* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WHPP Unit 1 Section 8 Greece
Regions of ancient Greece wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek religion wikipedia , lookup
Corinthian War wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek philosophy wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek literature wikipedia , lookup
Peloponnesian War wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of Greece and the Greek world wikipedia , lookup
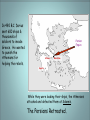
Unit 1 Section 8 Ancient Civilizations Greece TYWL: How were ancient civilizations and empires able to development, grow and create a lasting impact? How has conflict and innovation influenced political, religious, economic and social changes in medieval civilizations? Early Classical Fall Early People of the Aegean • Minoans – – Island of Crete. Civilization based on trade. Capital Knossos. Trojan War Fact or Fiction?? Fact..I think! It’s located in Turkey. • The Mycenaens learned from the sea traders. • The Trojan War 1250 B.C. b/w Mycenae (Greeks) & Troy. • Fought over trade routes. • Homer (700 BCE)—story teller of ancient Greece • Orator • Verbal histories become epics (tall tales with heroes and villains with a lesson) the “Iliad and the Odyssey”. • Odysseus and Achilles – These guys fought at the battle of Troy and reappear in Homers later stories The Greek City-States Around 800 BCE Phoenician traders reach out to Greece, bringing their writing w/ them. Greece accepts them & a new glorious Greece is launched!! Geography influenced cultural • Acropolis- was the hilltop of the citystate called the high city. Mountains & rocky terrain isolated settlements from one another. • 1st ruler king--central power. (monarchy heriditary) • Power shifted to a class of noble landowners. aristocracy. • Trade expanded-A gov’t in the hands of a small, elite, business class oligarchy. • Military technology (iron weapons). New fighting method: phalanx a massive formation of heavily armed foot soldiers was used. Persian Wars: 499– 480 BCE In 519 B.C. the Persians conquered Ionian Greeks. Athens sent warships That made the Persian King, Darius, very angry with Greece. Help! Persian Wars: Famous Battles $ Marathon (490 BCE) $ 26.2 miles from Athens Thermopylae (480 BCE) 300 Spartans at the Mountain pass vs. Xerxes In 490 B.C. Darius sent 600 ships & thousands of soldiers to invade Greece. He wanted to punish the Athenians for helping the rebels. Persian Empire Athens Marathon Sparta While they were loading their ships, the Athenians attacked and defeated them at Salamis. The Persians Retreated. Consequences of the Greek Victory o Athens became leader of a Greek alliance of several city-states. This is the start of Greek unification. o Athens enters its Golden Age. Notable Athenian Oligarchs • Draco: harsh laws – Athenian law code • Solon: wise laws Stop part 1 Cleisthenes: Father of Democracy • Citizens: male property owners over 21, born in Athens • Age of Pericles – Golden Age. – direct democracy- where large numbers of citizens take part in the day to day running of the government. Peloponnesian War • In 431 B.C., Sparta declared war on Athens. • Results: Athens lost its empire of wealth & for a long time, its democratic gov’t. Athens (A Limited Democracy) Attica north of the Peloponnesus – Limited democracy, or gov’t by the people. Sparta (A Nation of Soldiers) near the Peloponnesus, Southern Greece. – Rulers were two kings and a council of elders. – Rulers formed a military society. The Glory That Was Greece • Greek philosophers – Philosopher means “lover of wisdom” • Logic- rational thinking Socrates Developed the Socratic Methodusing questions to answer questions. A student of Socrates Socrates was eventually arrested for – “Golden Mean” “corrupting the youth of Athens”. [everything in Plato Aristotle moderation]. Plato’s most famous work was The Republic. It set Mentor of Alexander the Great He favored rule by a single, strong forth his vision of an ideal gov’t. leader. (Philosopher King) A student of Plato Macedonia and Alexander • Philip the II became King of Macedonia • Philip had a powerful army and invaded Greece. • Philip was murdered and his son Alexander immediately proclaimed himself king at 20 years old. • Alexander wanted complete his fathers dream of conquering Persia. Alexander the Great 1. took Anatolia (Turkey) from the Persians. 2. marched into Egypt where he was crowned Pharaoh. He also founded the city of Alexander at the mouth of the Nile. 3. turned East to Persia. 4. crossed into the Indus Valley. A powerful Indian army with 200 elephants blocked his path. 5. After winning the battle Alexander started having problems with his Army. The army had been fighting for 11years and marched more then 11,000 miles. The soldiers wanted to go home and Alexander agreed to go back. On the way home he dies. Conquering Begins Alexander the Great’s Empire Hellenistic Culture in Alexandria • Hellenism blended Greek, Persian, Egyptian, & Indian culture. • The center of the new culture is the city of Alexandria in Egypt.