* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 3: Energy systems
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
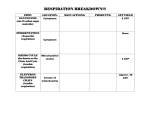
Unit 3: Energy systems Unit 3.3 Key learning intention (KLI) ‘Progress depends on effort not ability’ Nutrition and Energy Systems To evaluate, with detailed reference to your chosen athlete, the relative contributions of the three energy systems during different types of exercise and how that might influence dietary intake of different macronutrients and PED’s. To produce a mind map showing the complex interactions between the different macronutrients and how they eventually end up as energy. P63-73 Success criteria Resources Key words Phosphagen, Krebs cycle, electron transport chain, lactate, pyruvate, oxygen debt, oxygen deficit, respiration, ATP, Watch this great video on cell respiration to give you a background on what we will be studying over the next few weeks 3.3.1 Annotate a diagram of the ultrastructure of a generalized animal cell. Stick your photo of your animal cell made from sweets here and annotate it using the terms: Component Nucleus Mitochondria Lysosomes Ribosomes Golgi apparatus Endoplasmic reticulum description Unit 3: Energy systems 3.3.2 Annotate a diagram of the ultrastructure of a mitochondrion. 3.3.3 Define the term cell respiration. Definition with examples Cell respiration 3.3.4 Explain how adenosine can gain and lose a phosphate molecule. ‘Progress depends on effort not ability’ Unit 3: Energy systems ‘Progress depends on effort not ability’ 3.3.5 Explain the role of ATP in muscle contraction. Remember this video and also look at this excellent khan academy video. 3.3.6 Describe the re-synthesis of ATP by the ATP–CP system. The energy for all physical activity comes from the conversion of high-energy phosphates (adenosinetriphosphate—ATP) to lower-energy phosphates. Since our muscles don’t store much ATP, we must constantly resynthesize it. During short-term, intense activities, a large amount of power needs to be produced by the muscles, creating a high demand for__________. The phosphagen system (also called the ATP-CP system) is the quickest way to resynthesize ATP. Creatine phosphate (CP), which is stored in skeletal muscles, donates a _____________ to ___________ to produce ____________. No carbohydrate or fat is used in this process; the regeneration of ATP comes solely from stored CP. Since this process does not need oxygen to resynthesize ATP, it is ________________. As the fastest way to resynthesize ATP, the phosphagen system is the predominant energy system used for all-out exercise lasting up to about __________ seconds. However, since there is a ________________ amount of stored CP and ATP in skeletal muscles, fatigue occurs rapidly. Unit 3: Energy systems ‘Progress depends on effort not ability’ Creatine is a very popular supplement for athletes. Review the literature to comment on whether you think that this supplement would be beneficial for your athlete. 3.3.7 Describe the production of ATP by the lactic acid system. Unit 3: Energy systems 3.3.8 Explain the phenomena of oxygen deficit and oxygen debt. ‘Progress depends on effort not ability’ Unit 3: Energy systems 3.3.9 ‘Progress depends on effort not ability’ Describe the production of ATP from glucose and fatty acids by the aerobic system. Before attempting this task, watch this excellent tutorial that shows how macronutrients become ATP via the various systems. Unit 3: Energy systems ‘Progress depends on effort not ability’ This is also called the Krebs cycle. When oxygen is present, ________________ is produced from the pyruvate molecules created from glycolysis. When oxygen is present, the mitochondria will undergo aerobic respiration which leads to the Krebs cycle. However, if oxygen is not present, fermentation of the pyruvate molecule will occur, leading to _______________. In the presence of oxygen, when acetyl-CoA is produced, the molecule then enters the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) inside the mitochondrial matrix, and gets oxidized to ______________ while at the same time reducing NAD to ___________. ____________ can be used by the electron transport chain to create further ATP as part of oxidative phosphorylation. To fully oxidize the equivalent of one glucose molecule, two acetyl-CoA must be metabolized by the Krebs cycle. Two waste products, H2O and CO2, are created during this cycle. Thus, the total yield from 1 glucose molecule (2 pyruvate molecules) is _____ NADH, _____ FADH2, and _____ ATP. Beta-oxidation is the process by which _______________ molecules are broken down in the _____________ to generate ________________, which enters the _______________, and _______________ and _______________, which are used by the ________________________. Fat metabolism yields a lot ___________ ATP per molecule than glucose but the process is much _______________ and requires ________________. Unit 3: Energy systems 3.3.10 % of maximum power 90-100% ‘Progress depends on effort not ability’ Discuss the characteristics of the three energy systems and their relative contributions during exercise. Primary system Exercise time Characteristics Sporting example 75-90% 30-75% 0-30% 3.3.11 Evaluate the relative contributions of the three energy systems during different types of exercise. Look at the graph below showing the contribution of the various energy systems to all-out effort. Plot the graphs of 3 sports of your choice, showing how the contribution of each system would differ. Unit 3: Energy systems Unit 3.3 Key learning intention (KLI) Success criteria Resources Key words ‘Progress depends on effort not ability’ Nutrition and Energy Systems To evaluate, with detailed reference to your chosen athlete, the relative contributions of the three energy systems during different types of exercise and how that might influence dietary intake of different macronutrients and PED’s. To produce a mind map showing the complex interactions between the different macronutrients and how they eventually end up as energy. P63-73 Phosphagen, Krebs cycle, electron transport chain, lactate, pyruvate, oxygen debt, oxygen deficit, respiration, ATP,