* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 1 (Sections 1-3) Study Guide: Cell Structure and Function
Somatic cell nuclear transfer wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
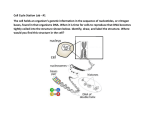
Name:_____________________________________Period:____Date:____________ Chapter 2 (Sections 1-3) Study Guide: From a Cell to an Organism Pages 88 - 107 Vocabulary: You may re-write vocabulary definitions here, prepare flashcards or printout eflashcards and attach to your study guide. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. cell cycle life cycle of a cell that includes phases of growth and development and reproduction interphase the phase of a cell cycle in which a cell is preparing to reproduce centromere a region near the middle of each chromatid that holds together the sister chromatids mitosis a process in which the nucleus of the cell divides cytokinesis the final stage of cell division when the cytoplasm of the cell divides prophase the first phase of mitosis in which the DNA that makes up a replicated chromosome twists into tight coils metaphase the second stage of mitosis, in which the replicated chromosomes move to the middle of the cell and the pairs of sister chromatids line up end to end across the center of the cell anaphase the third stage of mitosis, in which the sister chromatids of each replicated chromosome begin to separate telophase the final phase of mitosis, in which a new membrane forms around each set of chromosomes, creating two identical nuclei daughter cell two cells that form when the cytoplasm and its components divide cell plate a disk formed between the two new nuclei of a plant cell that is dividing homologous chromosome a pair of similar chromosomes sister chromatid copy of a chromosome made during S-phase of cell cycle cell differentiation a process in which cells become different types of cells stem cell cells that are able to produce different types of cells tissue similar cells that work together and perform a function organ groups of tissues that work together and perform one or more functions organ system organs that work together and perform one or more functions DNA deoxyribonucleic acid; genetic material located in the nucleus of a cell gene a section of DNA that has information about a specific trait of an organism RNA ribonucleic acid; a nucleic acid that plays an important role in the production of proteins mutation any permanent change in the DNA sequence of a gene or chromosome of a cell Main Ideas: Answer each question in complete sentences. 23. 24. 25. What are the phases of the Cell Cycle and briefly explain what occurs during each phase (start with interphase and end with cytokinesis)? Interphase: the cell grows and carries out its usual functions, DNA replicates Prophase: DNA of replicated chromosomes twists into coils; membrane around nucleus breaks apart Metaphase: Replicated chromosomes move to and line up along center of cell Anaphase: Sister chromatids begin to separate and move to opposite ends of the cell Telophase: New membranes form around each set of chromosomes, forming two identical nuclei Cytokinesis: cytoplasm divides List four reasons why mitosis and cell division are important? Growth of many-celled organisms Replacing old cells Reproduction in some organisms Replacing damaged or lost cells How is plant cell cytokines different from animal cell cytokinesis? In animal cells, the cell membrane pinches inward to divide the cytoplasm. In plant cells, a cell plate forms between the two new nuclei. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. What are the levels of organization from cells to organ systems? Give an example of each. Cells: muscle cell Tissues: muscle tissue Organs: heart Organ system: muscular system What are the functions of the following human organ systems and list organs within them? Integumentary: skin; protection and homeostasis Skeletal bones, cartilage, ligaments, joints; protection and support; mineral storage Muscular muscles; movement Nervous brain, spinal cord, nerves; response and regulation Endocrine glands such as pituitary and thyroid; produces hormones that control body functions Cardiovascular heart, blood vessels; transports blood carrying oxygen, nutrients, and wastes Lymphatic lymph nodes, tonsils, spleen, lymphatic vessels; returns fluid to blood and filters blood Respiratory bronchi, lungs; delivers oxygen and removes carbon dioxide Digestive stomach, small and large intestines; breaks down food and delivers nutrients and water to blood Urinary kidneys, bladder; removes wastes from blood Reproductive male and female reproductive organs; produces offspring What does DNA stand for and where is it located? Deoxyribonucleic acid, in the nucleus What is the structure of DNA? Be sure to discuss its shape, backbone (sides), and base pairs (rungs). Double helix (twisted ladder), sugar (deoxyribose)-phosphate backbone, A-T, C-G base pairs attach to sugar How are genes, chromosomes and DNA related? Each chromosome is composed of a long strand of DNA, a section of DNA on a chromosome is a gene How many chromosomes do humans have?46 chromosomes or 23 pairs Diagram1: Label the cell cycle with the correct phase name. Interphase Prophase Cytokinesis Metaphase Telophase Anaphase Diagram2: Label the structure of DNA. Sugar (deoxyribose) Guanine Nitrogen bases Adenine Phosphate Cytosine Thymine Online Review: Use these online sources to help you review for your chapter test. Place a check mark in the box when you have completed the review. √ Standards Assessment Chapter 2 http://glencoe.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/007874184x/student_view0/unit1/chapter2/standard_assessment-english.html √ Vocabulary eFlashcards Chapter 2 √ Interactive Tutor Chapter 2 http://glencoe.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/007874184x/student_view0/unit1/chapter2/vocabulary_eflashcards.html http://glencoe.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/007874184x/student_view0/unit1/chapter2/interactive_tutor.html