* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Powerpoint
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Marine biology wikipedia , lookup
History of navigation wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Marine habitats wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Hotspot Ecosystem Research and Man's Impact On European Seas wikipedia , lookup
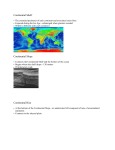
1. Continental Shelf – 0-200 meters deep. Contains 8% of the oceans surface area Biologically richest part of the ocean Contain submarine canyons – canyons eroded by glaciers which channel sediments to the ocean floor 2. Shelf Break – 120-200 meters deep (slope gets steep!) 3. Continental slope – (200-3000 meters) descends all the way to the deep sea floor. 4. Continental Rise – consists of a thick layer of sediments which accumulate in a deposit called a deep sea fan. Abyssal Plain – deep sea floor 3,000-5,000 meters Contains seamounts - underwater volcanoes with a pointy top Contains guyots (tablemounts) - flat topped seamounts that were once volcanic islands that eroded and sunk. Trenches – where the ocean plate descends into the continental plate. (subduction zone) converging boundary Example – Mariana Trench – deepest place in the ocean 11,022 meters. Found in the Western Pacific (Compare to Grand Canyon at 1.6 km) Mid ocean ridge – Formed where plates are diverging (moving apart). Molten rock from the mantle pushes up the ocean crust. BUT…the plates are pulling apart at the ridge so this forms a rift valley in the middle of the ridge.