* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Comprehensive Revision
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Planned obsolescence wikipedia , lookup
Affiliate marketing wikipedia , lookup
Visual merchandising wikipedia , lookup
Consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Social media marketing wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Brand awareness wikipedia , lookup
Advertising management wikipedia , lookup
Brand loyalty wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Brand equity wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product placement wikipedia , lookup
Brand ambassador wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Emotional branding wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Internal communications wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
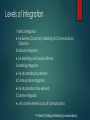
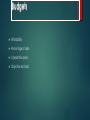
Comprehensive Revision MARKETING COMMUNICATIONS “I’d rather solve one problem using one thousand methods than try to solve one thousand problems using one method…” - Rene Descartes IMC - Definitions The concept under which a company carefully integrates and co-ordinates its many communications channels to deliver a clear, consistent and compelling message about the organisation and its products Kotler Value Creation and Delivery Sequence Choose the value Provide the value Communicate the value Kotler, 2006 Advertising Sales promotions Company Products Services Prices Events and experiences Distribution channels Target customers Public relations Direct marketing Personal selling Source: Kotler, 2006, Marketing Management Marketing Mix Decisions Marketing Mix Product mix Design Features Packaging Distribution mix When where placing Price mix retail price discounts rebates Marcommix Advertising PR/ direct Sales promo Roles of marketing communications Differentiate Remind and reassure Inform Persuade DRIP (Chris Fill) Levels of Integration 1 Vertical Integration link Business (Corporate), Marketing and Communications Objectives 2 Horizontal Integration link Marketing and Finance, HRM etc. 3 Marketing Integration link all marketing mix elements 4 Communications Integration link all promotional mix elements 5 Creative Integration unify creative themes across all communications P R Smith (Strategic Marketing Communications) A simple communication model Buyer Behaviour Key first step in developing a marketing strategy is understanding the target market and their buying behaviour Who is the buyer? Why do they buy? How, when and where do they buy? Advertising and promoting to individuals in role: To initiators – to make them aware of the category need and propose our brand as a possible purchase candidate To influencers – to communicate the reasons they should communicate our brand To deciders – to persuade them to select our brand To purchasers – to “lock in” the selection of our brand To users – to ensure that they actually use and, perhaps more rapidly use our brand High and Low involvement Decision Process High High involvement decision Spend lots of effort on expensive, personal or emotion-laden products e.g. cars Low involvement decision Acquiring products purchased regularly e.g. milk Low Hierarchy of Effects models Model Cognitive Affective Conative AIDA Attention Interest, desire Action AIDCA Attention Interest, desire, conviction Action ACCA (or DAGMAR) Awareness, comprehension Conviction Action Lavidge and Steiner Awareness, knowledge Liking, preference, conviction Purchase AIETA Awareness Interest, evaluation Trial, adoption Budgets Affordability Percentage of sales Competitive parity Objective and task Target Markets Which segments? Influencers? Decision Makers? Internal audiences? Distribution chain audience? Push v Pull strategy Pulling the product through the distribution chain by creating demand amongst customers e.g. via heavy advertising Pushing the product through the distribution chain e.g. via dealer incentives Combination of push and pull Product categories and marketing communication mix Product Life Cycle stage Introduction Heavy promotion to create awareness Growth Increasing competition Create differentiation Maturity Maintain differentiation Nurture segments e.g. heavy users Decline Rejuvenate or re-position What is Positioning? The act of designing the company’s image and value offer so that the target customers understand and appreciate what the company stands for in relation to its competitors. P Kotler The Key Output of Positioning: Positioning Statement “For _______________ , the _________________ offers [Highest Ranked Segment [Product Family Name] _________________________________________ because [Highest Weighted Benefit] ________________________________________________. ” [Competitive advantage company possesses] Positioning Statement Examples EXAMPLE : AVIS “For business people who rent cars, Avis is the company who will provide the best service because the employees own the company.” EXAMPLE : HOME DEPOT “For do-it-yourselfers, Home Depot offers the best prices because we are the largest building supply company.” EXAMPLE : BODY SHOP “For people seeking wellness, the Body Shop offers the most natural bath and cosmetic products because we are the most environmentally friendly cosmetics company.” EXAMPLE : SOUTHWEST AIRLINES “For short-route travelers, Southwest Airlines offers the best prices with reasonable and dependable service because we don’t charge customers for amenities.” A hard sell •Is an informational message that is designed to touch the mind and create a response based on logic. •The assumption is that the target audience wants information and will make a rational product decision •The approach emphasizes tangible product features A soft sell •Uses emotional appeals or images to create a response based on attitudes, moods dreams and feelings. •The assumption is that the target audience has little interest in undertaking an information search and will respond more favorably to a message that touches their emotions Straightforward •A factual or informational message conveys information without any gimmicks, emotions, or special effects Demonstration •Focuses on how to use the product or what it can do for you Comparison Slice of life Endorsers Teasers •Contrasts two or more products and finds that the advertisers brand is superior •An elaborate version of problem solution staged in the form of drama •Use of celebrities or characters •Mystery ads that don’t identify the product or don’t deliver enough information to make sense Brand awareness What is it? Who is it for? Category need User What does it offer? Brand Benefits Brand attitude John R. Rossiter, Larry Percy, Advertising Communications & Promotion Management, 1998, McGraw Hill Conveyo r Product representation Attribute prompt Thank you for your attention and good luck in the exam!