* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
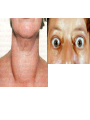
Graves' disease wikipedia , lookup
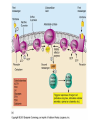
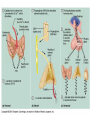
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM TYPES OF GLANDS Endocrine Exocrine Endocrine glands; Endocrine tissue Pineal gland Pituitary gland Thyroid gland Parathyroid glands Thymus Adrenal gland Pancreas Ovaries / Testes Stomach Duodenum Kidney Chemistry of Hormones Amines - simple hormones synthesized from tyrosine Proteins and Peptides - chains of amino acids hooked together Steroids - lipid soluble hormones derived from cholesterol Eicosanoids - hormones derived from arachidonic acid (from lipids) Mechanisms of Hormone Action Alters plasma membran permeability Stimulates synthesis of protein Activates or deactivates enzymes Induces secretory activity Stimulates mitosis Lipid Soluble Hormones Thyroid and steroid hormones cross the cell membrane and bind to INTRACELLULAR receptors in the cytoplasm or nucleus The hormone- receptor complex triggers activation or inactivation of specific genes Synthesis of new protein alters cellular activity causing a physiological response Water Soluble Hormones Protein and catecholamine hormones act by binding to receptors located on the cell membranes of target cells Hormones act as the 1st messenger which in turn activates a series of events involving cAMP as the 2nd messenger cAMP activates protein kinases G-proteins link the first messenger and the second messenger Hormone Release Humoral - hormones released in response to changing blood levels Neural - nerve fibers stimulate release Hormonal - one hormone stimulates the release of another Endocrine Glands Pituitary Gland Master gland Located within the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone Associated closely with the hypothalamus Differentiated into the anterior pituitary, or glandular portion, the posterior pituitary, or nervous portion and the avascular pars intermedia located in between Posterior lobe Neurohypophysis Connected with the hypothalamus via the supraopticohypophyseal tract Oxtocin (OT) Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) diabetes insipidus Anterior lobe (Adenohypophysis) Controlled by releasing and inhibiting hormones produced by the hypothalamus Growth hormone (GH) somatotropin dwarfism, giantism, acromegaly Thyroid - stimulating hormone (TSH) Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) Acromegaly Anterior lobe of the Pituitary Follicle - stimulating hormone (FSH) Luteinizing hormone (LH) Prolactin (PRL) Melanocyte - stimulating hormone (MSH) Thyroid Gland Located below the larynx, two lobes connected by an isthmus Hormones synthesized from iodine and tyrosine Follicle cells manufacture thyroglobin and store it as colloid Triiodothyronine (T3) / Thyroxine (T4) Goiter, Graves Disease, Cretinism, Myxedema Calcitonin (CT) - lowers calcium levels Parathyroid gland Four tiny glands located on posterior thyroid Parathyroid hormone (PTH) Raises blood calcium Adrenal Glands Located retroperitoneally and superior to the kidney Can be subdivided into outer cortex and inner medulla Adrenal Medulla Consists of hormone-producing cells called chromaffin cells Epinephrine / Norepinephrine (NE) Sympathomimetic hormones Released under stress by direct innervation from the autonomic nervous system Adrenal Cortex Manufactures steroid hormones called corticosteroids Divided into three regions: zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata, zona reticularis Zona glomerulosa (outer) - releases mineralocorticoids, principally aldosterone which controls electrolyte balance in the kidneys Adrenal Cortex Zona fasciculata (middle) - produces glucocorticoids such as cortisol and cortisone; controlled by ACTH Addison’s Disease, Cushing’s Disease Zona reticularis (inner) - produces adrenal sex hormones such as estrogens and androgens virilism, gynecomastia Cushings Disease Thymus Gland Located posterior to the sternum and between the lungs Thymosin Pineal Located in the roof of the 3rd ventricle of the brain Melatonin Pancreas Located posterior and inferior to the stomach Both exocrine and endocrine Islets of Langerhans Alpha cells - glucagon Beta cells - insulin Delta cells - somatostatin Diabetes mellitus - Type I, TypeII Ovaries Located in the pelvic cavity Estrogens Estradiol, estriol, estrone Progesterone Inhibin Relaxin Testes Located in the scrotum Testosterone Inhibin