* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture`Outline` Biogeochemical`Cycles`
Climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Iron fertilization wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Decarbonisation measures in proposed UK electricity market reform wikipedia , lookup
Carbon pricing in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Climate-friendly gardening wikipedia , lookup
Reforestation wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Business action on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Blue carbon wikipedia , lookup
Carbon sequestration wikipedia , lookup
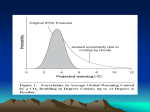
Lecture'Outline' • The$Global$Carbon$Cycle$and$Carbon$Fluxes$ – Sources'and'Sinks'for'Atmospheric'C' – Time'scales'of'C'exchange' – Carbon<Climate'Feedback'Systems' • Changes$to$the$“Natural”$Carbon$Cycle$ – Fossil'Fuels'and'Land'Use'Change' – An'imbalanced'system' Biogeochemical'Cycles' Re(cycling)'of'elements'within'the'Earth'System'is'essenFal'for' maintenance'of'a'living'planet.' EssenFals'for'life' – Water:'hydrologic'cycle' – Energy/sunlight:'radiaFve'balance' – Carbon:'building'block'of'life.' ! Carbon'100x'more'concentrated'in'living'maNer' ! Carbon'cycle:'biophysical'processes'that'recycle'carbon' among'the'components'of'the'Earth'System' – Nutrients:'Nitrogen,'Phosphorous,'etc.' Inputs'to'Atmospheric'Reservoir' (all'carbon'containing)' • Carbon'Dioxide'(CO2)' • Methane'(CH4)' • Fluorocarbons'(including'CFCs)' ' CO2:'So'Simple…yet' Natural,'colorless,'odorless'gas' ' Not'associated'with'aestheFc'“polluFon”'issues' Carbon'(C),'the'4th'most'abundant'element'in'the'Universe' ' Global'Warming'PotenFal'(GWP)' Strength'of'a'given'mass'of'greenhouse'gas'to'posiFve'radiaFve' forcing'over'a'specific'Fme'scale'(typically'100yrs)'relaFve'to' equivalent'mass'of'carbon'dioxide.' 'Factors'to'consider' – wavelength'(opaqueness'of'atm'at'given'wavelength)' – RadiaFve'efficiency' – atmospheric'lifeFme' Greenhouses'Gases:'Carbon'Dioxide' The'Notorious'CO2' ' Natural$Sources:'vegetaFon,'fires,'ocean,' volcanoes.'Part'of'the'carbon'cycle' (photosynthesis/respiraFon)' ' Anthropogenic$Sources:'Incomplete'combusFon' of'fossil'fuels,'biomass'burning' ' Life@me:'20<100'years' ' GWP:$1'(by'definiFon)' ' Greenhouses'Gases:'Methane' ' • Natural$Sources:'peat'bogs,'soil' • Anthropogenic$Sources:'Industrial'and'auto' emissions,'agriculture'(belch!)' • Life@me:'10<20'years' • GWP:$25'' Fluorocarbons$ CFCs:'SyntheFc'compound'of'ozone'hole'notoriety' Replaced'by'HFCs'and'PFCs' ' Natural:'None' ' Anthropogenic:'Refrigerants,'propellants,'solvents' ' Life@me:'100y'to'1000y' ' GWP:$5000'to'25000' ' Carbon'Reservoirs' Total carbon reservoir on Earth = 1x1023g : 1x108 GT Carbon'Fluxes' Flux: exchange between reservoir Photosynthesis 60 Gton/yr Respiration and Decomposition 60 Gton/yr Atmospheric'CO2' 600'Gtons' Steady State: balanced inflow/outflows, constant over time Atmosphere'as'Transfer'StaFon'for'C'exchange' Carbon'bathtub:'Nat'Geo'12<09' Residence'Time' Residence'Time'(yr)' ='average'amount'of'Fme'a'substance'stays'in'a'given'reservoir'at' steady'state'(also'can'be'calculated'by'half<lives)' =''amount'in'reservoir'(g)' ' ' input or output rate (g/yr) Example:'Water'Vapor'Residence'Time' – Global'Mean'Water'Vapor':'2.5cm' – Global'Mean'PrecipitaFon'Rate':'2.5mm/day' ' Residence'Fme'determines'speed'of'carbon'cycling' Try'this'out'for'photosynthesis/respiraFon' ' Where'is'most'of'the'carbon'today?' Answer:'In'the'Lithosphere'(10,000x'ATM)' ' • Most'Carbon'is'‘locked’'away'in'the'crust' – Carbonates'(containing'carbon),'i.e.' Limestone'(CaCO3)' – Inorganic'Carbon'(non<living)' • Carbon'was'once'living,'therefore'the'term' “fossil'fuel”'comes'from'the'fossilized' sediments'in'rock' #2'Reservoir:'Global'Oceans'(50x'atmosphere)' ' Other'Carbon'Reservoirs' Vegeta@on$(1x$ATM)$ • carbon'='life'for'plants'' • rhythm'of'season'(later)' • forests'store'>85%'of'veg'carbon' ' ' Soils$(2x$ATM)$ • decomposing'plants'+'roots' • mostly'stored'in'climate'where' precipitaFon>evapotranspiraFon'' • boreal'ecosystems,'forests' • Increases'in'evaporaFon'in'a' warming'climate'might'limit'the' ability'of'soils'to'“hold”'carbon' Global'Carbon'Cycle' 1.'Carbon'is'conserved' 'Total'carbon'of'Earth:'fixed' 'Steady'State'implies'that'for'each'reservoir'' ' 'Input'='Outputs' ' 2.'Hierarchy'of'cycling'across'reservoirs'and'Fmescales' Short'term'cycle'(seconds'to'years)' Long'term'cycle'(years'to'thousands'of'years)' 3.'Currently'not'in'steady'state'due'to'man<made'inputs' Global'Carbon'Cycle' Source'or'Sink:'Reference'Frame'Atmosphere' • Source'<'a'process'that'puts'carbon'into'the'atmosphere''' – Fossil'fuel'combusFon'' – Plant'respiraFon' – Fire'and'volcanic'emissions' ' • Sink'<'a'process'that'takes'up'carbon'from'the'atmosphere' – Plants/vegetaFon'(long'lived'trees)' – Burial'of'organic'maNer' – Oceans'(water,'marine'sediments,'etc.)' Short'Term'Carbon'Cycle' Biosphere CO2 Added by Respiration CO2 Removed by PhotoSynthesis Primary Productivity C Photosynthesis: the conversion of carbon dioxide and water into plant biomass using sunlight. Carbon flux from atmosphere to organic carbon in vegetation. Carbon Dioxide + Water + Sunlight = Sugar+ Oxygen Respiration: Release of carbon from plant biomass into atmospheric carbon dioxide (opposite of photosynthesis, accelerated by enzymes) Carbon'Cycle' Net'primary'producFvity'–'amount/rate'at'which'biomass' accumulates'in'an'ecosystem.''' Darker green = more productive (carbon in biosphere) White = non-productive environment (little carbon) Seasonal CO2 Variations Why the funny zig-zag in the graph? From Mauna Loa, Hawaii :Keeling Curve Carbon'Dioxide'FerFlizaFon' As'CO2'levels'increase,'plants'photosynthesize'faster' Biosphere'increases'CO2'absorpFon'from'atmosphere' Atmospheric'CO2'declines' NegaFve'Feedback:'Stabilizes'Climate'System' Limited'by'temperature'and'precipitaFon'constraints'' – Forests'won’t'grow'outside'of'temp/precip'values' Tipping'Points'For'Feedback' Growth rate – CO2 absorbed • • • • • Mean Temperature Plants$Need$CO2,'But…' Secondary'Fate'of'VegetaFon' When'plants'decay,'some'carbon'is' buried'and'stored'in'soils'' – Anaerobic'decomposiFon' (creates'CH4'and'CO2)' – May'be'exposed'by'erosion' and'released'to'atmosphere' – May'be'buried'and' incorporated'in'the'lithosphere' (long'storage)' – Eroded'and'transported'by' rivers'to'oceans' CO2 Put Into Atmosphere by Decay C Organic Soil Carbon C Biosphere'Carbon'DistribuFon' Soil'Carbon'Storage' Ocean'Carbon'Cycling' Surface'Ocean'Reservoir' Ocean<atmosphere'exchange'(fluxes)'' – Flux'of'CO2'is'down<gradient' Currently'Atm>Ocean,'so'Atm'"'Ocean' – Ocean'acts'as'buffer'system' – Have'absorbed'1/3'of'man<made'CO2' emissions':'“Carbon$Sink”$ – Solubility'of'Carbon'in'Ocean'' ' 'inversely'proporFonal'to'temperature'' • Warm'soda'analog' – Solubility'limited'by'Ocean'ph'(bio'uptake)' CO2(g) CO2(aq) Oceanic'Carbon'Feedbacks' Ocean'Carbon'Uptake'Feedback:'Air'temperature,'ocean' temperature,'ocean'carbon'uptake,'atmospheric'CO2' ' ' Oceanic'Carbon'Solubility'Feedback:'Air'temperature,'ocean' temperature,'aqueous'solubility,'oceanic'CO2,'atmospheric'CO2' ' '*'biological'pump<pH'feedback' ' '*'mixed<layer'stability'(oceanic'convecFon)' ' Atmospheric$CO2$ Ocean$Dissolved$ CO2$ Sea<Air'Carbon'Flux' Air$ Temp$ Atm$ CO2$ Ocean$Temp$ Carbon$ Solubility$ Atmospheric$CO2$ Ocean$CO2$ Upper Ocean Ocean$pH$ Biota$ Deep Ocean Long-term Carbon Cycle Sources Outgassing from Earth's interior at ocean ridges, and volcanism Sinks Burial of deep sea sediments and undecayed biomass in soils + chemical weathering Volcanic'ErupFon'' Can inject large amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere, also sulfate aerosols Limestone'(A'Carbonate'Rock)' Granite: Silicate Limestone: Carbonate Most Carbon is ‘locked’ away in the earth’s crust (i.e. rocks) as Carbonates (containing carbon) Carbonates are formed by via silicates through the carbon cycle In'Case'That'was'not'Clear' Coke'='Rainwater ' ' ' ' 'Menthos'='Silicate'Rock' Silicate<to<Carbonate'Conversion' Rain 2. Acid Dissolves Silicates (carbonic acid, removal from atm) 1. CO2 Dissolves in Rainwater 3. Dissolved Material Transported to Oceans 4. CaCO3 Forms in Ocean and Settles to the Bottom Calcium carbonate Chemical$weathering$is$a$func@on$of$temperature$ 1. EvaporaFon'rate'increases'with'temperature' 2. PrecipitaFon'rate'increases'with'evaporaFon' 3. More'precipitaFon'means'more'weathering' ' Draw'a'feedback'diagram'involving'the'following'components' (a) Temperature' (b) EvaporaFon' (c) PrecipitaFon' (d) Weathering' (e) Atmospheric'Carbon'Dioxide' Plant'growth'modifies'feedback?' ' Atmoapheric [CO2] (ppmv) 9 8 Emissions 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 4001850 380 1870 1890 1910 1930 1950 1970 1990 2010 [CO2] 360 340 320 2 ppm/year 300 280 0.81850 perature (deg C) 1. Carbon'emissions' exponenFally'increasing**' 2. Atmospheric'CO2'increased' 100'ppm'in'last'150'years' 3. Increased'GHG'Effect' reflected'in'global' temperatures' ' Spring'2012:'397'ppm' ' ' Fossil Fuel Emission (GtC/y) Emissions,'ConcentraFons,'Temperatures' 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 -0.2 1870 1890 1910 1930 1950 1970 1990 Temperature 0.2 C/decade 2010 The'Rise'of'Atmospheric'Carbon' Two$Primary$Culprits$ ' – Fossil'fuels'' • Carbon'from'lithosphere'to'atmosphere' – Land'use'change'' • Carbon'from'Bio/soils'to'atmosphere' Fossil'Fuels' • Fossil'fuels:'hydrocarbons'within'top'layer'of'Earth’s'crust' • Fossilized'remains'of'dead'plants'and'animals'exposed'to'heat/ pressure'of'Earth'for'thousands<millions'years' • World'derives'86%'of'energy'from'fossil'fuels' • Non<renewable'resource:'Using'up'organic<rich'sediments'faster'than' they'accumulate' Forests Deforestation in Progress Agriculture Deforesta@on:$Carbon$from$biosphere$into$atmosphere$ – Forests$(sink)$replaced$by$agriculture$(source)$ – Soil$disturbance$releases$soil$carbon$to$atmosphere$ – Inhibits$amount$of$carbon$stored$in$biosphere$and$soils$ Historical Emissions from Land Use Change Carbon Emissions from Tropical Deforestation 2000-2007 1.60 Africa 1.40 Latin America 1.20 S. & SE Asia SUM 1.00 1.5 GtonC y-1 (16% total emissions) 0.80 0.60 0.40 0.20 R.A. Houghton, unpublished 2000 1990 1980 1970 1960 1950 1940 1930 1920 1910 1900 1890 1880 1870 1860 0.00 1850 Pg C yr-1 1.80 Other perturbations: Fire US Wildfires release 4-6% of Fossil Fuel Emissions Other perturbations: Ecosystem Disturbance Insects Drought Stress Missing'Sink' Sources Fossil Fuel Combustion Land Use Change Sinks Atmosphere Oceans Missing Sink 7.5 Gt C/yr 1.5 Gt C/yr 9 Gt C/yr 4.2 Gt C/yr 2.3 Gt C/yr 6.5 Gt C/yr 2.5 Gt C/yr Hypotheses'for'Missing'Sink' Ocean-Sediment Route 1. Nutrification of coastal waters accelerates CO2 uptake, then deposited to sediment and not found 2. Fish Biosphere 1. Reforestation of previously deforested areas 2. Enhanced plant growth (carbon-photo feedback) 3. Tropical rainforests or Boreal Forests Anthropogenic Sinks Landfills, Carbon Capture & Sequestration Fate of Anthropogenic CO2 Emissions (2000-2007) 1.5 Pg C y-1 4.2 Pg y-1 Atmosphere 46% 2.6 Pg y-1 Land 29% + 7.5 Pg C y-1 2.3 Pg y-1 Oceans 26% Canadell et al. 2007, PNAS (updated) The'New'Carbon'Cycle' Atmosphere now ~760 Not ALL anthropogenic carbon emitted to atm stays there Drivers of Accelerating Atmospheric CO2 1970 – 1979: 1.3 ppm y-1 1980 – 1989: 1.6 ppm y1 1990 – 1999: 1.5 ppm y-1 2000 - 2007: 2.0 ppm y-1 To: • Economic growth • Carbon intensity • Efficiency of natural sinks 65% - Increased activity of the global economy 17% - Deterioration of the carbon intensity of the global economy Carbon intensity = CO2 tons/GDP 18% - Decreased efficiency of natural sinks " Feedbacks Canadell et al. 2007, PNAS GT'Carbon'Equiv' Carbon'dioxide'represents'¾'of'GHG' emission'today' Emissions'have'increased'70%'since'1970' Heaviest'growth'due'to'transportaFon' 125%' Demands'and'populaFon'growth'by'far' offset'increases'in'energy'efficiency' IPCC WG2 SPM Fig. 1.1 New'Geography:'Carbon'Emissions' Per capita US emits 20 tons of CO2/per person India emits 0.8 tons of CO2/ per person