnetic field can be controlled by varying the direction and the size of the _________________ passing through it. The magnetic field of an electromagnet can be made stronger by – increasing the _________________ through the coil, – increasing the _________________________ per unit length of the coil, and – inserting a ______________________ into the coil. Electromagnets are used in – electromagnetic cranes, – electric bells and buzzers, – relays and circuit breakers, – earpieces of telephone receivers, and – maglev trains. Follow-up Checkpoint ( p.275) Exercise ( p.279) 11. NSS Physics in Life In-class Worksheets ►►►►►►►►►►►►►►►► 26.5 Physics Comb. Sci. Current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field Learning objectives Study the force acting on a current-carrying wire in a magnetic field and represent the force with an equation. Define the ampere with the force between currents in long straight parallel wires. Key ideas A current-carrying conductor may experience a _____________________ in a magnetic field. When a current-carrying straight wire is placed in a uniform magnetic field at right angles, the relative directions of the force, the field and the current can be predicted by ____________________________________. A _____________________ is a set-up that can be used to study the magnetic force on a current-carrying wire quantitatively. The magnetic force F acting on a wire segment of length l which carries a current I and makes an angle θ with an external magnetic field B is given by Currents in _____________________ direction attract each other, while currents in __________________ directions repel each other. 12. Physics Comb. Sci. NSS Physics in Life In-class Worksheets ◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄ Example 26.7A Magnetic force ( p.287) A metal rod PQ of 0.8 m long is put in a magnetic field as shown. When the source is switched on, a force of 5 N has to be applied to the rod to keep it stationary. The magnitude of the magnetic field is 1.5 T. conducting rail applied force current source conducting rail (a) What is the direction of the current flowing through the rod? Explain briefly. (b) What is the size of the current? Solution (a) _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ (b) _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 13. NSS Physics in Life In-class Worksheets ►►►►►►►►►►►►►►►► Example 26.8A Physics Comb. Sci. Magnetic force acting on a wire ( p.287) A uniform magnetic field of 3 T makes an angle of 30 with the horizontal. A wire of length 15 cm and carries a current of 5 A which flows from Q to P. It is put on the same plane as the magnetic field. Find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic force acting on the wire. 5A 30° Solution 14. Physics Comb. Sci. Example 26.9A NSS Physics in Life In-class Worksheets ◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄ Resultant magnetic force due to current-carrying wires ( p.290) Each of the wires P, Q and R carries a current of 3 A. 0.05 m 0.1 m (a) Draw the magnetic forces acting on R by P and Q. (b) What is the magnitude of the resultant magnetic force per unit length acting on R? Solution (a) 0.05 m 0.1 m (b) _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 15. NSS Physics in Life In-class Worksheets ►►►►►►►►►►►►►►►► Physics Comb. Sci. 26.6 Applications of magnetic forces on currents Learning objectives Determine the turning effect on a current-carrying coil in a magnetic field and know how a d.c. motor and related appliances work. Key ideas A magnetic field may produce a turning effect on a current-carrying coil placed in the field. For an N-turn coil of area A which carries a current I and makes an angle with a uniform magnetic field B, the corresponding moment is given by A _________________________________ is a sensitive device used for measuring small electric currents or voltages. It makes use of the _________________ on a current-carrying coil in a magnetic field. A d.c. motor can rotate a coil in one direction continuously with the help of a ____________________ and a pair of _______________ to reverse the current flowing through the coil in each half-cycle. A practical motor contains several coils of many turns wound on a soft iron core at different angles. The coil and core together are called an _______________. 16. Physics Comb. Sci. Example 26.10A NSS Physics in Life In-class Worksheets ◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄◄ Motor ( p.300) A simple motor is composed of a coil of 100 turns, two magnets with opposite poles facing each other and a cell. The length and width of the coil are 3 cm and 2 cm respectively. The magnitude of the magnetic field between the magnets is 3 T. The current flowing in the coil is 1.5 A. (a) What is the moment about the turning axle of the coil when the normal of the coil makes an angle of (i) 60, (ii) 45, and (iii) 30 with the magnetic field? (b) What is the advantage of replacing the pair of magnets with another pair with cylindrical surfaces? Solution (a) (i) _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ (ii) _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 17. NSS Physics in Life In-class Worksheets ►►►►►►►►►►►►►►►► Physics Comb. Sci. (iii) _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ (b) _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 18.